Method for specific signal amplification and detection of DNA targeted sequence
A target sequence and signal amplification technology, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient sensitivity and indistinct distinction of single base mismatches
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1
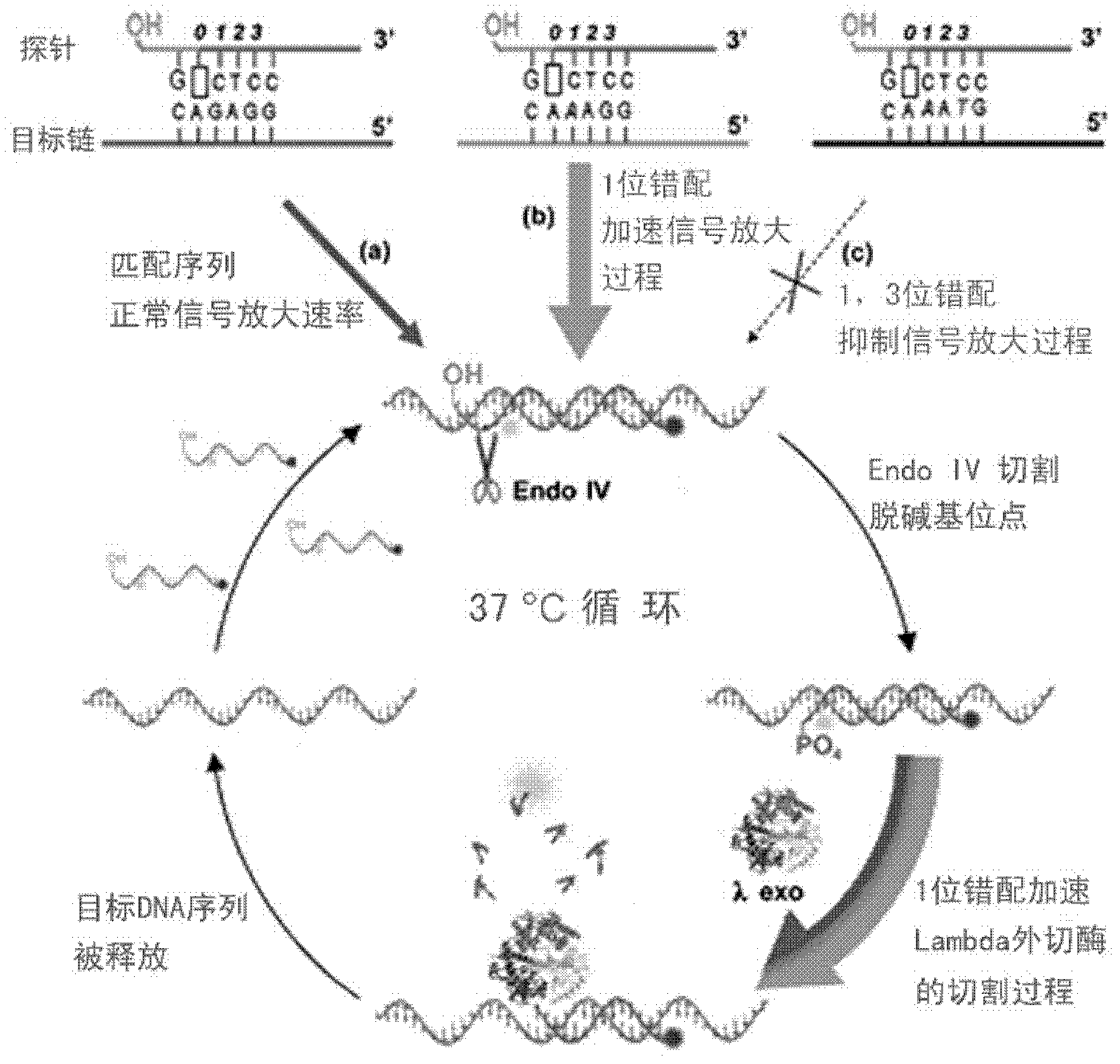
[0040] In this embodiment, the target is a DNA single strand, and the probe is completely matched with the target DNA single strand except for the abasic site. In the experiment, a series of concentration gradients of DNA single strands were set up, hoping to detect as few target strands as possible. For detection principle see figure 1 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0041] 1. Design and synthesize a double-labeled fluorescent probe containing uracil deoxynucleotide residues, and then use UDG enzyme to obtain a single abasic probe;
[0042] 2. Mix the obtained single abasic probe with different concentrations of the target DNA sequence, then add endonuclease IV and Lambda exonuclease, and quickly measure the change of the fluorescence value of the mixed solution over time.
[0043] In this embodiment, the designed probe sequence is as follows:
[0044] 5'-TCGUCT(-FAM)CCACAGACACATACTCCA-BHQ 1-3'(SEQ ID No.1)
[0045] The 5' end of the probe is -OH, th...
Embodiment 2
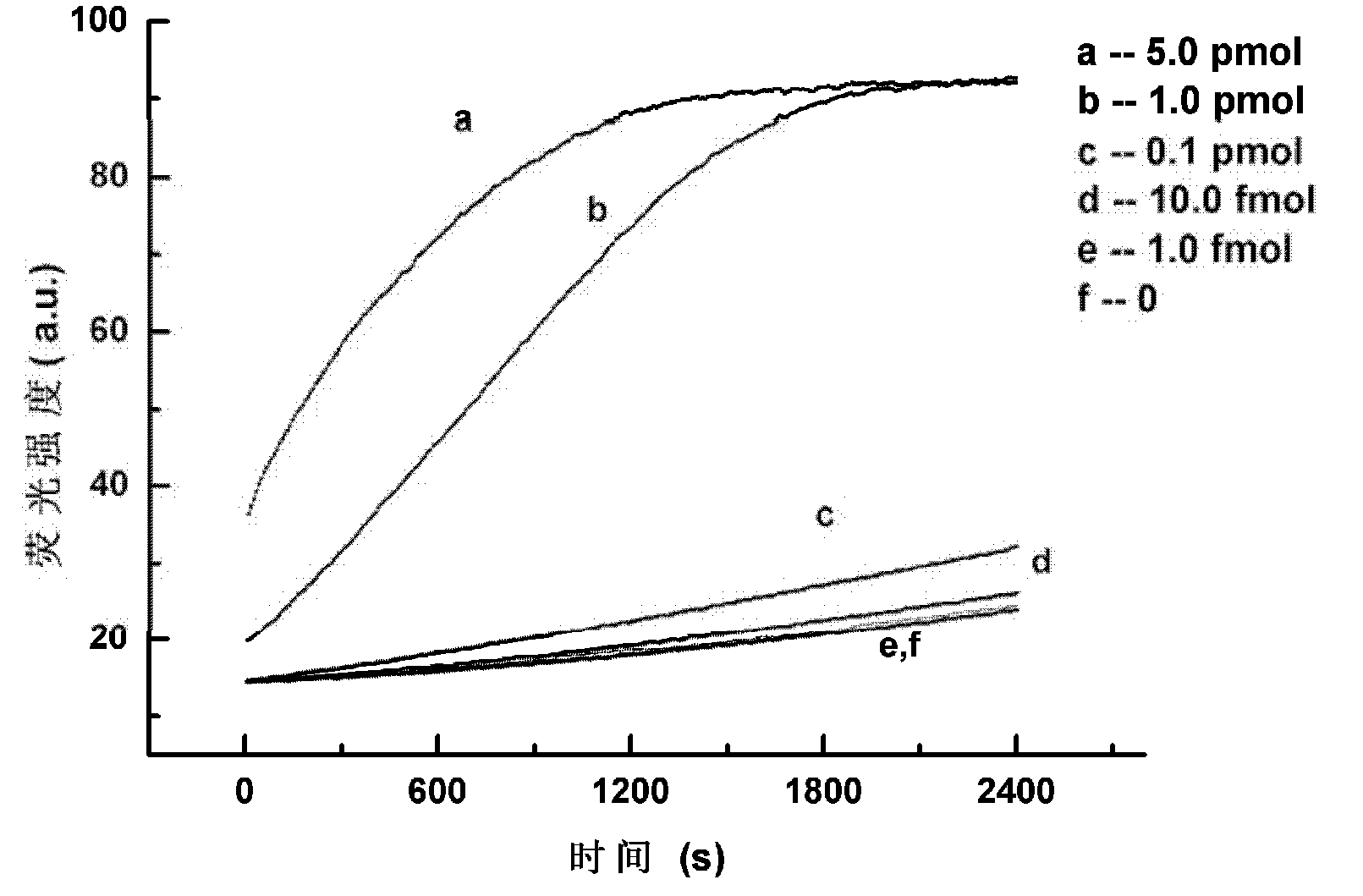
[0052] Test results: Fluorescence value change curve such as figure 2 As shown, the curves a, b, c, d, e and f correspond to the addition of 5pmol, 1pmol, 0.1pmol, 10fmol, 1fmol and 0 of the target sequence amount respectively. After 30 minutes, the fluorescence value reached a plateau in the reaction system with more than 1 pmol of the target sequence. Example 2
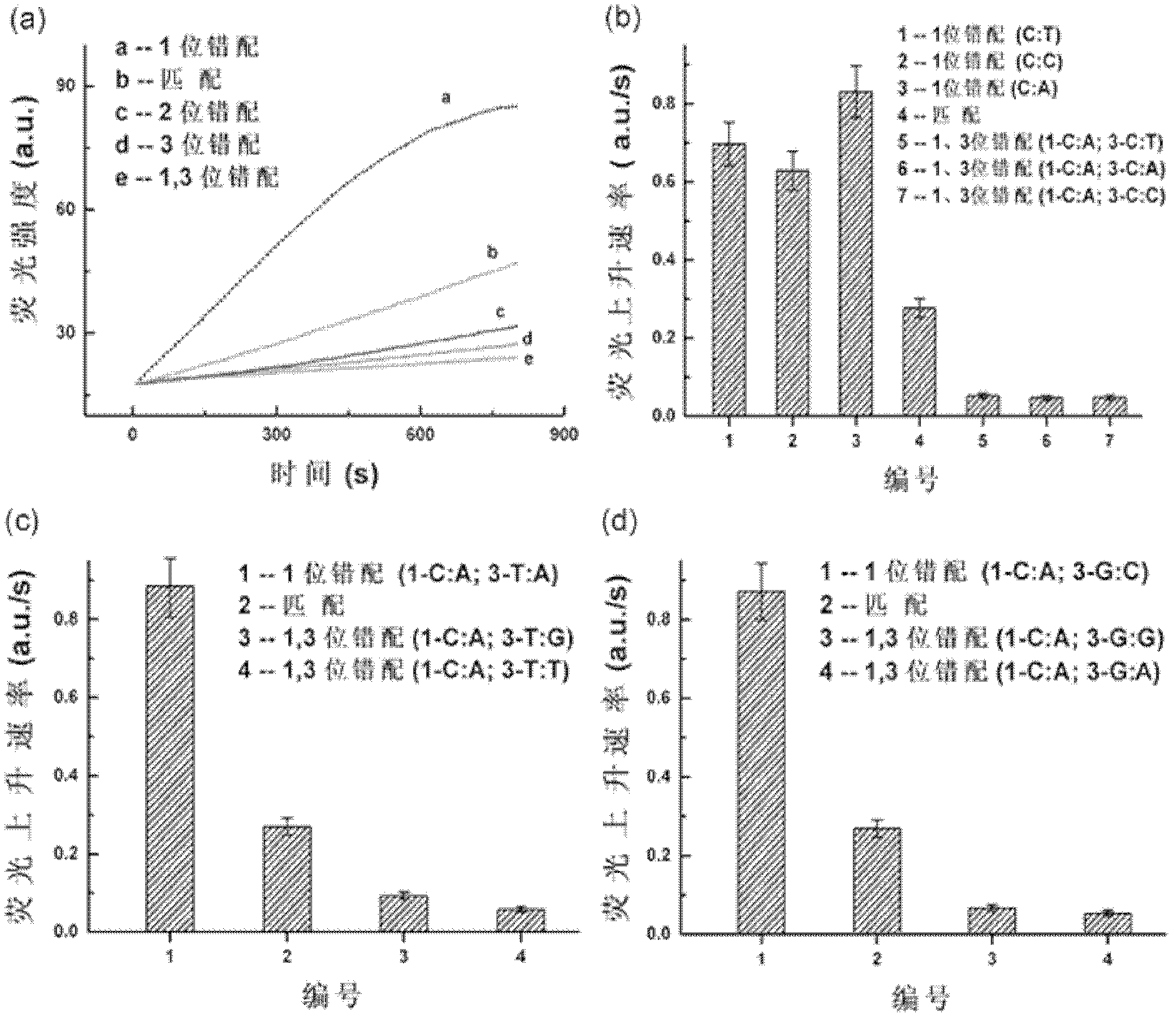
[0053] In this example, the target is a single strand of DNA. A series of different types of DNA single strands were set up in the experiment: In addition to the abasic site, the single abasic double fluorescent label probe was mismatched with these single strands, 1 mismatch, perfect match, 2 mismatches, 3 mismatches Or 1, 3 mismatches. For detection principle see figure 1 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0054] 1. Design and synthesize a double-labeled fluorescent probe containing uracil deoxynucleotide residues, and then use UDG enzyme to obtain a single abasic probe;
[0055] 2. Mix the obtained single ...
Embodiment 3
[0107] Example 3
[0108] In this embodiment, the target is a DNA single strand, and except for the abasic site, the probe is mismatched with the target DNA single strand at position 1. In the experiment, a series of concentration gradients of DNA single strands were set up, hoping to detect as few target strands as possible. For detection principle see figure 1 ,Specific steps are as follows:
[0109] 1. Design and synthesize a double-labeled fluorescent probe containing uracil deoxynucleotide residues, and use UDG enzyme to obtain a single abasic probe;
[0110] 2. Mix the obtained single abasic probe with different concentrations of target DNA sequences, then add endonuclease IV and Lambda exonuclease, and quickly measure the change of the fluorescence value of the mixed solution over time.
[0111] In this embodiment, the designed probe sequence is as follows:
[0112] 5'-TCGUCT(-FAM)CCACAGACACATACTCCA-BHQ 1-3'(SEQ ID No.1)
[0113] The 5' end of the probe is -OH, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com