Double-effect fermentation and biological acid reduction brewing method for fruit wine
A technology for fermenting organisms and fruit wine, applied in the field of fruit wine brewing, can solve problems such as limited range, and achieve the effects of large acid reduction range, significant effect and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
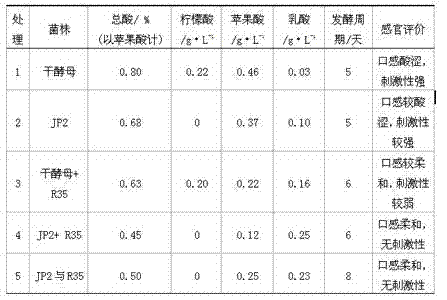
[0035] Example 1: Single-strain fermentation of yeast without acid-reducing function, single-strain fermentation of yeast with acid-reducing function, double-effect fermentation of yeast and lactic acid bacteria with acid-reducing function, and segmentation of yeast and lactic acid bacteria with acid-reducing function Comparative experiment on the acid reduction effect of fermentation:
[0036] Take the loquat juice containing 0.80% acid and put them in glass fermentation bottles, respectively, and ferment them in the following ways: ①"Angel" dry yeast single-strain fermentation; ②Saccharomyces cerevisiae JP2 single-strain fermentation; ③"Angel" dry yeast and Double-effect fermentation of Lactobacillus casei R35: inoculate "Angel" dry yeast, and inoculate Lactobacillus casei R35 after the specific gravity drops to 0.994. ④Double-effect fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae JP2 and Lactobacillus casei R35: first inoculate Saccharomyces cerevisiae JP2 for fermentation, and then...
example 2
[0041] Example 2: Double-effect fermentation biological acid reduction method of loquat wine
[0042] The method includes the following steps:
[0043] 1. Juicing: After the fresh loquat is cored, crushed, and squeezed, 120mg / L of sulfur dioxide is added, and the soluble solid content is adjusted to 20% of the total with sucrose. At this time, the acid content of the juice reaches 0.9% (apple Acid meter).
[0044] 2. Alcohol fermentation: adjusted loquat juice, press about 9.99×10 7 The inoculation amount of cfu / mL will be the previously expanded Saccharomyces cerevisiae JP2 ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae JP2) Put it into loquat juice, and carry out temperature-controlled fermentation at 20-25℃. At the same time of alcohol fermentation, Saccharomyces cerevisiae JP2 can metabolize part of the malic acid and all the citric acid, and initially reduce the acidity of the loquat wine.
[0045] 3. Double-effect fermentation: In the process of alcohol fermentation, detect the specific gravi...
example 3
[0052] Example 3: Double-effect fermentation biological acid reduction method of mountain wine
[0053] The method includes the following steps:
[0054] 1. Pre-treatment: After destemming and crushing of fresh wild grapes, 120mg / L of sulfur dioxide is added, and sucrose is used to adjust the soluble solid content to 20% of the total. At this time, the acid content of the juice reaches 1.0% (calculated as malic acid) .
[0055] 2. Alcohol fermentation: adjusted mountain grape juice (with skin), press about 1.00×10 6 The inoculation amount of cfu / mL is connected to the previously expanded Saccharomyces cerevisiae J4 ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae J4). Temperature controlled fermentation at 20-25°C. At the same time of alcohol fermentation, Saccharomyces cerevisiae J4 can metabolize and consume part of malic acid and all of citric acid, and initially reduce the acidity of mountain wine.
[0056] 3. Double-effect fermentation: In the process of alcohol fermentation, detect the specific g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com