Method for preparing glucosyl mesoporous carbon-coated ZnFeO used for electromagnetic wave absorbing coating
A glucose-based mesoporous technology is applied in the field of electromagnetic wave absorption coating preparation, which can solve the problems of enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption and complex purification process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0013] Preparation of glucose-based mesoporous carbon-coated ZnFeO materials with a molar ratio of Zn and Fe of 0:1 and heat treatment at 500 °C after glucose coating
[0014] (1) 2.70g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in 80 mL of ethylene glycol to form a clear solution. Add 7.2g of sodium acetate and 2.0g of polyethylene glycol PEG2000 to it, and stir vigorously for 6h.
[0015] (2) Encapsulate the reaction mixture into a polytetrafluoroethylene kettle, and perform solvothermal reaction at 200° C. for 12 hours.
[0016] (3) The obtained product was separated by centrifugation, washed three times with distilled water and ethanol, and dried under vacuum at 60°C. The resulting sample is denoted as ZnFeO (0:1), where (0:1) is the molar ratio of Zn and Fe.
[0017] (4) Take 0.5 g of ZnFeO particles, add it to 80 mL of glucose solution (0.5 M), and disperse it by ultrasonic wave for 30 min.
[0018] (5) Pour the mixture into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, and conduct a hydrother...
specific Embodiment 2
[0022] Preparation of glucose-based mesoporous carbon-coated ZnFeO materials with a molar ratio of Zn and Fe of 1:2 and heat treatment at 500 °C after glucose coating
[0023] (1) 5.40g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 1.36 g ZnCl 2 Dissolve in 80mL ethylene glycol to form a transparent solution. Add 7.2g of sodium acetate and 2.0g of polyethylene glycol PEG2000 to it, and stir vigorously for 6h.
[0024] (2) Encapsulate the reaction mixture into a polytetrafluoroethylene kettle, and perform solvothermal reaction at 200° C. for 12 hours.
[0025] (3) The obtained product was separated by centrifugation, washed three times with distilled water and ethanol, and dried under vacuum at 60°C. The obtained sample is recorded as ZnFeO (1:2), (1:2) being the molar ratio of Zn and Fe.
[0026] (4) Take 0.5 g of ZnFeO particles, add it to 80 mL of glucose solution (0.5 M), and disperse it by ultrasonic wave for 30 min.
[0027] (5) Pour the mixture into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, and conduc...
specific Embodiment 3
[0031] Preparation of glucose-based mesoporous carbon-coated ZnFeO materials with a molar ratio of Zn and Fe of 1:1 and heat treatment at 500 °C after glucose coating
[0032] (1) 2.70g FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 1.36 g ZnCl 2 Dissolve in 80mL ethylene glycol to form a transparent solution. Add 7.2g of sodium acetate and 2.0g of polyethylene glycol PEG2000 to it, and stir vigorously for 6h.
[0033] (2) Encapsulate the reaction mixture into a polytetrafluoroethylene kettle, and perform solvothermal reaction at 200° C. for 12 hours.
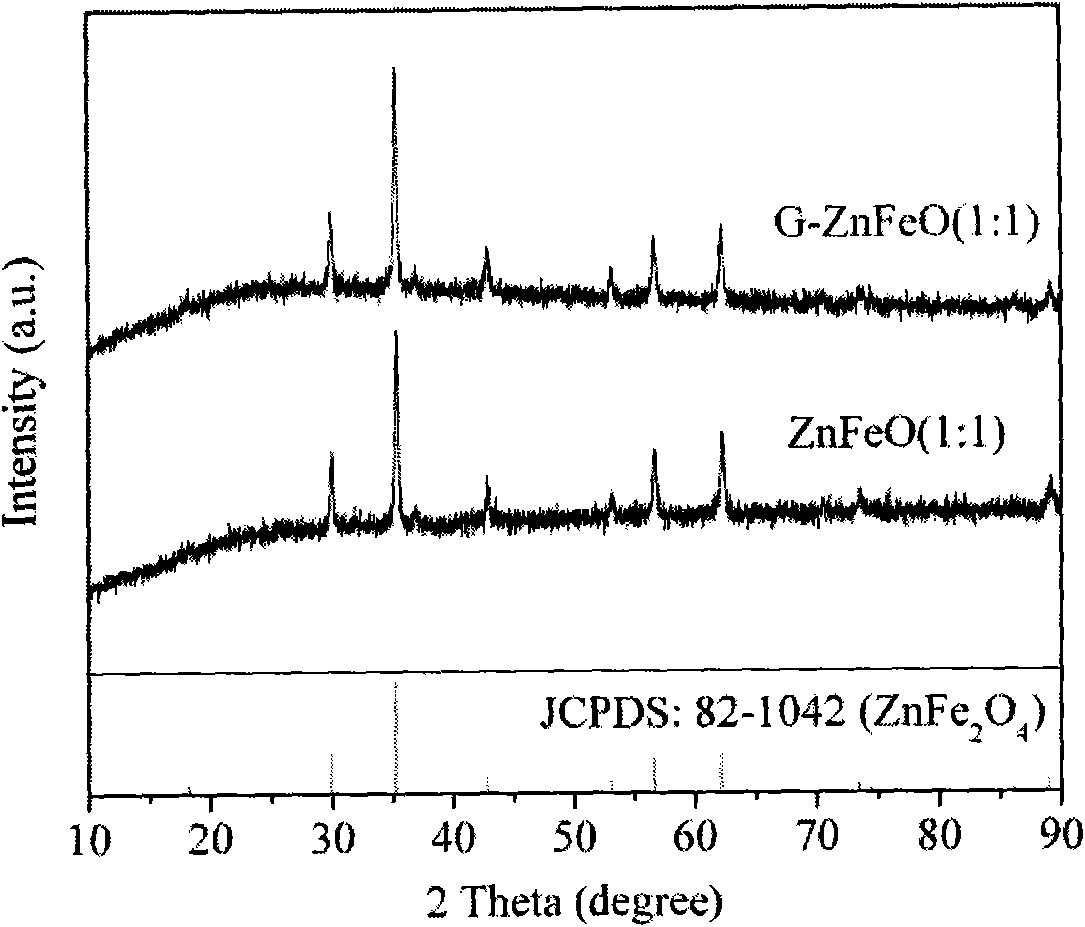
[0034] (3) The obtained product was separated by centrifugation, washed three times with distilled water and ethanol, and dried under vacuum at 60°C. The obtained sample is recorded as ZnFeO (1:1), where (1:1) is the molar ratio of Zn and Fe.
[0035] (4) Take 0.5 g of ZnFeO particles, add it to 80 mL of glucose solution (0.5 M), and disperse it by ultrasonic wave for 30 min.
[0036] (5) Pour the mixture into a hydrothermal reaction kettle, and con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com