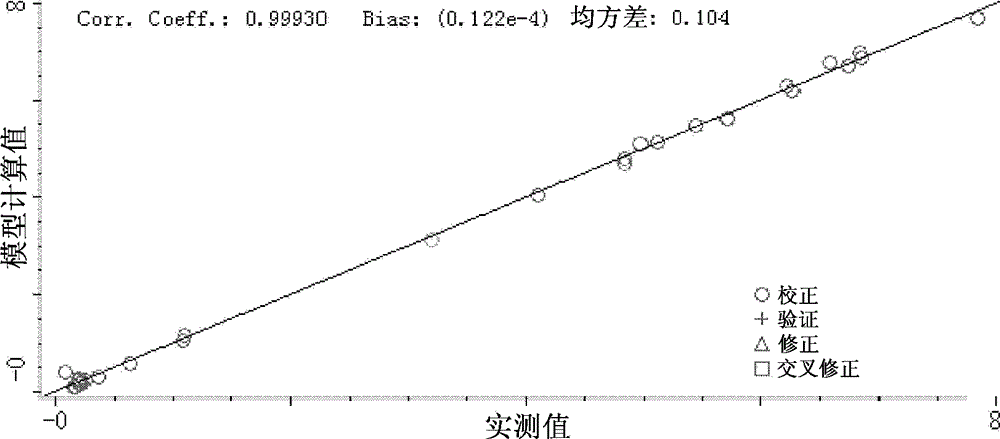
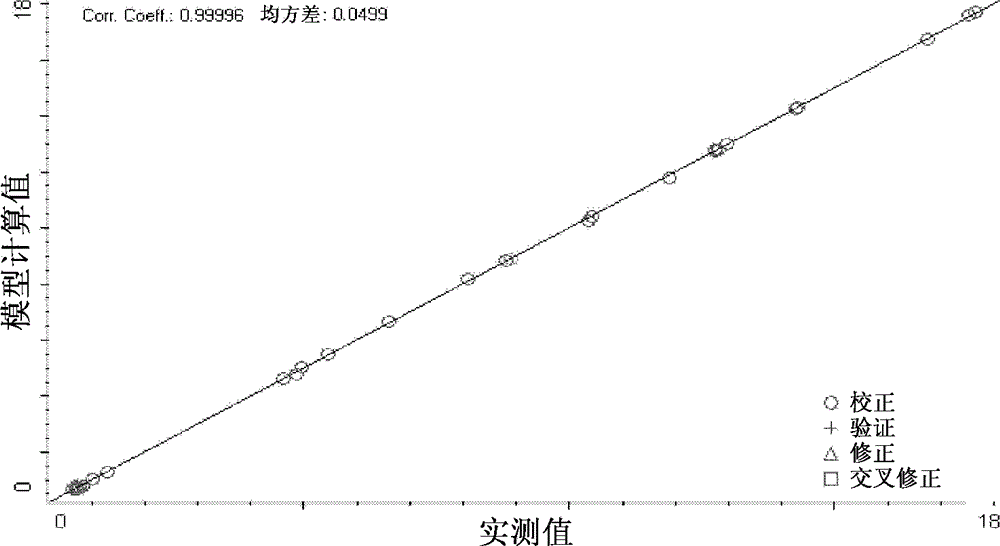
Method for treating leather by using tannery wastewater and method for producing leather
A technology for tanning wastewater and leather, which is applied in animal processing wastewater treatment, small hide/big hide/leather/fur treatment, tanning treatment, etc. issues such as recycling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0140] Embodiment 1: wet blue leather (cowhide upper leather) neutralization process
[0141] (I) Main chemical materials:
[0142] TANIGAN PAK-N-C (phenols), product of LAXESS.
[0143] Wet blue leather (cowhide upper leather);
[0144] (II) Process (the amount added here is for the weight of the processed hide, based on 100 parts of the tare weight)
[0145] Process: (blue leather) peeling → weighing → washing → neutralization (to pH5.0) → retanning → washing → fatliquoring → adjusting pH → washing → drumming.
[0146] After the blue skin is evenly peeled, weighed, and washed with water, it begins to be neutralized and divided into four groups: A, B, C, and D. The details are as follows:
[0147] A. It is a blank sample without adding TANIGAN PAK-N-C,
[0148] 150 parts of water (40°C) and 1.5 parts of sodium formate and 0.5 parts of baking soda were treated at about 40°C for 60 minutes.
[0149] B. With fresh water, the amount of material TANIGAN PAK-N-C added is 4% of...
Embodiment 2
[0174] Embodiment 2: simple retanning process of wet blue leather:
[0175] (I) Main material
[0176] TANIGANLT-C, product of LANXESS.
[0177] Leather to be treated: Neutralized wetblue (cowhide upper leather).
[0178] (II) Process
[0179] Technological process (the amount added here is for the weight of the processed hide, based on 100 parts of the tare weight)
[0180] Process: (blue leather) peeling → weighing → washing → neutralization (to pH5.0) → retanning → washing → fatliquoring → adjusting pH → washing → drumming.
[0181] After the blue skins are evenly shaved, weighed, washed, and neutralized, retanning begins, and they are divided into four groups: A, B, C, and D, as follows:
[0182] A. It is a blank sample without adding TANIGAN LT-C,
[0183] Add 100 parts of water, treat at 40°C for 60 minutes, and then add 0.5 parts of 85% formic acid for 20 minutes.
[0184] B. With fresh water, the amount of material TANIGAN LT-C added is 6% of the tare weight,
...
Embodiment 3
[0208] Embodiment 3: standard retanning process
[0209] (I) Main material
[0210] TANIGAN LT-C (phenols), product of LANXESS.
[0211] LEVOTAN 1084 (acrylic), product of LANXESS.
[0212] RATINGAN R7 (dicyandiamides), product of Lanxess.
[0213] Leather to be treated: wet blue (cowhide upper leather).
[0214] (II) Process
[0215] Technological process (the amount added here is for the weight of the processed hide, based on 100 parts of the tare weight)
[0216] Process: (blue leather) peeling → weighing → washing → neutralization (to pH5.0) → retanning → washing → fatliquoring → adjusting pH → washing → drumming.
[0217] After the blue leather is shaved, weighed, washed, and neutralized, retanning begins, and it is divided into two groups, A and B, as follows:
[0218] A. For fresh water plus tanning material treatment,
[0219] First add 100 parts of water, then add 6 parts of TANIGAN LT-C, 4 parts of LEVOTAN 1084, 6 parts of RETINGAN R7 and treat at 40°C for 60 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com