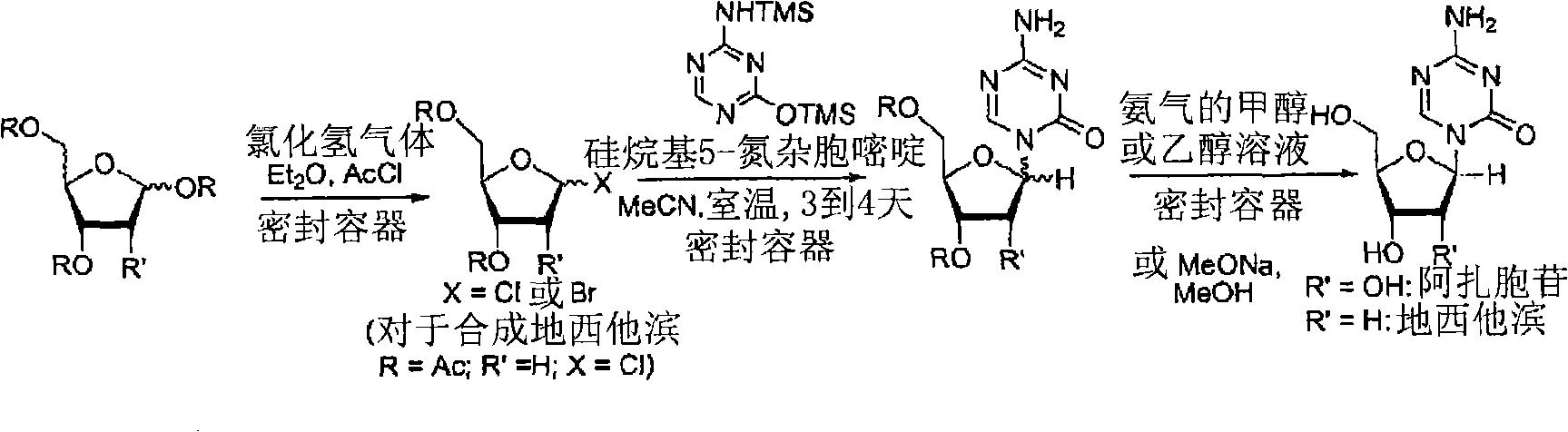
Process for making 5-azacytosine nucleosides and their derivatives
A kind of technology of azacytidine nucleoside compound and azacytidine nucleoside, which is applied in the field of preparation of 5-azacytidine nucleoside, which can solve the problem of difficult removal of tin, separation by difficult filtration steps, and not suitable for the synthesis of albino Zacitidine and decitabine, etc., to save time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0087] Preparation of 2-[(trimethylsilyl)amino]-4-[(trimethylsilyl)oxy]-s-triazine(silyl 5-azacytosine)
[0088]
[0089] A mixture of 5-azacytosine (7.33 Kg), HMDS (33.9 Kg) and ammonium sulfate (0.44 Kg) was heated at reflux (about 115 to 135° C.) and stirred for 16 hours. After the reaction was complete, the slurry was cooled to 118°C, then filtered through a pad of celite and rinsed with HMDS (5.6 Kg). The silylated 5-azacytosine solution was cooled to 35°C, and the solution was cooled to 18°C, stirred at 18°C for not less than 6.5 hours, and then filtered. The solid was washed twice with HMDS, 5.6 Kg each time, and dried under vacuum at ≤70° C. for 9.5 hours to obtain 14.19 Kg of white silyl 5-azacytosine (87%).
example 2
[0091] Coupling and deprotection of silyl 5-azacytosine to sugars
[0092]
[0093] At 55°C, 2-[(trimethylsilyl)amino]-4-[(trimethylsilyl)oxy]-s-triazine (4.5Kg), 1-O-acetyl-2 , a mixture of 3,5-tri-O-benzoyl-β-D-ribofuranose (8.8 Kg), anhydrous MeCN (34.6 Kg) and TfOH (600 g) was heated for 12.5 hours. The reaction mixture was cooled to 45 °C, DMSO (29 Kg) was added, and MeCN was evaporated under vacuum at an internal temperature of less than 50 °C until the solution was about 54 L. The solution was cooled to 23°C. MeOH (13.9 Kg) was added followed by a solution of 30% NaOMe in MeOH solution (2.5 Kg) previously diluted with MeOH (7.0 Kg). The solution was stirred at 23°C for 35 minutes. When the reaction was complete, MeOH (90.4 Kg) was added and the resulting slurry was stirred at 22° C. for 3 hours 10 minutes, then filtered and washed 3 times with 7.0 Kg of MeOH. Under vacuum, the filter cake was dried at less than 70°C for 9 hours and 20 minutes to obtain 3.2 Kg of ...
example 3
[0095] Purified Crude Azacitidine
[0096] Crude azacitidine (3.2 Kg) was dissolved in DMSO (11.8 Kg) at 20 to 40°C, filtered and the collected solids rinsed with DMSO (10.1 Kg). The filtrate was cooled to 20 to 25°C and MeOH (9.7 Kg) was added over a period of 30 minutes followed by azacitidine seed (30.6 g) and the mixture was stirred at 23°C for about 1 hour. Additional MeOH was added over a period of 4 hours 13 minutes and the mixture was stirred at 20 to 25 °C for at least 10 hours, filtered and washed 3 times with 10 Kg of MeOH. Under vacuum, the filter cake was dried at ≤70° C. for 33 hours to obtain 2.6 Kg of API grade azacitidine (86% yield based on crude azacitidine).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com