Collaborative filtering method on basis of scene implicit relation among articles
An implicit relationship, collaborative filtering technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as high computational complexity, poor scalability, and difficulty in obtaining accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
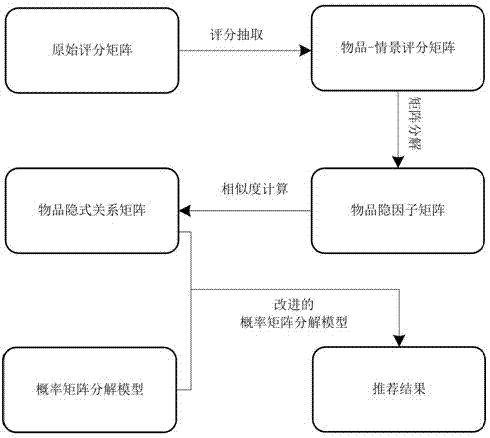
[0040] 1) Establishment of the movie-time rating matrix: from the original user-movie-time rating data, the ratings obtained by each movie at different times are obtained by means of weighted average, so as to establish the movie-time rating matrix. First, calculate the user's activity level at different times: D ik =N ik / N i , where D ik Indicates the activity level of user i at time k, N ik Indicates the number of ratings of user i at time k, N i Indicates the total number of ratings of user i; from the user-movie-time three-dimensional rating matrix Extract movie-time matrix from Here the matrix R ic In the jth row, the element r of the kth column jk denotes the rating of movie j at time k, and has in Denotes the rating of movie j by user i at time k.
[0041] 2) Movie implicit feature extraction: The movie-time rating matrix is decomposed by matrix decomposition method, and the hidden factor matrix of the movie is obtained: where I n×f That is, the late...
Embodiment 2
[0045] 1) Establishment of the restaurant-location scoring matrix: From the original user-restaurant-location scoring data, the scores obtained by each restaurant in different locations are obtained by weighted average, so as to establish the restaurant-location scoring matrix. First, calculate how active the user is in different locations: D ik =N ik / N i , where D ik Indicates the activity level of user i at location k, N ik Indicates the number of ratings of user i under location k, N i Indicates the total number of ratings of user i; from the user-restaurant-location three-dimensional rating matrix Extract restaurant-location matrix from Here the matrix R ic In the jth row, the element r of the kth column jk represents the rating of restaurant j relative to location k, and has in Indicates user i's rating on restaurant j at location k; in general, the closer to the restaurant, the higher the corresponding rating.
[0046] 2) Restaurant implicit feature extrac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com