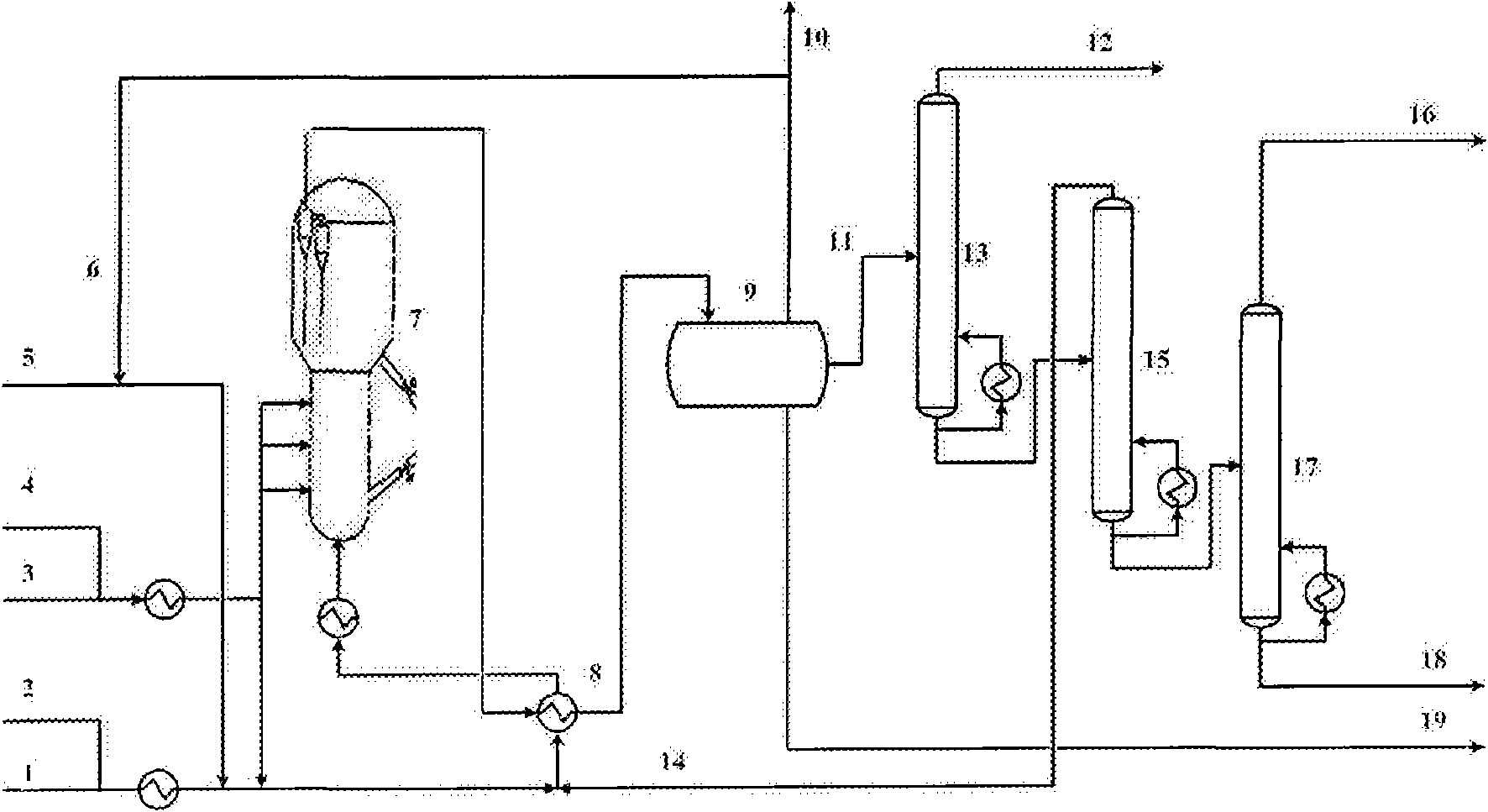
Method for preparing fluidized bed of para-xylene by aromatics alkylation
A technology for the alkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons and p-xylene, which is applied in the field of fluidized beds, and can solve problems such as poor catalyst stability, many side reactions of alkylating reagents, and large temperature rise of the reaction bed.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~3
[0034] The alkylation reaction was carried out according to the steps and conditions described in Comparative Example 1, wherein the aromatic hydrocarbon raw material was a mixture of benzene and toluene in different proportions, and the specific proportions and reaction evaluation results were listed in Table 1 for comparison.
[0035] Table 1
[0036]
[0037] The data in Table 1 shows that the use of benzene and toluene as mixed aromatics feed has no effect on the control of the temperature rise of the catalyst bed, but the side reactions of methanol itself and the deep alkylation reaction are still significantly suppressed, and the methyl utilization rate The selectivity of p-xylene and xylene was significantly improved, and the selectivity of p-xylene was slightly improved, while the conversion rate of aromatics decreased to a certain extent.
Embodiment 4~7
[0039] Carry out the alkylation reaction according to the steps and conditions described in Example 2, wherein the alkylation reagent feed is selected from a mixture of methanol and dimethyl ether, and the molar percentage of the methyl group contained in the dimethyl ether in the alkylation reagent is changed, specifically The ratio and reaction evaluation results are listed in Table 2 for comparison.
[0040] Table 2
[0041]
[0042] The data in Table 2 show that as the content of dimethyl ether in the alkylating agent increases, the exothermic heat of the reaction and the temperature rise of the catalyst bed show a downward trend, thereby inhibiting the side reactions of the alkylating agent itself, the deep alkylation reaction and the heterogeneous reaction. structuring reaction.
Embodiment 8~11
[0044] The alkylation reaction was carried out according to the steps and conditions described in Example 7, and the molar ratio of methyl groups and aromatic hydrocarbons contained in the alkylating agent in the feed was changed. The specific ratios and reaction evaluation results are listed in Table 3 for comparison.
[0045] table 3
[0046]
[0047] The data in Table 3 shows that the amount of alkylating agent has a great influence on various performance indicators. The larger the amount of alkylating agent is, the higher the conversion rate of aromatics is, but the worse the product selectivity and methyl utilization rate are.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com