Fusion proteins the process to preparation and utilization in expression systems of recombinant proteins
A fusion protein and calcium-binding protein technology, applied in recombinant DNA technology, expression enhancement stability/folded protein fusion, peptides containing affinity tags, etc., can solve problems such as low yield, difficult to operate and precipitate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
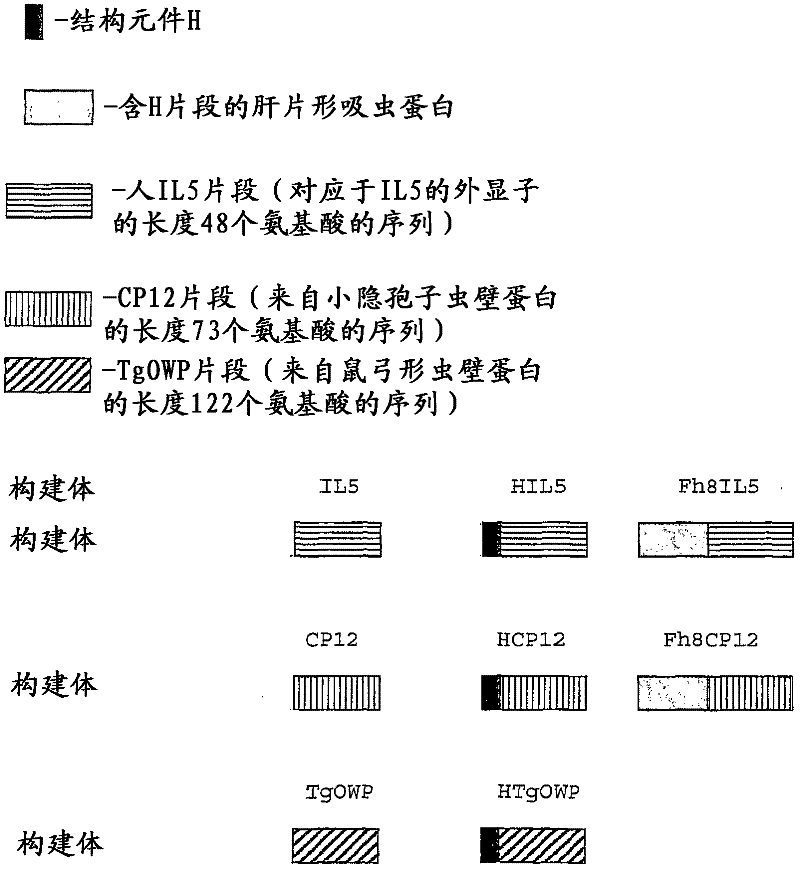
[0100] [Example 1: HCP12 and HIL5 constructs]
[0101] To obtain these constructs, we first obtained the H fragment. PCR was performed using primers H and Fh8Rev (see Table 1). Primer H allows insertion of a SacI restriction site after the codon for the 11th amino acid of Fh8. The PCR product was isolated and then digested with SacI restriction enzyme. The SacI-digested N-terminal fragment (H fragment) was then isolated.
[0102] Second, IL5 (primers IL5Sac and IL5Kpn) and CP12 (primers CP12Sac and CP12Kpn) fragments were amplified using isolated human genomic DNA (gDNA) and Cryptosporidium parvum gDNA as templates, respectively. After isolation of the PCR products, they were digested with SacI and the corresponding isolation of the Sac-digested fragments was performed.
[0103] Sac-digested H fragments were combined with SacI digested IL5 and CP12 fragments. The HIL5 fragment was obtained by PCR using this conjugate as a template, and primer H and primer IL5Kpn as primer...
Embodiment 2
[0104] [Example 2: HTgOWP construct]
[0105] To obtain the HTgOWP fragment, the pQEHCP12 vector was digested with KpnI and SacI, thereby removing the CP12 fragment from the vector, and thus obtaining pQE30H.
[0106] The TgOWP fragment was generated by PCR using gDNA of Toxoplasma gondii as a template, and primers TgOWPSac and TgOWPKpn.
[0107] The PCR reaction allows the addition of SacI and KpnI enzyme restriction sites to the DNA template sequence of TgOWP. This product was then purified on an agarose gel and bound to pGEM vector. Subsequently, digestion with KpnI and SacI restriction enzymes was performed, followed by isolation of the TgOWP fragment digested with SacI and KpnI. This fragment was incorporated into pQE30H vector digested with SacI and KpnI, thereby obtaining construct pQEHTgOWP.
[0108] This fragment was incorporated into pQE30H vector digested with SacI and KpnI, thereby obtaining construct pQEHTgOWP.
Embodiment 3
[0109] [Example 3: pQECP12, pQEIL5 and pQETgOWP constructs]
[0110] Vectors containing H fragments (pQEHCP12, pQEHIL5 and pQEHTgOWP) were used to prepare corresponding negative controls. HCP12, HIL5 and HTgOWP fragments were used as starting points for obtaining negative controls as described.
[0111] Since the procedures of the three vectors are similar, the following provides an example of preparing the pQECP12 recombinant vector. The pQEHCP12 vector was digested with Sad enzyme and then purified on an agarose gel.
[0112] After the purification step, the pQEHCP12 vector was also digested with EcoRI restriction enzyme, present in the pQE30 vector sequence. This digestion allowed removal of the H fragment as well as a small portion of the pQE30 vector. The pQEHCP12, pQEHIL5, and pQEHTgOWP vectors digested with SacI and EcoRI restriction enzymes were purified on agarose gels, followed by digested fragments of the pQE30 empty vector. For this purpose it was necessary to ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com