Composite electrode of light-emitting diode chip and manufacturing methods thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and composite electrodes, which is applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, complicated electrode production process, and difficult storage of products, and achieve the effects of cost reduction and strong environmental adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
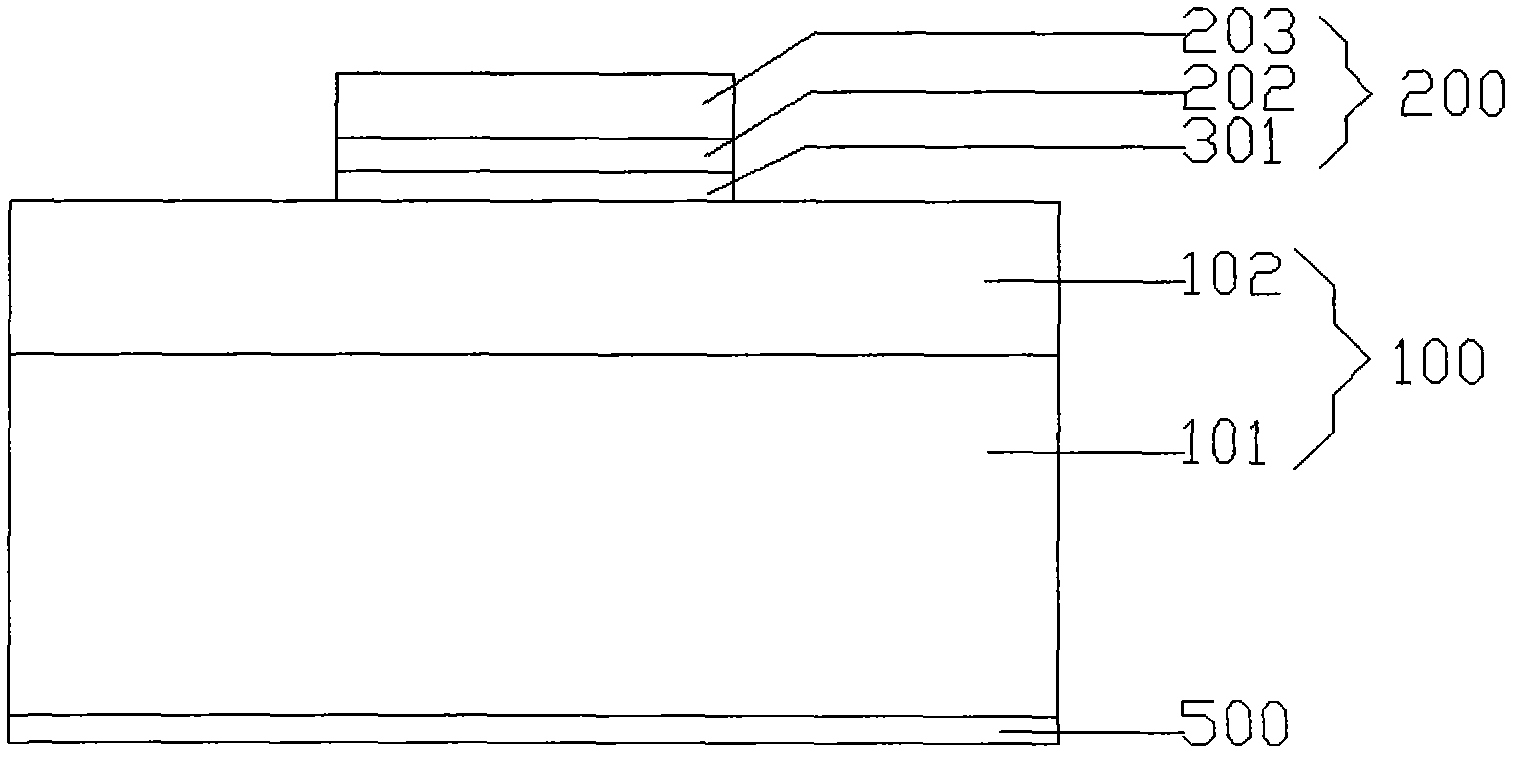
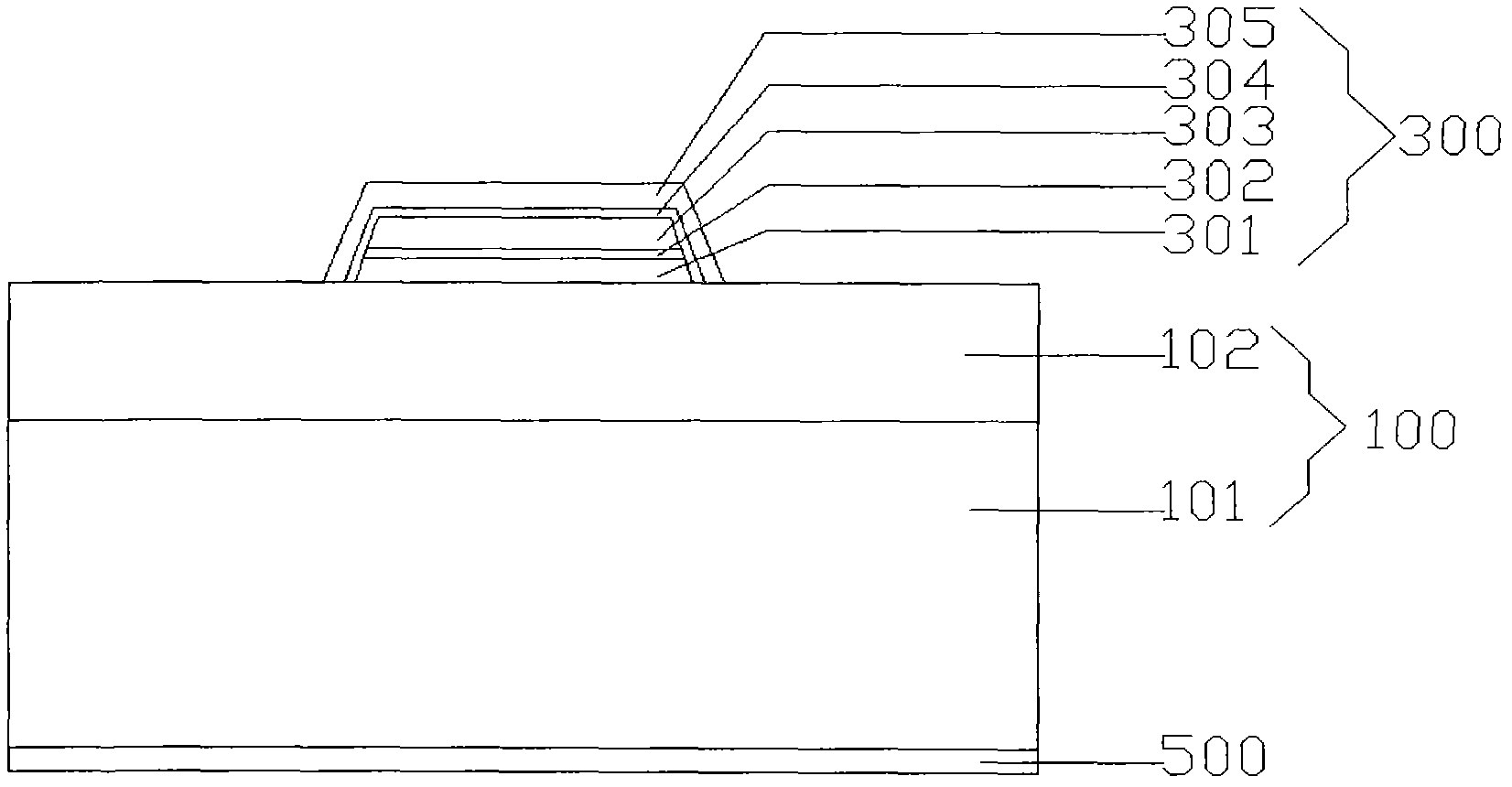
[0076] A compound electrode (300) of a light-emitting diode chip, the structure of which is respectively from bottom to top: an ohmic contact metal layer (301), a first isolation metal layer (302), a filling metal layer (303), and a second isolation metal layer (304), the surface metal layer (305), wherein the second isolation metal layer (304) and the surface metal layer (305) cover the ohmic contact metal layer (301), the first isolation metal layer (302) and the filling metal layer The top and side of (303) completely wrap these three electrode layers inside the electrode, such as figure 2 . Wherein, the ohmic contact metal layer (301) is an AuBe alloy with a thickness of 10nm; the first isolation metal layer (302) is Ti with a thickness of 5nm; the filling metal layer (303) Al is 100nm; the second isolation metal layer (304 ) is Ti with a thickness of 5nm; the surface metal layer (305) is Au with a thickness of 50nm.
[0077] The manufacturing method of the composite el...
Embodiment 2
[0092] A composite electrode (300) for a light emitting diode chip, the structure of which is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0093] The difference from Example 1 is that the method for making the composite electrode (300) of the LED chip includes the following steps:
[0094] a) providing a piece of LED epitaxial wafer (100);
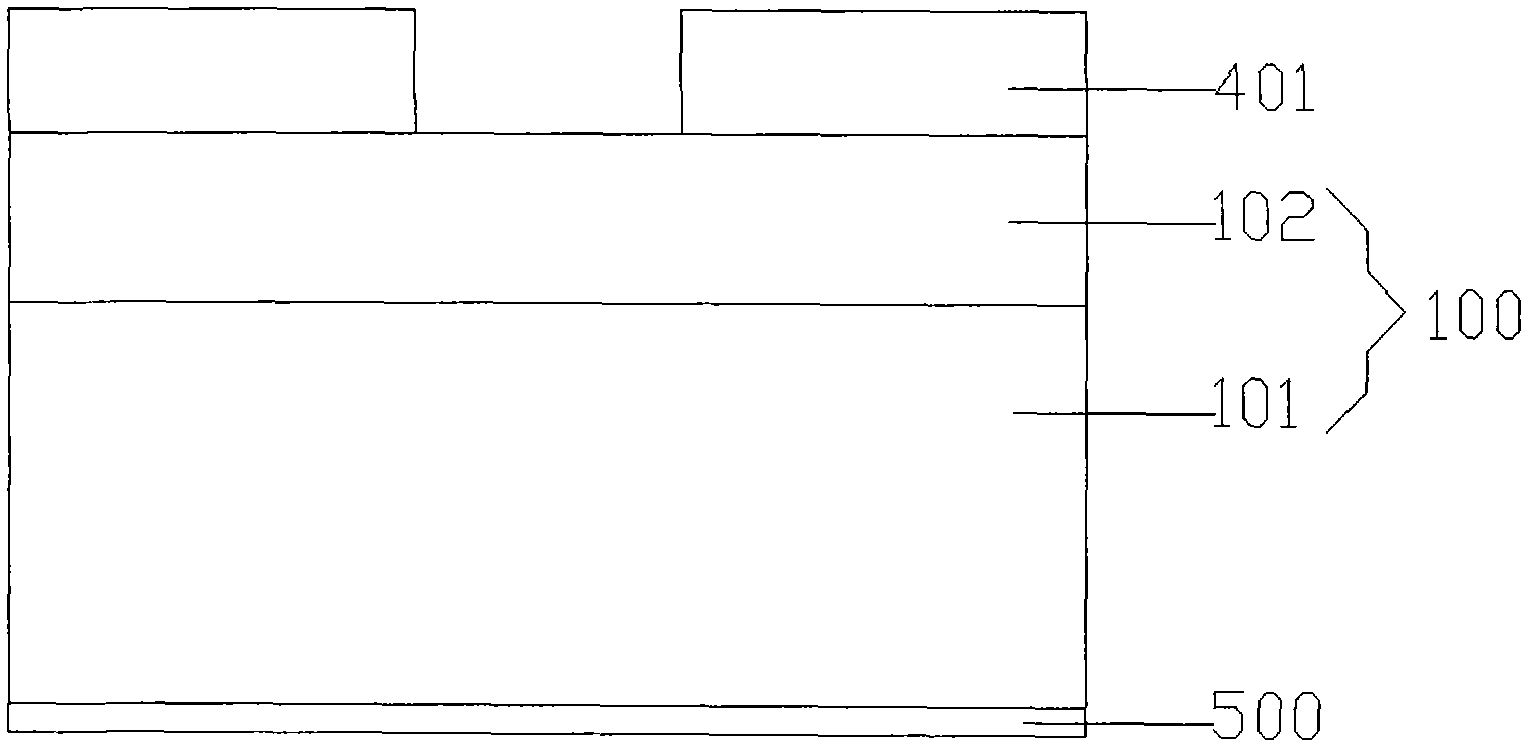
[0095] b) Fabricate the first covering layer (401) and the second covering layer (402) sequentially from bottom to top on the upper surface of the light-emitting epitaxial layer (102) of the LED epitaxial wafer (100), such as Figure 8 ;
[0096] c) exposing the second cover layer (402) to make electrode patterns;
[0097] d) Perform wet etching on the exposed epitaxial wafer, etch and remove the second covering layer (402) and the first covering layer (401) at the electrode pattern to form an inverted funnel-shaped hollow area, exposing the light-emitting epitaxial layer below The upper surface of (102), such as Figure 9 ;
[0098] e) Use ev...
Embodiment 3
[0106] A compound electrode (300) of a light-emitting diode chip, its structure is different from Embodiment 1 in that: its ohmic contact metal layer (301) is Ti and Zn, the thickness is 300nm, and the first isolation metal layer (302) is W , its thickness is 50nm; The filling metal layer (303) is Ag, and its thickness is 1000nm; The second isolation metal layer (304) is Pt, and its thickness is 50nm; Surface metal layer (305) is Au, and its thickness is 200nm.
[0107] The fabrication method of the composite electrode (300) is the same as that in Example 1, except that the thickness of the first covering layer (401) is 2000 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com