Radius compensation algorithm for convex contour closed-angle linear and circular arc composite transitional cutting tool
A tool radius and convex profile technology, applied in computer control, instruments, simulators, etc., can solve problems such as long dwell time, sharp corner burns, difficulty in increasing processing speed, etc., achieve smooth and continuous tool center trajectory, and solve sharp corner burns Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0062] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
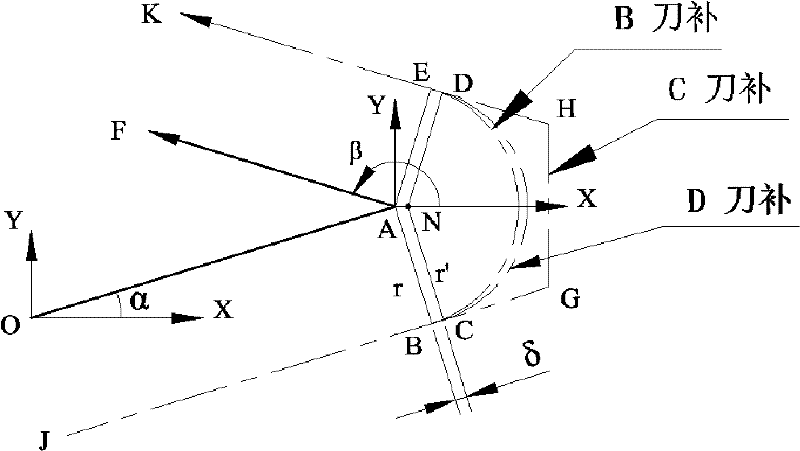
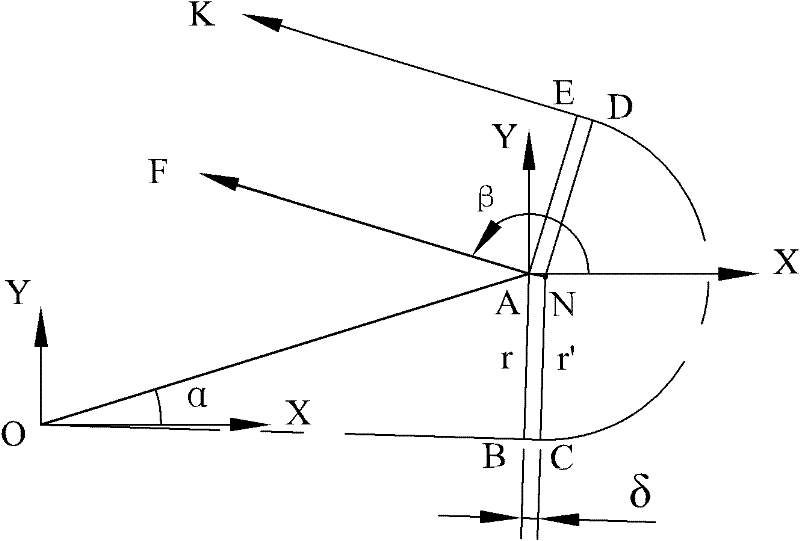
[0063] figure 1 It shows the algorithms and tool center trajectory of B tool compensation, C tool compensation and D tool compensation. Line segment JB, arc BE with radius r and line segment EK are tool center loci for B tool compensation; line segment JB, line segment BC, arc CD with radius r′, line segment DE and line segment EK are tool center loci for D tool compensation ; Line segment JB, line segment BG, line segment GH, line segment HE and line segment EK are the tool center trajectory of C tool compensation.
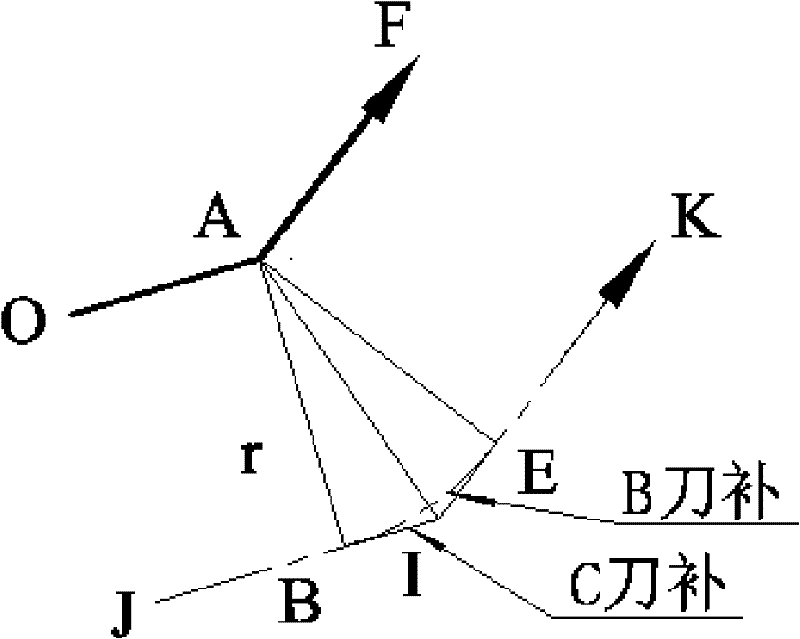
[0064] figure 2 It shows the analysis of the tool compensation algorithm when the sharp corner of the cam profile is an obtuse corner. The line segment JB, line segment BI, line segment IE and line segment EK are the tool center trajectory of the C tool compensation; the line segment JB, arc BE and line segment EK are the tool center trajectory of the B t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com