Method and device for recycling substrates by thermally cracking wasted printed circuit boards
A technology of thermal cracking and waste printing, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve problems such as hindering gas discharge, variable gas production, and increasing operating costs, so as to enhance stability, reduce operating risks, and increase recycling. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
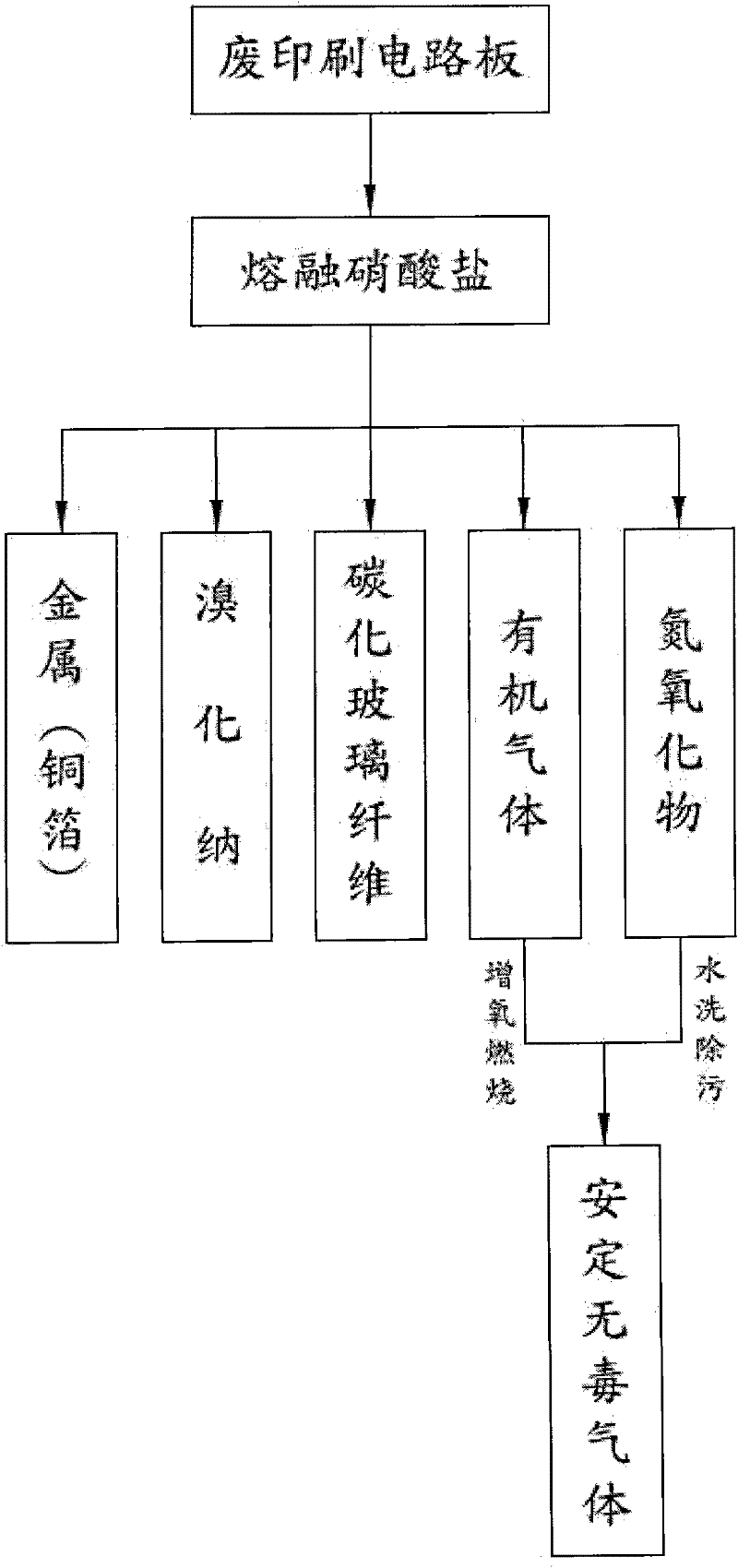
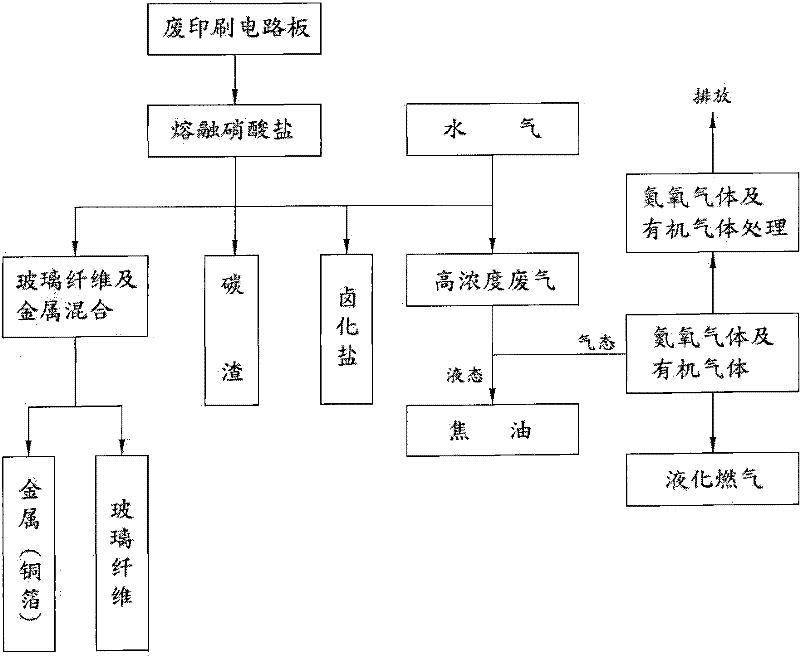
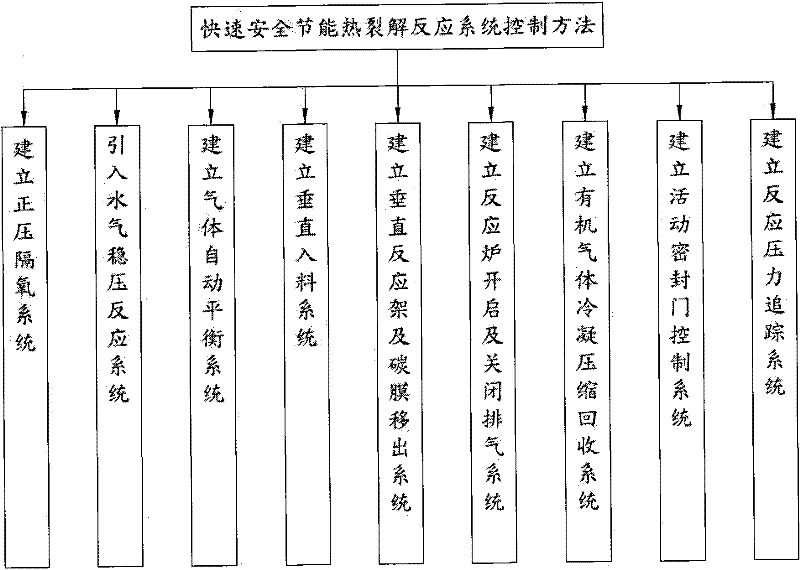
[0042] see figure 2 As shown, it is the thermal cracking recovery flow chart of the method for recycling waste printed circuit boards of the present invention and its device. The waste printed circuit boards are directly put into molten nitrate at 300°C to 550°C, and the waste printed circuit boards are allowed to The thermal cracking reaction of the brominated epoxy resin in the brominated epoxy resin forms a high-concentration waste gas of organic gas, nitrogen and oxygen gas and carbon residue, and for the bromine element in the epoxy resin, the highly active metals of lithium, sodium and potassium in the nitrate can be used to decompose Capture and form stable bromide salts, increase the introduction of water vapor during the reaction process to stabilize the thermal cracking reaction, prevent excessive nitrate reactions (explosive hazards), and use water vapor to heat and expand to form water vapor to maintain the normal operation of the system pressure, and then force t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com