Method for pulse-based ultra-broadband communication between at least one transmitting node and at least one receiving node
A technology of ultra-wideband communication and sending nodes, applied in transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as interference with data transmission, inability to communicate simultaneously, and data transmission conflicts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
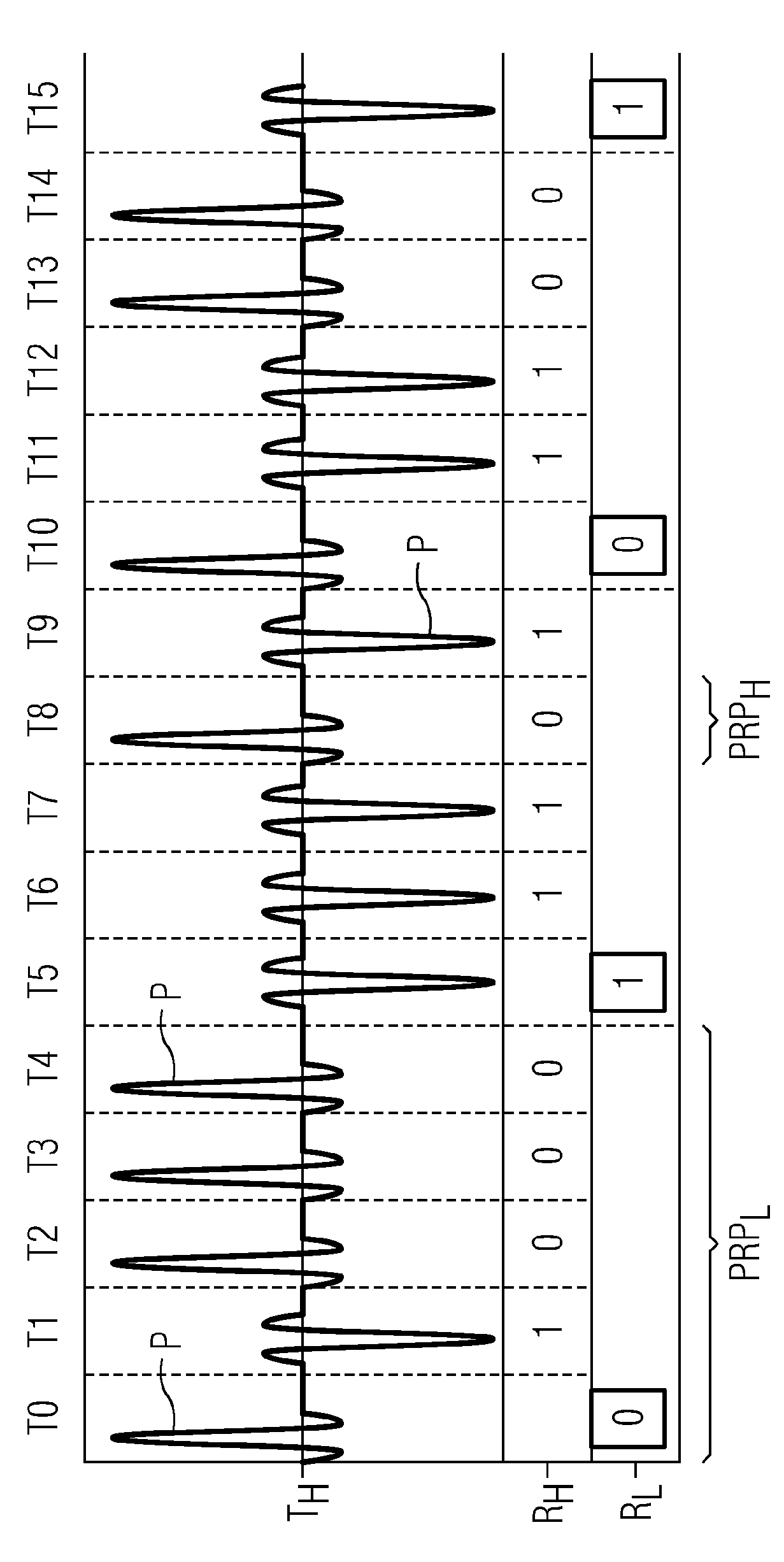
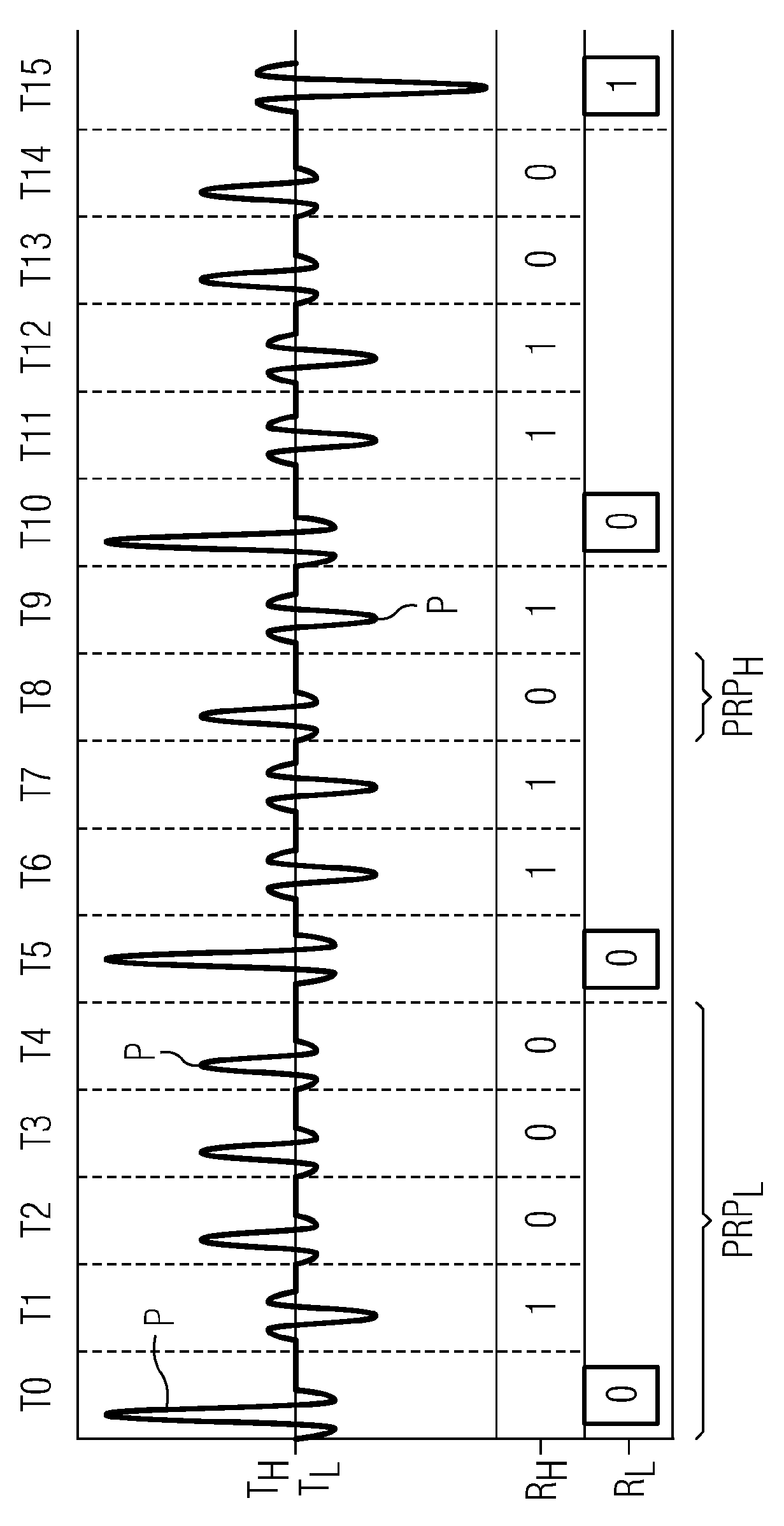
[0025] In the following, two embodiments of the method according to the invention will first be explained, in which the transmission of the UWB signal takes place consecutively by means of pulses in mutually consecutive time windows. In this case, a first data transmission with a low pulse rate and a high range and a second data transmission with a high pulse rate and a low range take place in the UWB signal based on these pulses.
[0026] figure 1 A UWB signal according to a first embodiment of the method according to the invention is shown. exist figure 1 , the time axis extends in the horizontal direction, wherein the corresponding time windows in which a single pulse is transmitted in each case are denoted by T0, T1, . . . , T15. By way of example, some of these pulses are shown here with the reference symbol P. exist figure 1 scenario, through a so-called transceiver TH To generate UWB signals, the transceiver transmits at a high pulse rate. The transceiver is here a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com