Methods and compositions for reducing or preventing vascular calcification during peritoneal dialysis therapy
A technology of vascular calcification and peritoneal dialysis, applied in the field of medical treatment, can solve the problems of reduced applicability and patients' inability to excrete drugs, and achieve the effect of preventing vascular calcification and reducing the progress of vascular calcification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Pharmacokinetic / Bioavailability Studies
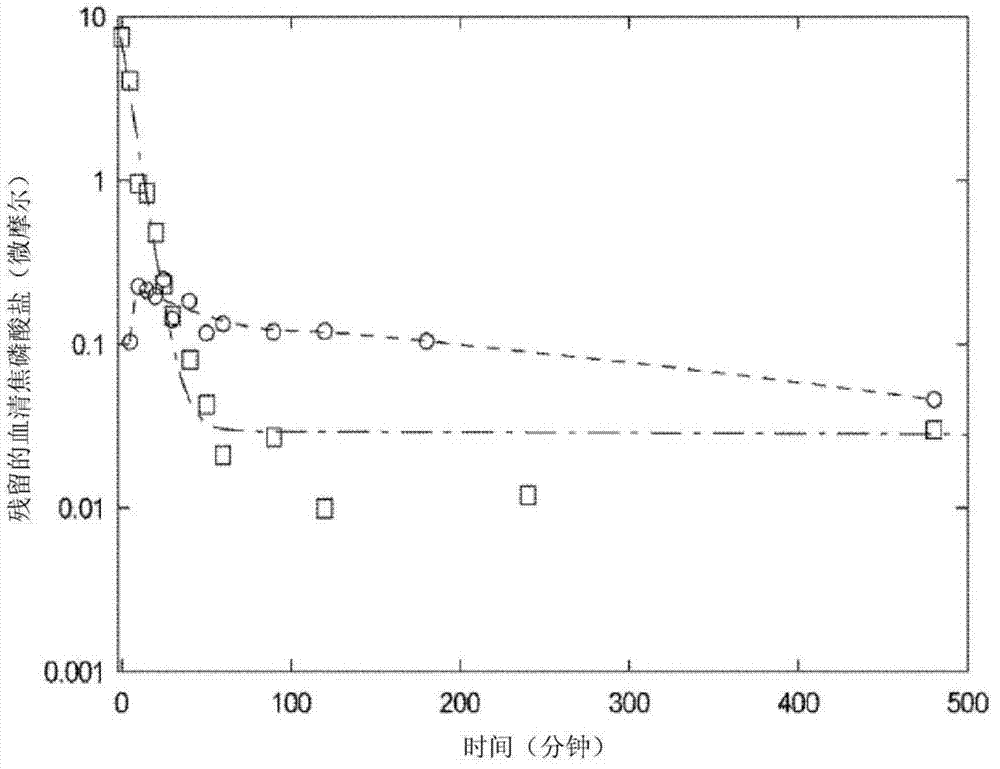
[0055]Fifty-four male Sprague Dawley rats, each approximately 250 g, were randomly divided into two groups, intravenous ("IV") administration and intraperitoneal ("IP") administration. Both groups received a pyrophosphate ("PPi") dose of 2.0 mg / kg. As a single bolus, Group 1 was administered pH-adjusted (7.4), 4 mL / kg via tail vein infusion, containing PPi 2.25 mM and P-32-labeled PPi (50 μCi, specific activity 84.5 Ci / mmol). saline solution, and then rinsed with 0.2 mL of saline. Group 2 was administered PPi and P-32-labeled PPi (50 μCi, specific activity 84.5 Ci / mmol) via a single intraperitoneal injection at 40 0.15mM solution in dialysis solution at a dose of 60mL / kg. Blood (IV) as well as blood (IP) and peritoneal fluid (IP) were collected at various time points up to 8 hours post-dose.
[0056] Plasma and peritoneal fluid were analyzed by two methods: a liquid scintillation method to analyze total radioactivity, and...
Embodiment 2
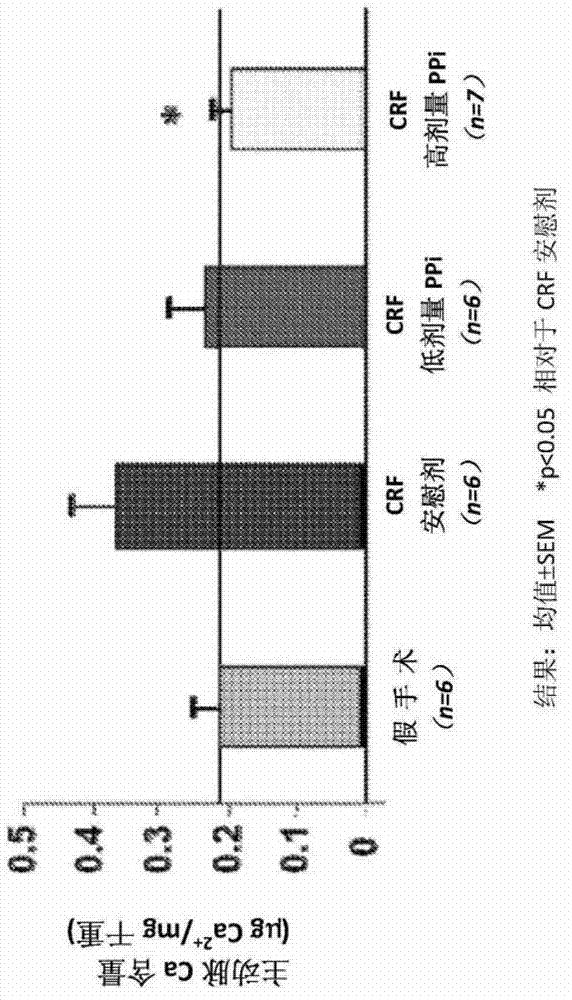
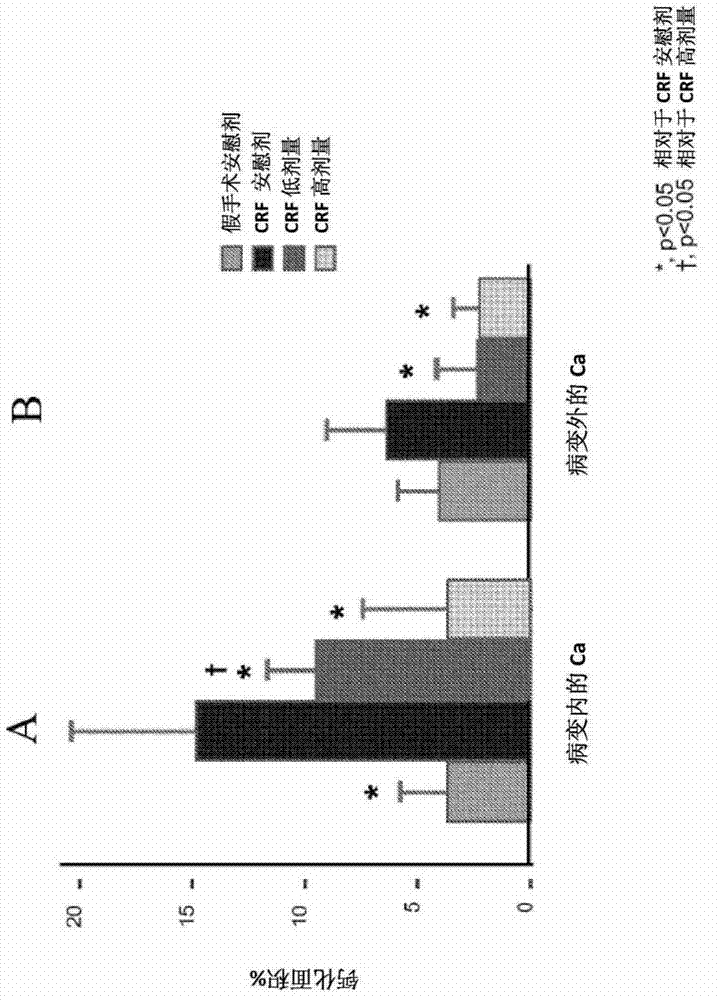
[0064] Establishing vascular calcification as a model of human disease in the dialysis population
[0065] The homozygous apolipoprotein E knockout (apoE - / - ) mice were housed in polycarbonate cages in a pathogen-free, temperature-controlled (25°C) room with a strict 12-h light / dark cycle, and had ad libitum access to laboratory chow and water. All procedures were in accordance with the National Institutes of Health ("NIH") Guidelines for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publication No. 85-23).
[0066] In 8-week-old female apoE - / - Chronic renal failure ("CRF") was established in mice, which were then randomly assigned to 4 groups as follows:
[0067] 1) Non-CRF-EKO (ApoE knockout) animals (control group, 6 mice);
[0068] 2) CRF / EKO animals treated only with dialysis solution without PPi (CRF placebo group, 8 mice);
[0069] 3) CRF / EKO animals (CRF PPi low dose group, 8 mice) treated with low dose PPi (30 μM, about 0.21 mg PPi / kg body weight / day) in dialysi...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The maximum tolerated dose study was conducted according to the study design in Table 3. The administered solution consisted of dextrose concentrate or modified dextrose concentrate mixed with buffer concentrate or modified buffer concentrate in a 3:1 ratio (dextrose:buffer). The compositions of the concentrates are shown in Tables 4-7. PPi was contained in the buffers or modified buffer solutions shown in Tables 5 and 7. As a bolus injection, each test article or control article was intraperitoneally administered once daily in a volume of 40 mL / kg to each of five different female rats through a butterfly needle for 7 consecutive days. Necropsy was performed one day after the last dose.
[0081] Septal tissue samples from all rats were trimmed, processed, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned. Hematoxylin and eosin stained slides were prepared and examined by light microscopy. Microscopic observations were subjectively graded according to the relative severity of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com