Displacement control mode of rotor of direct-drive switched-reluctance planar motor
A technology of switched reluctance and planar motors, which is applied in the direction of electric components, electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., and can solve problems such as large fluctuations, unstable operation, and inability to meet the high precision and high speed of direct-drive switched reluctance planar motors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
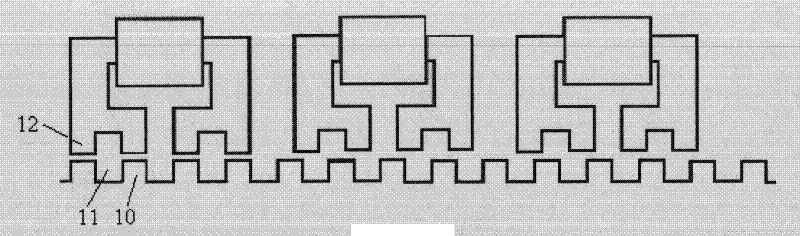
[0037] The displacement movement of the mover 7 changes periodically, and the movement cycle is equal to the stator pole distance 9, which is 12mm. Each cycle is divided into six equal parts, and the six different positions of the mover 7 relative to the stator 8 determine the position of the mover winding. power-on state.
[0038] When the mover 7 moves to the right in the x direction, the winding sequence is as follows:
[0039] I, X C The phase mover winding 1 is energized, at this time the mover teeth 12 of phase A are aligned with the stator teeth 10, and the mover 7 moves to the right by 1 / 6 of the stator pole pitch 9, which is 2mm;
[0040] II, X C Phase mover winding 1 and X B The phase mover winding 2 is energized at the same time, at this time, the B phase mover teeth 13 are aligned with the stator slot 11, and the mover 7 moves to the right by 1 / 6 of the stator pole pitch 9, which is 2mm;
[0041] III, X B The phase mover winding 2 is energized, at this time th...
Embodiment approach 2
[0050] The displacement movement of the mover 7 changes periodically, and the movement cycle is equal to the stator pole distance 9, which is 18mm. Each cycle is divided into six equal parts, and the six different positions of the mover 7 relative to the stator 8 determine the position of the mover winding. power-on state.
[0051] When the mover 7 moves to the right in the x direction, the winding sequence is as follows:
[0052] I, X C The phase mover winding 1 is energized, at this time the mover teeth 12 of phase A are aligned with the stator teeth 10, and the mover 7 moves to the right by 1 / 6 of the stator pole pitch 9, which is 3mm;
[0053] II, X C Phase mover winding 1 and X B The phase mover winding 2 is energized at the same time, at this time the B phase mover teeth 13 are aligned with the stator slot 11, and the mover 7 moves to the right by 1 / 6 of the stator pole pitch 9, which is 3mm;
[0054] III, X B The phase mover winding 2 is energized, at this time the...
Embodiment approach 3
[0059] The displacement movement of the mover 7 changes periodically, and the movement cycle is equal to the stator pole distance 9, which is 24mm. Each cycle is divided into six equal parts, and the six different positions of the mover 7 relative to the stator 8 determine the position of the mover winding. power-on state.
[0060] When the mover 7 moves to the right in the x direction, the winding sequence is as follows:
[0061] I, X C The phase mover winding 1 is energized, at this time the A phase mover teeth 12 are aligned with the stator teeth 10, and the mover 7 moves to the right by 1 / 6 of the stator pole pitch 9, which is 4mm;
[0062] II, X C Phase mover winding 1 and X B The phase mover winding 2 is energized at the same time, at this time, the B phase mover teeth 13 are aligned with the stator slot 11, and the mover 7 moves to the right by 1 / 6 of the stator pole pitch 9, which is 4mm;
[0063] III, X B The phase mover winding 2 is energized, at this time the C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com