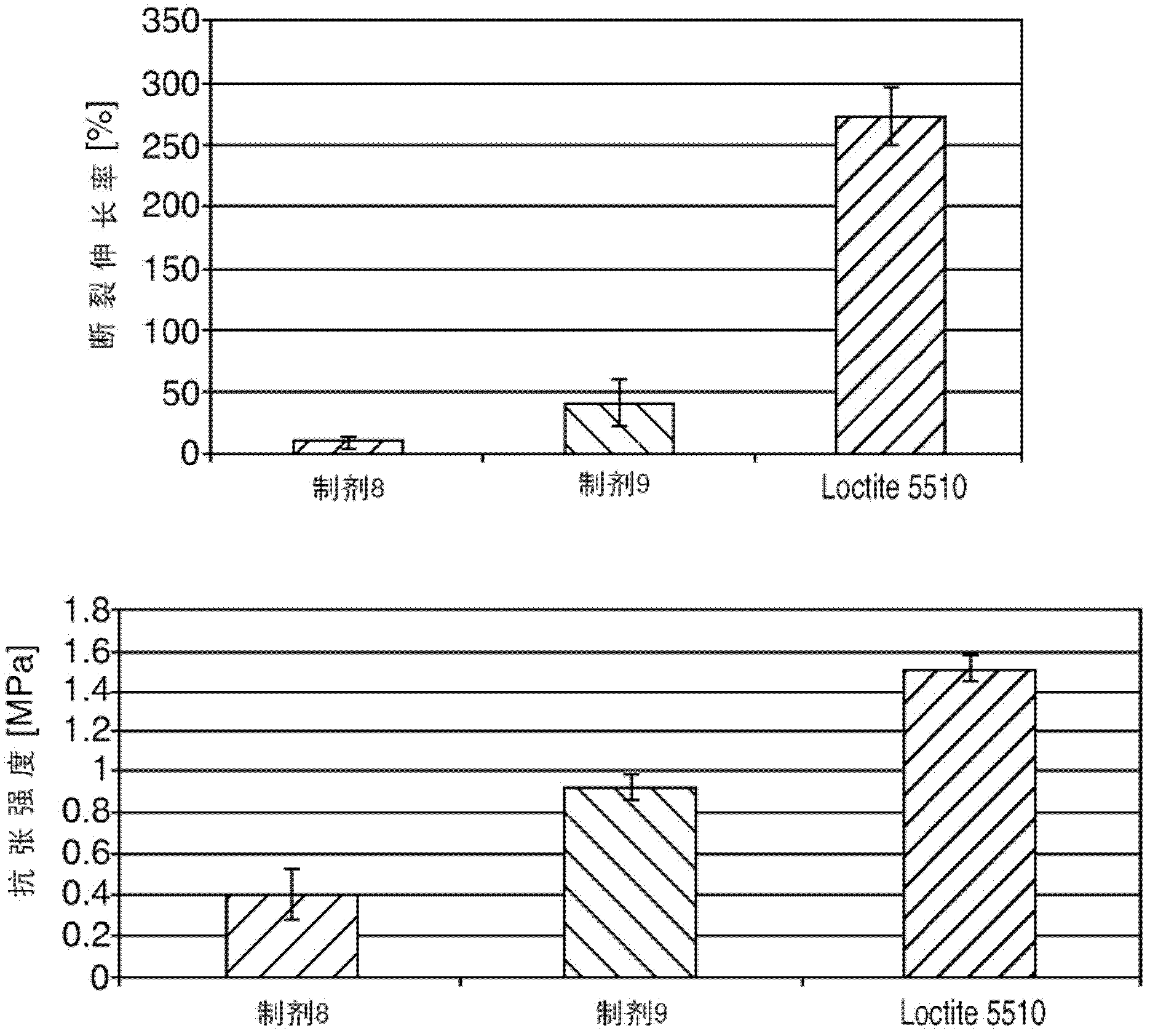
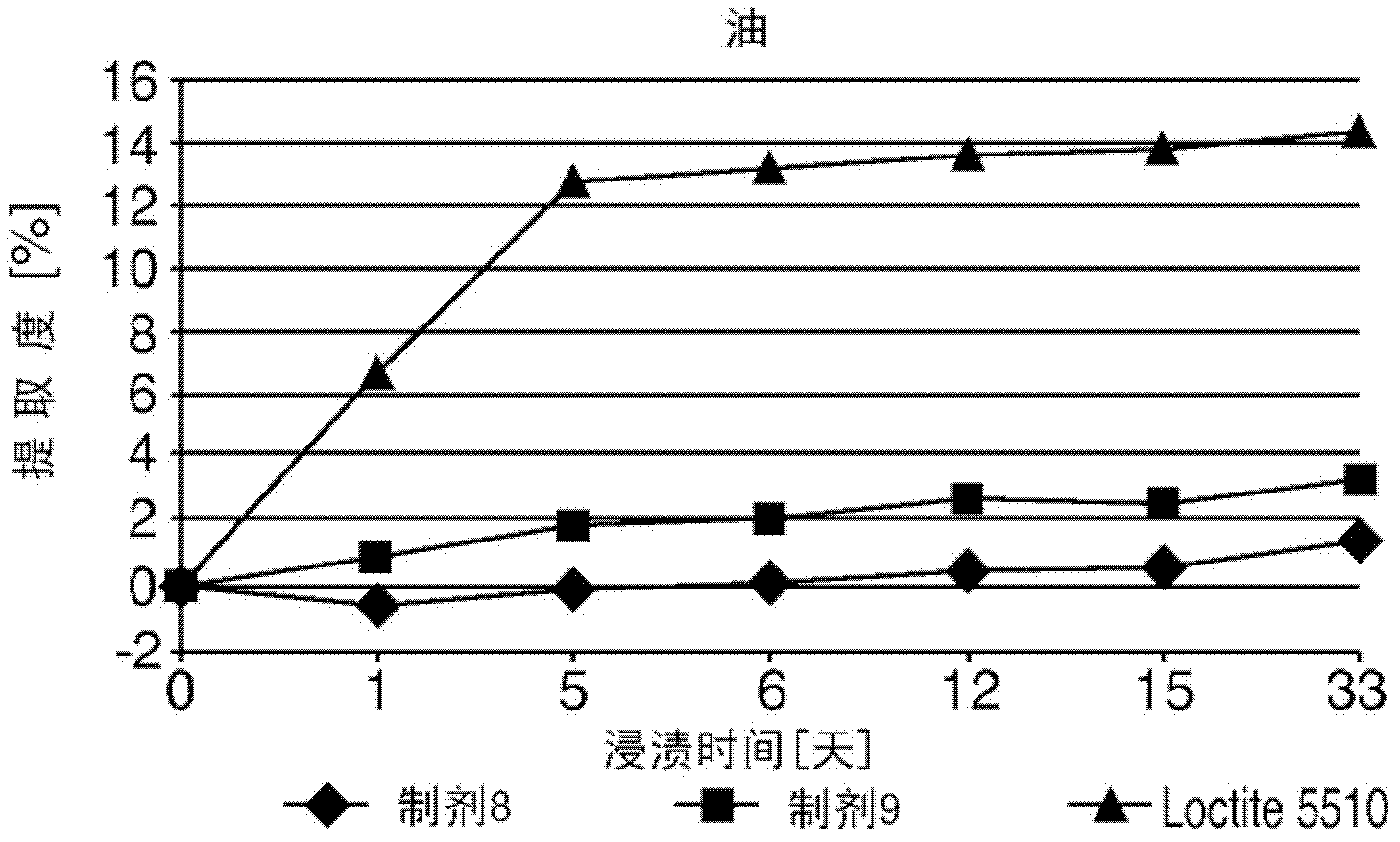
Moisture curable polydisulfides
A polydisulfide, moisture curing technology, applied in the field of polydisulfide, can solve the problems of short tank life and toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example
[0093] In each of the following synthesis examples, liquid polysulfide materials purchased from LP North America Distribution were used, and the specifications as received are shown in Table 1. The thiol equivalent weight was determined by potentiometric titration.
[0094] Table 1: Specifications of Liquid Polydisulfide
[0095]
[0096] Source: Technical Data Sheet from LP North America Distribution, Inc.
[0097] * Determined by potentiometric titration (Na 2 the s 2 o 3 / I 2 )
[0098] The general branched structures of these polydisulfides are shown below. LP 55 was prepared without branching agent, which has a linear di-telechelic structure. It can be used to prepare chain-extended linear polymers by reaction with other difunctional compounds.
[0099]
[0100] Trimercapto Capcure and trimethylolpropane-tris(3-mercapto-propionate) were supplied by Sigma Aldrich and Cognis, respectively. Vinyltrimethoxysilane and allyltrimethoxysilane purchased from Sigma ...
Embodiment 1
[0102] Example 1 : Reaction of polydisulfide LP-3 and vinyltrimethoxysilane via radical mercapto-ene addition
[0103]
[0104] To a 100-mL three-necked reaction flask equipped with a magnetic stirrer, thermocouple, and nitrogen inlet was added 183.7 g (0.18 mole) of polydisulfide LP-3 with a thiol equivalent weight of 510 g / eq and 53.3 g (0.36 mole) of vinyltrimethoxysilane.
[0105] The mixture was stirred to obtain a homogeneous solution, 2.7 g (0.008 mole) of 2,2'-azobis(4-methoxy-2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile) ("V-70") was added and dissolved. The headspace was flushed with nitrogen and the solution was heated to 60°C during which time bubbling nitrogen gas was formed due to the decomposition of the azonitrile initiator. Aliquots of the mixture were removed periodically and analyzed for unreacted vinyl by infrared spectroscopy. After 6 hours, the vinyl was completely consumed. The reaction mixture was cooled to give the product α,ω-bis(trimethoxysilane) functional pol...
Embodiment 2
[0110] Example 2 : Reaction of polydisulfide LP-3 and allyltrimethoxysilane via radical mercapto-ene addition
[0111]
[0112] To a three-necked 300-mL reaction flask equipped with a nitrogen headspace purge, magnetic stirrer, heating mantle, and thermocouple was added 51.054 g (~0.05 mole) of polydisulfide LP-3 with a thiol equivalent weight of 510 g / eq. , 16.219 g (0.1 mole) of allyltrimethoxysilane and 0.681 g (2.21 mmole) of 2,2'-azobis(4-methoxy-2,4-dimethylvaleronitrile). Stir the mixture and heat. At 45°C, a homogeneous pale yellow solution was formed, and at 50°C a strongly exothermic reaction occurred, driving the temperature to 85°C. The exothermic reaction ended with evolution of nitrogen. The mixture was cooled to 60°C and stirred for 5 hours, during which time gas evolution ceased. The mixture was cooled and the trimethoxysilane-functional polydisulfide was isolated in high yield.
[0113] The structure of the product was confirmed by spectroscopic analy...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com