In-situ remediation method for organic contaminated underground water
A technology of organic pollution and in-situ remediation, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of groundwater acidification and heavy metal pollution, persulfate decomposition loss, consumption of oxidants, etc. Achieve the effect of avoiding acidification and heavy metal release secondary risks, avoiding secondary risks, and extending electrolysis time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] In a sealed reactor to simulate the groundwater organic contamination area, add 410 mL of 52 mg / L trichlorethylene (TCE) and Na 2 S 2 o 8 , Na 2 S 2 o 8 The concentration is 12.5 times that of TCE, insert iron sheet (length × width × height = 76 × 9.5 × 3.2 mm) and titanium mesh (length × width × height = 85 × 15 × 1.8 mm) to act as two electrodes, two electrodes The distance between them is 2–30cm. Use wires to connect the electrodes to the two output terminals of the regulated DC power supply. After sealing, use the iron sheet as the positive electrode and apply a positive current of 50mA to activate the persulfate radicals, thereby realizing the organic matter oxidative degradation, the current value can be adjusted between 10–500mA during the degradation process, when the organic pollutant repair reaches 95% by mass, change iron as the negative electrode and apply a negative current of 50mA to inhibit the activity of persulfate radicals and the current during th...
Embodiment 1
[0021] In the sealed reactor to simulate organic pollution waters, add 410mL of 52mg / L trichlorethylene (TCE) and Na 2 S 2 o 8 , Na 2 S 2 o 8 The concentration is 12.5 times that of TCE, insert cast iron sheet (length × width × height = 76 × 9.5 × 3.2mm) and titanium mesh (length × width × height = 85 × 15 × 1.8 mm) to act as two electrodes, change after sealing The electrode polarity and current magnitude applied to the iron electrode, the removal effect of TCE is as follows figure 1 shown. Obviously, the degradation effect of TCE is accelerated with the increase of positive current, and is more significantly inhibited with the increase of negative current. When the negative current reaches -50mA, the degradation of TCE is almost completely inhibited.
Embodiment 2
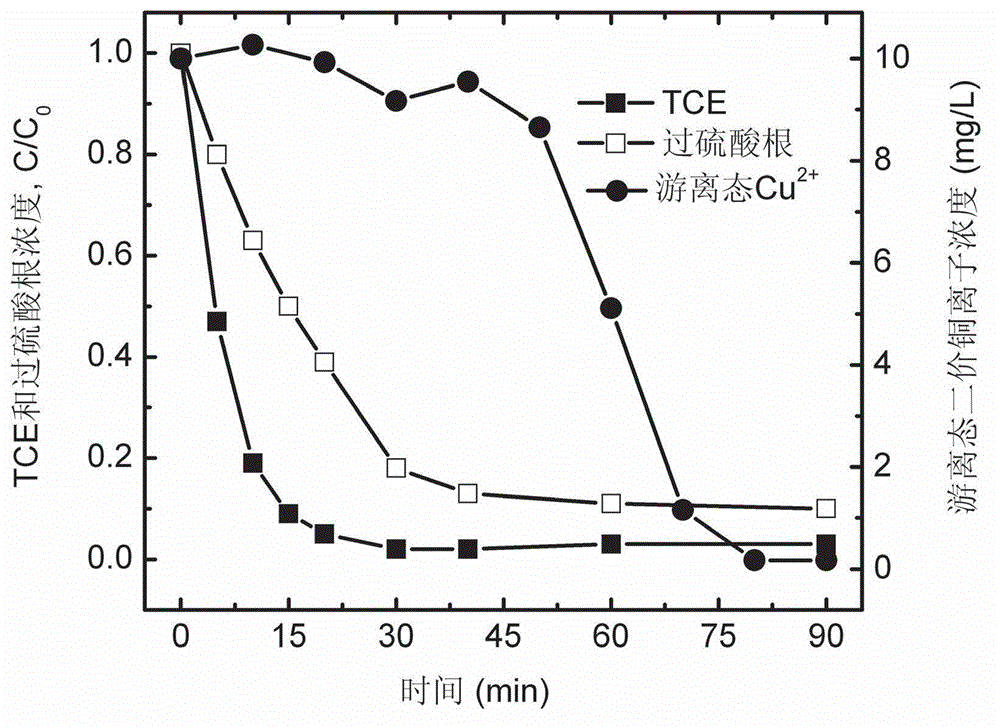
[0023] Using the same reactor, in another set of experiments, the Na 2 S 2 o 8Concentration, which is 4 times the concentration of TCE, was continuously applied to the iron electrode at +100mA. Experimental results such as figure 2 shown by figure 2 It can be seen that the concentration of TCE and persulfate decreased significantly with time. After 30 minutes, TCE was completely degraded. Continue to apply +100mA current to the iron electrode, and the concentration of persulfate continued to decrease. After 50 minutes, the free heavy metal copper ions (Cu 2+ ) concentration began to decrease significantly. Depend on image 3 The corresponding pH and oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) changes showed that the pH of the aqueous solution began to increase significantly at 50 min, and reached the neutral range at 90 min.
[0024] The pollutant TCE in the above examples can be replaced by other substances in chlorinated solvents, benzene series and polycyclic aromatic hydro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com