PCR (polymerase chain reaction) nucleic acid detection method
A nucleic acid, technology for nucleic acid, applied in the field of molecular biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
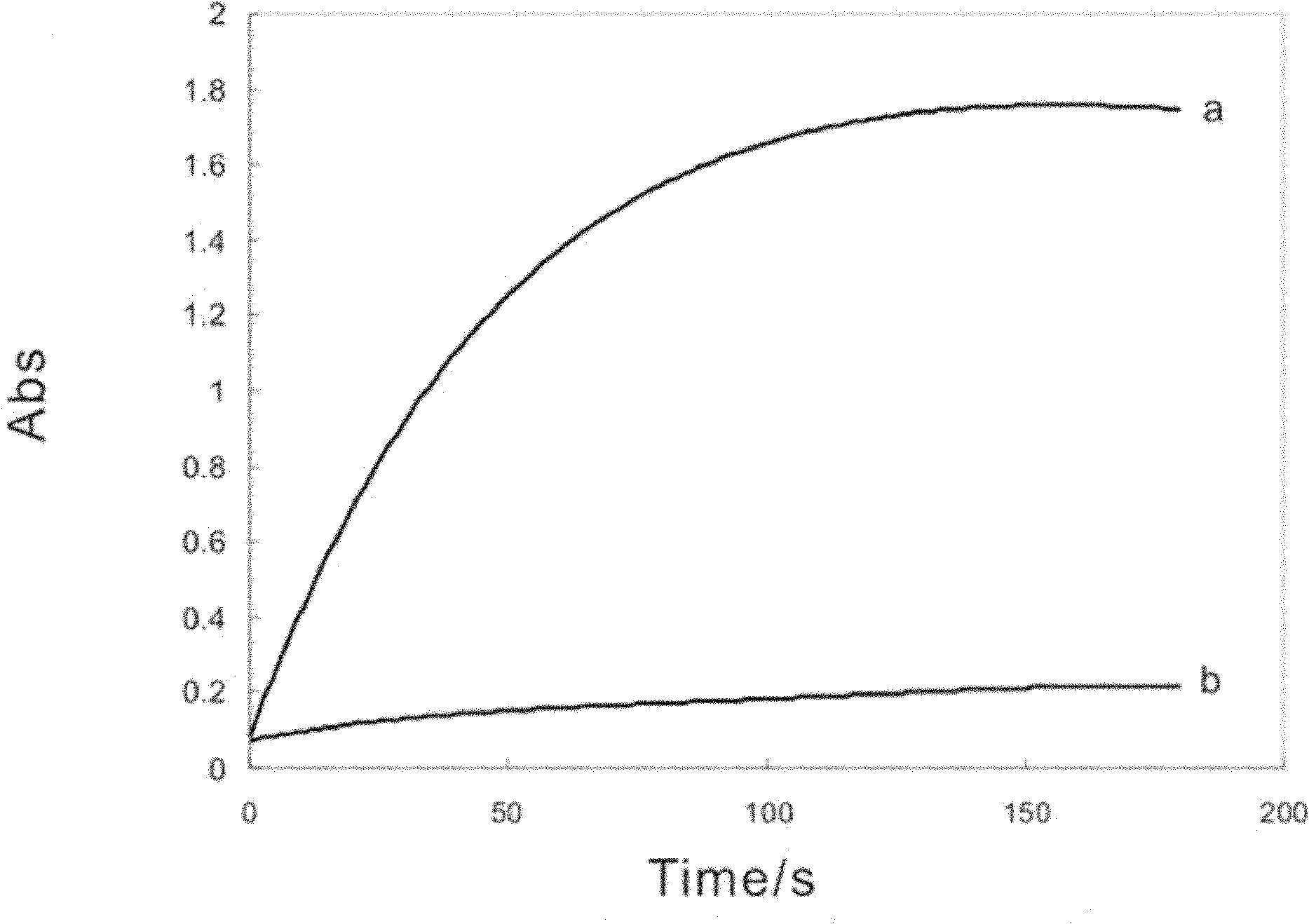
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1, detect DNA T-1 with oligonucleotide probe 1
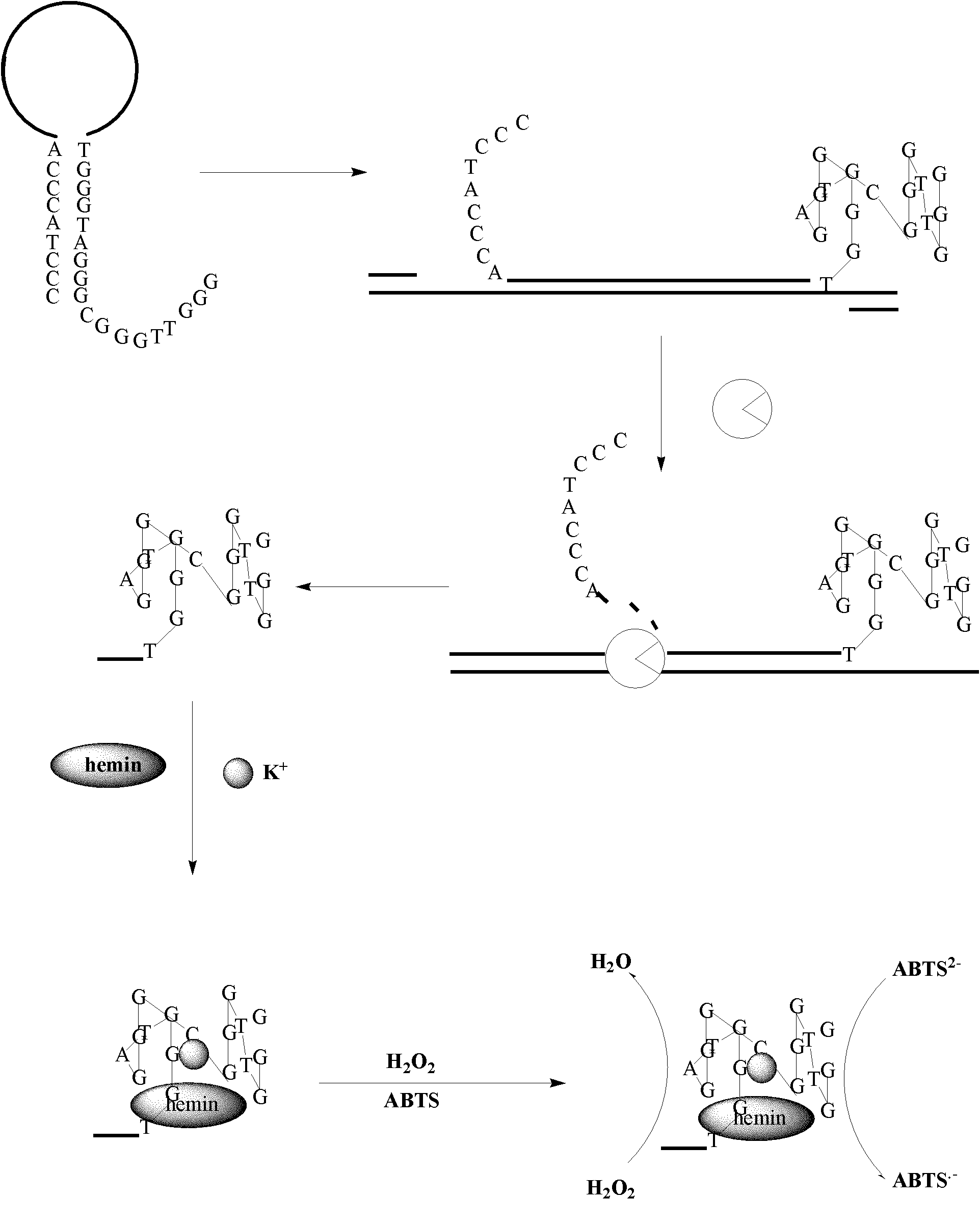
[0045] For the reaction steps for detecting nucleic acids, see figure 1 . One end of the oligonucleotide probe 1 is labeled with a DNAzyme sequence that combines with porphyrin iron and the like and has peroxidase activity, and the other end is a sequence that can form a partial complementarity with the DNAzyme sequence. Partial complementarity makes the oligonucleotide probe 1 form a stem-loop hairpin structure with a short single strand at one end, and the loop portion of the hairpin structure of the oligonucleotide probe 1 can be complementary to the target nucleic acid sequence DNA T-1.
[0046] After adding oligonucleotide probe 1 to the PCR system, under denaturing conditions, the double strand of the DNA T-1 to be tested and the hairpin structure of probe 1 are opened; under annealing conditions, the forward primer and probe Both hybridize with one strand of DNAT-1; under the action of Taq enzyme, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2, detect DNA T-1 with oligonucleotide probe 2
[0068] For the reaction steps for detecting nucleic acids, see figure 2. Oligonucleotide probe 2 contains two fragments A and B, both of which contain part of the DNAzyme sequence and a complementary sequence. After adding fragment A of oligonucleotide probe 2 to the PCR system, under denaturing conditions, the double strand of DNA T-1 to be tested and the hairpin structure of probe 2 are opened; under the conditions of annealing, the forward primer and Probe 2 hybridizes with one strand of DNAT-1; under the action of nucleic acid polymerase, the forward primer is extended; when extending to probe 2, due to the exonuclease activity of the nucleic acid polymerase from the 5' end to the 3' end , the part of probe 2 hybridized with DNAT-1 is digested and degraded, and fragment C containing part of the DNAzyme is released. At this time, fragment B of oligonucleotide probe 2 is added, and fragment C and fragment ...
Embodiment 3
[0090] Example 3. Detection of Aeromonas hydrophila with oligonucleotide probe 3 (No.: EU678635.1)
[0091] (1) Forward and reverse primers 2, oligonucleotide probe 3, partial sequence of Aeromonas hydrophila
[0092] Forward primer 2: 5'-GCC ATG CCG CGT GTG TGA AG-3'
[0093] Reverse primer 2: 5'-AGC CGG TGC TTC TTC TGC GA-3'
[0094] Oligonucleotide probe 3: 5’-CCC TAC CCA GGG TTG TAA AGC ACT TTC AGC GAG GAG GAA AGG TTG ATG TGG GTA GGG CGG GTT GGG-3’
[0095] Partial sequence of Aeromonas hydrophila: 5′-GCC ATG CCG CGT GTG TGA AGA AGG CCT TCG GGT TGT AAA GCA CTT TCA GCG AGG AGG AAA GGT TGA TGC CTA ATA CGT GTC AAC TGT GAC GTT ACT CGC AGA AGA AGC ACC GGC T-3′
[0096] (2) Reaction system and PCR conditions
[0097] Forward primer 1 μM
[0098] Reverse primer 1 μM
[0099] Taq Enzyme 5U
[0100] dNTPs 0.4mM
[0101] The concentration is 100 / μl Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria liquid 2μl
[0102] 10x Taq buffer 5μl
[0103] Make up the system to 50 μl with ultrapure water...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com