Electrostatic discharge protecting device and method thereof
An electrostatic discharge protection, power supply voltage technology, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, circuit devices, emergency protection circuit devices for limiting overcurrent/overvoltage, etc., can solve the problem that general products and methods have no suitable structure and method, Inconvenience, affecting the operation of internal circuits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0058] figure 1 is a schematic structural view of the electrostatic discharge protection device according to the first embodiment of the present invention, wherein figure 1 The internal circuit 10 and the bonding pad 20 are also shown. see figure 1 As shown, the internal circuit 10 operates at a power supply voltage VDD and receives an input voltage through the bonding pad 20 . In addition, the ESD protection device 100 is used to protect the internal circuit 10 to avoid damage to the internal circuit 10 caused by an electrostatic signal.
[0059] The ESD protection device 100 includes a protection unit 110 and a control unit 120 . Further, the protection unit 110 includes a diode D2, an N-type transistor N3, and an N-type transistor N4. Wherein, the anode end of the diode D2 is electrically connected to the pad 20 and the internal circuit 10 . The drain terminal of the N-type transistor N3 is electrically connected to the cathode terminal of the diode D2 , and the gate t...
no. 2 example
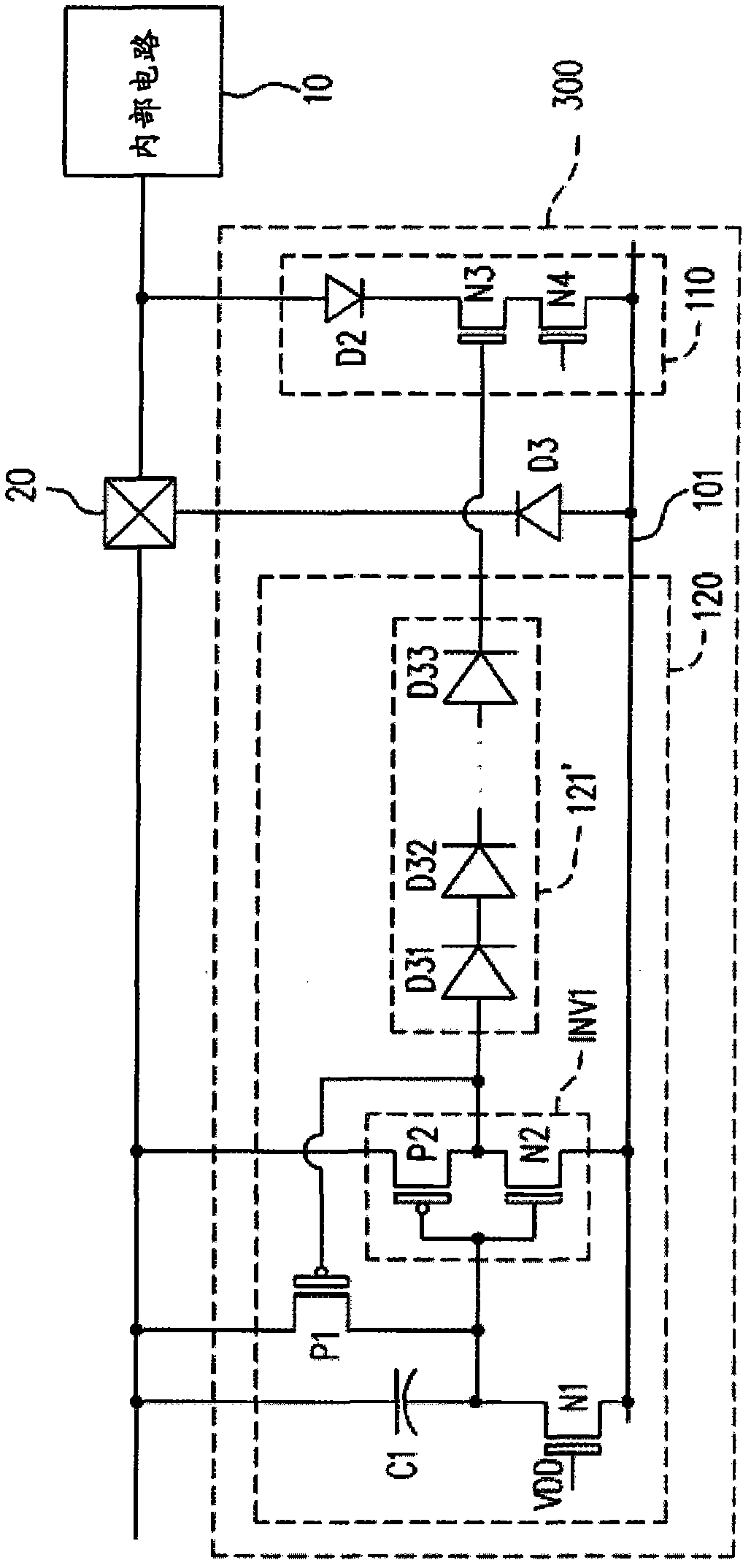
[0072] image 3 is a schematic structural diagram of an electrostatic discharge protection device according to a second embodiment of the present invention. see image 3 As shown, this embodiment is substantially the same as the first embodiment, and image 3 The same or similar component numbers represent the same or similar components, and will not be repeated in this embodiment.
[0073] The main difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that in the ESD protection device 300 described in this embodiment, the isolation circuit 121' is composed of a plurality of diodes D31-D33. Wherein, the diodes D31 - D33 are connected in series to form a diode series. In addition, the anode end of the diode series, that is, the anode end of the diode D31, is used as the first end of the isolation circuit 121', and the cathode end of the diode series, that is, the cathode end of the diode D33, is used as the isolation circuit 121' of the second end. In this way, wh...
no. 3 example
[0075] Figure 4 is a schematic structural diagram of an electrostatic discharge protection device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. see Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment is substantially the same as the first embodiment, and Figure 4 The same or similar component numbers represent the same or similar components, and will not be repeated in this embodiment.
[0076] The main difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that: in the electrostatic discharge protection device 400 described in this embodiment, the isolation circuit 121 "is composed of an N-type transistor N5. Wherein, the N-type transistor N5 The gate terminal is electrically connected to the drain terminal to form the first terminal of the isolation circuit 121", and the source terminal of the N-type transistor N5 is used as the second terminal of the isolation circuit 121". In this way, when the isolation circuit 121" is the first terminal When the voltage level of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com