Ionizing radiation degradation method for sea cucumber polysaccharide
The technology of sea cucumber polysaccharide and ionizing radiation is applied in the field of degradation method of polysaccharide compounds, which can solve the problems of detachment of sulfate group and branched-chain sulfated fucose, complicated operation of oxidative decomposition method, difficult process control, etc. Loss, product molecular weight uniformity, no environmental pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: The ionizing radiation degradation method of sea cucumber polysaccharide:
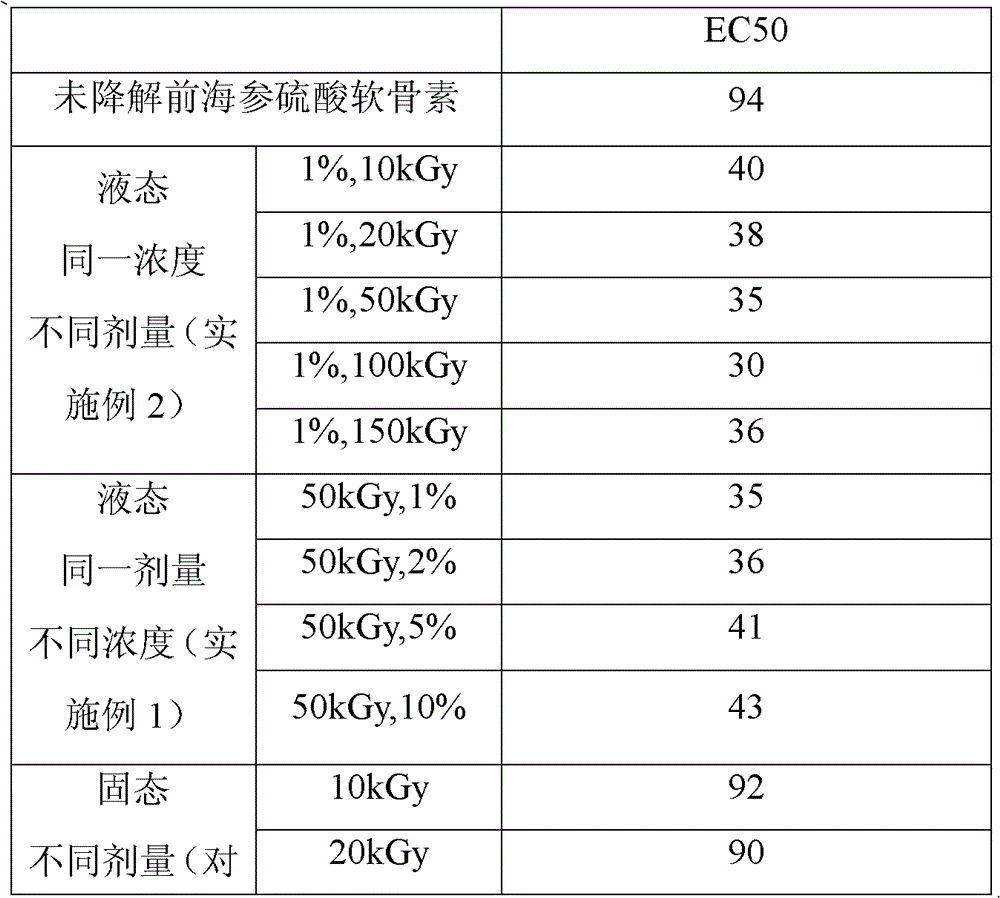
[0023] Weigh four parts of Philippine sea cucumber chondroitin sulfate (50 mg each) and prepare them into aqueous solutions with mass percentage concentrations of 1%, 2%, 5%, and 10%. All were treated with ionizing radiation, the absorbed dose was 50kGy, and the radiation dose rate was 45kGy / min; after irradiation, it was allowed to stand for 1.5 hours, the non-degradable matter settled to the bottom of the container, and the supernatant was taken.
[0024] The four supernatants were vacuum freeze-dried (-40° C.) to obtain 42 mg, 39 mg, 40 mg, and 35 mg of low molecular weight chondroitin sulfate (ie, low molecular weight oligosaccharides).
[0025] HPLC high performance gel permeation chromatography (TSK3000, 4000) was used to determine the relative molecular weight, number average molecular weight, weight average molecular weight, and molecular weight distribution index of different concen...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: The ionizing radiation degradation method of sea cucumber polysaccharide:
[0030] Weigh 5 parts of Philippine sea cucumber chondroitin sulfate (50 mg each), and prepare them into an aqueous solution with a mass percentage concentration of 1%. They were treated with 5 different doses of ionizing radiation, the absorbed doses were 10KGy, 20KGy, 50KGy, 100KGy, 150KGy, and the radiation dose rate was 45kGy / min; 1.5 hours after the irradiation, the non-degradable matter settled to the bottom of the container, and take it Clear liquid.
[0031] The five supernatants were vacuum freeze-dried (-40°C) to obtain 39 mg, 38 mg, 42 mg, 41 mg, and 37 mg of low-molecular-weight chondroitin sulfate (ie, low-molecular-weight oligosaccharides).
[0032] HPLC high performance gel permeation chromatography (TSK3000) was used to determine the relative molecular weight of the same concentration of chondroitin sulfate under different irradiation doses. Details are shown in Table 2.
[0...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com