Node management method and control plane
A node management and control plane technology, applied in the field of optical communication, can solve problems such as interruption and inability to perform section switching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
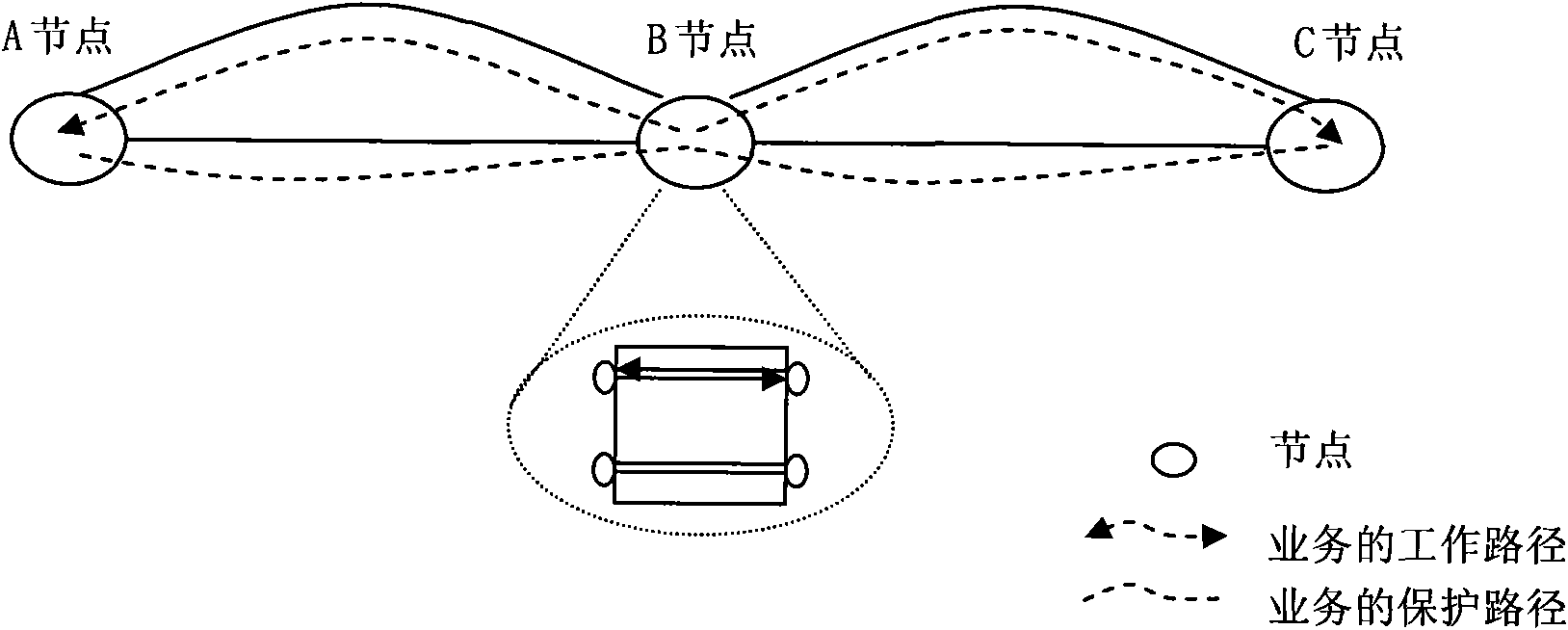
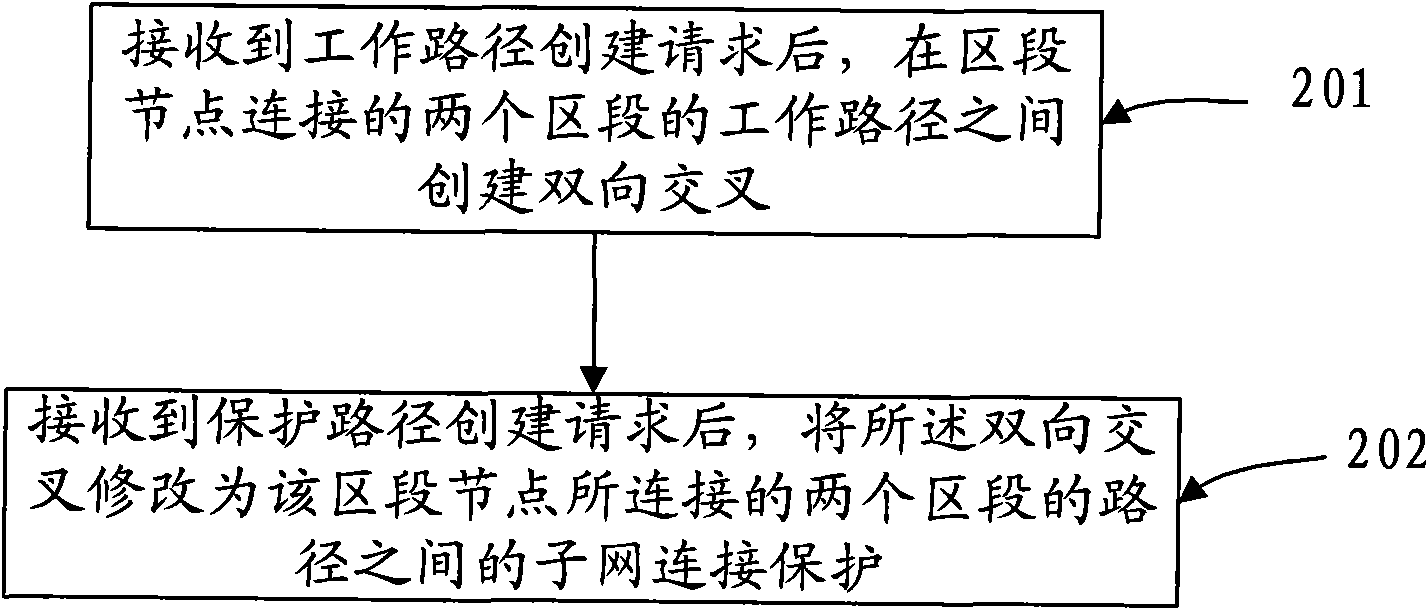
[0045] This embodiment provides a node management method, such as Figure 5 As shown, the method includes:
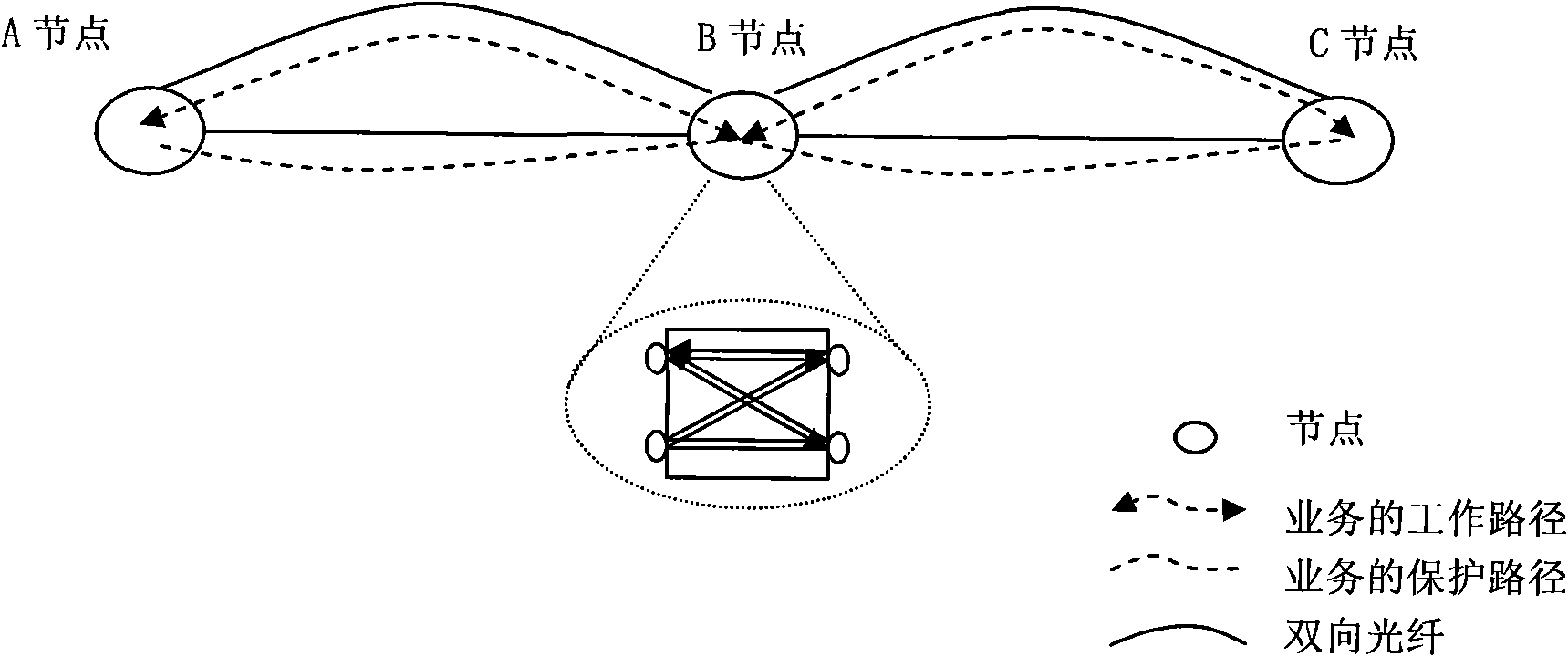
[0046] 501. After receiving a working path creation request, create a bidirectional intersection between the working paths of the two sections connected to the section nodes, and the working path creation request is sent to each node through control plane control. After the bidirectional crossover is created through the control plane on the section node, the section node can forward the service on the working path to the working path of the next section through the bidirectional crossover.
[0047] 502. After receiving a protection path creation request, modify the bidirectional crossover to subnet connection protection between paths of two sections connected to the section node, and the paths of the two sections include two zones The segment's working path and protection path, the protection path creation request is sent to each node through the control plane control....
Embodiment 2
[0091] It can also be applied to the following scenarios: the optical network carries optical layer services. Before the node management method and control plane in the embodiment of the present invention are applied, the optical layer service signals can be directly forwarded to the In the next section, an electrical relay is introduced in this embodiment, and the application Figure 5 and Figure 6 After corresponding to the node management method and the control plane, the section switching of the optical layer service can be realized. In the embodiment of the present invention, the electrical relay is implemented by back-to-back OTUs (wavelength conversion units). In this embodiment, after the optical layer service signal is crossed at the optical layer of the section node, it goes down to the electrical layer and is converted into an electrical signal in the electrical relay, and the electrical relay converts the transmitted electrical signal into an optical signal and s...
Embodiment 3
[0110] The scenario of the optical network in this embodiment is different from that in Embodiment 2. This embodiment includes multiple section nodes, such as Figure 13 As shown, nodes B and D in the figure are both section nodes, so that there are multiple sections between node A and node C, and section switching can be performed independently in each section. Four SNCPs are configured on nodes B and D through the control plane.
[0111] If the optical fiber between node A and node B is interrupted, only the section switching between node A and node B can be performed, and other sections do not need to be switched again. If the optical fiber between node B and node D is interrupted, section switching can only be performed between node B and node D. If the service requires dynamic rerouting, rerouting calculation is performed, and the specific calculation process is the same as that of Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2.
[0112]The sections in all the above-mentioned embodiment...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com