Recognition method for weld defect signal in ultrasonic testing of austenitic stainless steel
A technology for austenitic stainless steel and ultrasonic testing, applied in the direction of processing detection response signals, etc., can solve problems such as difficult identification of defect signals, influence of noise suppression effect, identification of noise suppression defect signals, etc., to overcome the difficulty of identifying weld defects and Quantitative measurement, good noise suppression effect, and defect signal enhancement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
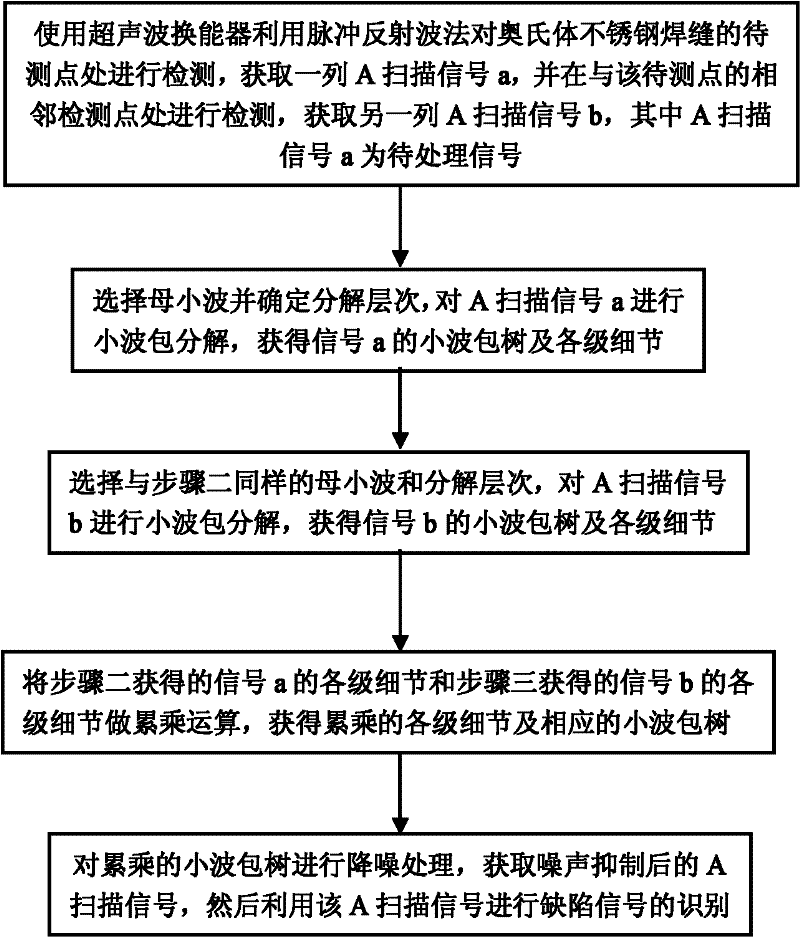
[0014] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, the method for identifying defect signals of ultrasonic detection of austenitic stainless steel welds described in this embodiment, the specific steps are:
[0015] Step 1: Use the ultrasonic transducer to detect the point to be measured of the austenitic stainless steel weld by the pulse reflected wave method, obtain a series of A-scan signals a, and perform detection at the detection point adjacent to the point to be measured , to obtain another column of A-scan signal b, wherein A-scan signal a is a signal to be processed;
[0016] Step 2: Select the mother wavelet and determine the decomposition level, perform wavelet packet decomposition on the A-scan signal a, and obtain the wavelet packet tree and details at all levels of the signal a;
[0017] Step 3: Select the same mother wavelet and decomposition level as in Step 2, and perform wavelet packet decomposition on the A-scan signal ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
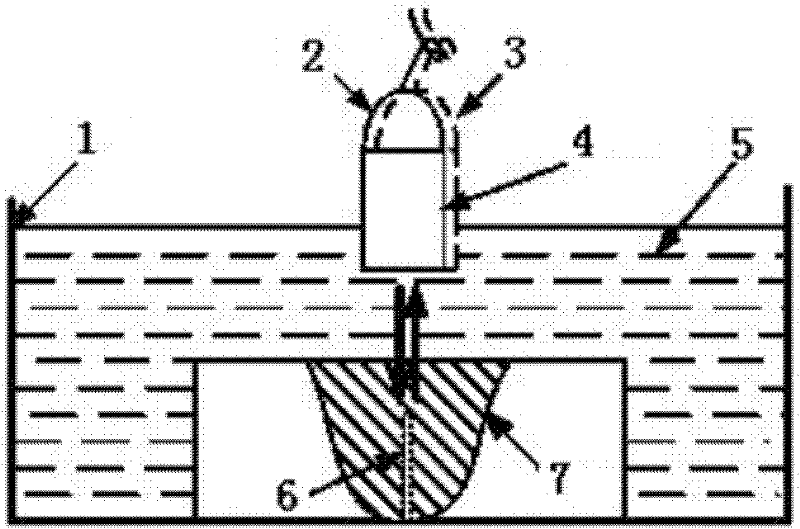
[0022] Specific Embodiment 2: This embodiment is an illustration of a method for identifying defect signals in ultrasonic detection of austenitic stainless steel welds. The following combination figure 2 Description of this method: the detection object of this embodiment is a flat-bottomed hole in an austenitic stainless steel weld with a thickness of 23.5mm, the diameter of the flat-bottomed hole is 2.0mm, the depth is 8mm, the depth of the water layer is 25mm, the system gain is 50dB, and the excitation voltage is 200V ; figure 2 Among them, 1 is the water tank, 2 is the position X, 3 is the position X', 4 is the ultrasonic probe, 5 is the water, 6 is the flat bottom hole, and 7 is the weld test piece;
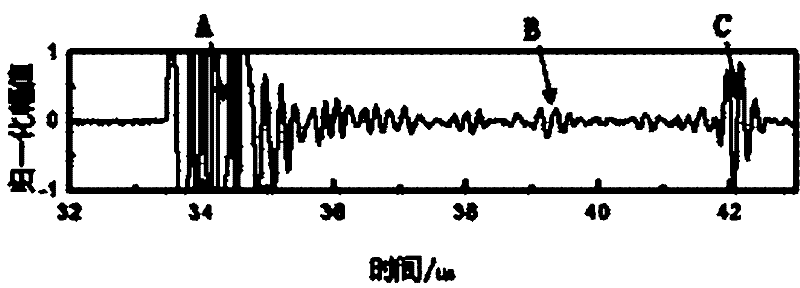
[0023] Step 1: If figure 2 As shown, the ultrasonic probe 4 is used to detect the position X2 directly above the flat-bottomed hole 6 in the austenitic stainless steel weld to obtain a series of A-scan signals a, as shown in image 3 As shown, where A is the surface wa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com