Method and device for measuring dynamic light scattering nanoparticles based on band-pass filtering
A dynamic light scattering and nanoparticle technology, applied in measurement devices, particle and sedimentation analysis, particle size analysis, etc., can solve the problems of limiting particle size reliability, wrong particle size distribution, particle size distribution deviation, etc. Data processing time, fast measurement, and the effect of measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Example 1 (scattered light from particles is directly detected by a photodetector):
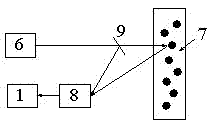
[0040] Depend on figure 2 As shown, it includes a semiconductor laser 6, a measurement area 7, a photodetector 8 and an analog circuit 1. The light beam emitted by the laser 6 irradiates the measurement area 7 . The light scattered by the particles in the measurement area 7 is received by the photodetector 8 , and finally the power spectral density function is obtained through the analog circuit 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2 (the scattered light of the particle interferes with part of the light of the original laser and is detected by the photodetector):
[0042] Depend on image 3 As shown, it includes a semiconductor laser 6, a beam splitter 9, a measurement area 7, a photodetector 8 and an analog circuit 1. The beam splitter 9 is placed between the laser 6 and the measurement area 7 , and the beam emitted by the laser 6 is split into two beams by the beam splitter 9 . One beam passes through the beam splitter and irradiates the measurement area 7; the other beam is reflected by the beam splitter as intrinsic light. The light scattered by the particles in the measurement area 7 interferes with the intrinsic light, and is detected by the photodetector 8 , and finally the power spectral density function is obtained through the analog circuit 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 (the light scattered by the particles is fed back into the laser cavity, self-mixed, and then the laser output is modulated and detected by the photodetector):
[0044] Depend on Figure 4 As shown, it includes a semiconductor laser 6, a measurement area 7, a photodetector 8 and an analog circuit 1. The photodetector 8 is placed behind the laser 6, and the light beam emitted by the laser 6 is irradiated to the measurement area 7, and the backscattered light from the particles is fed back into the laser resonant cavity to mix with the original laser. The backward output light of the laser is detected by the photodetector 8, and finally the power spectral density function is obtained through the analog circuit 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com