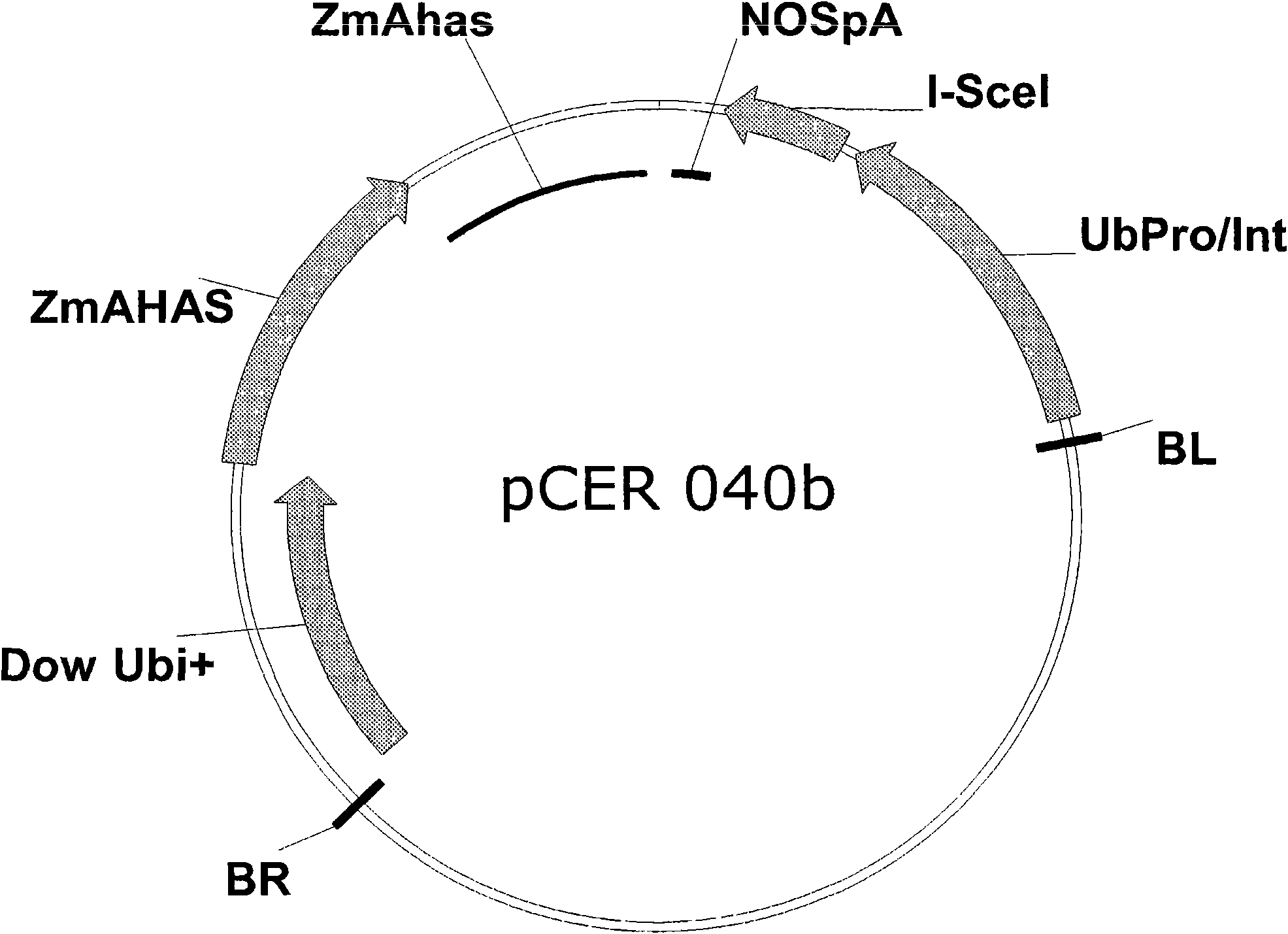
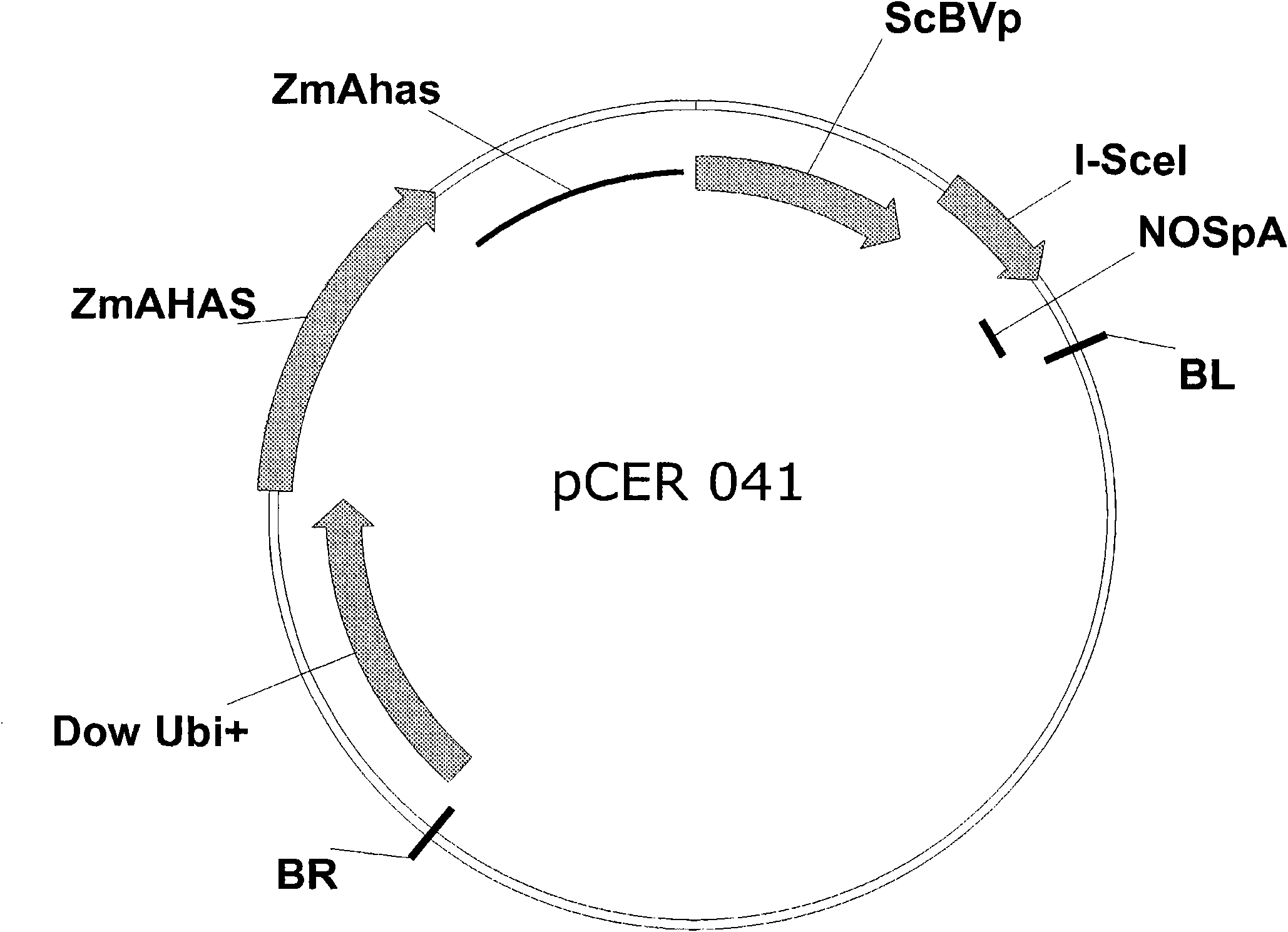
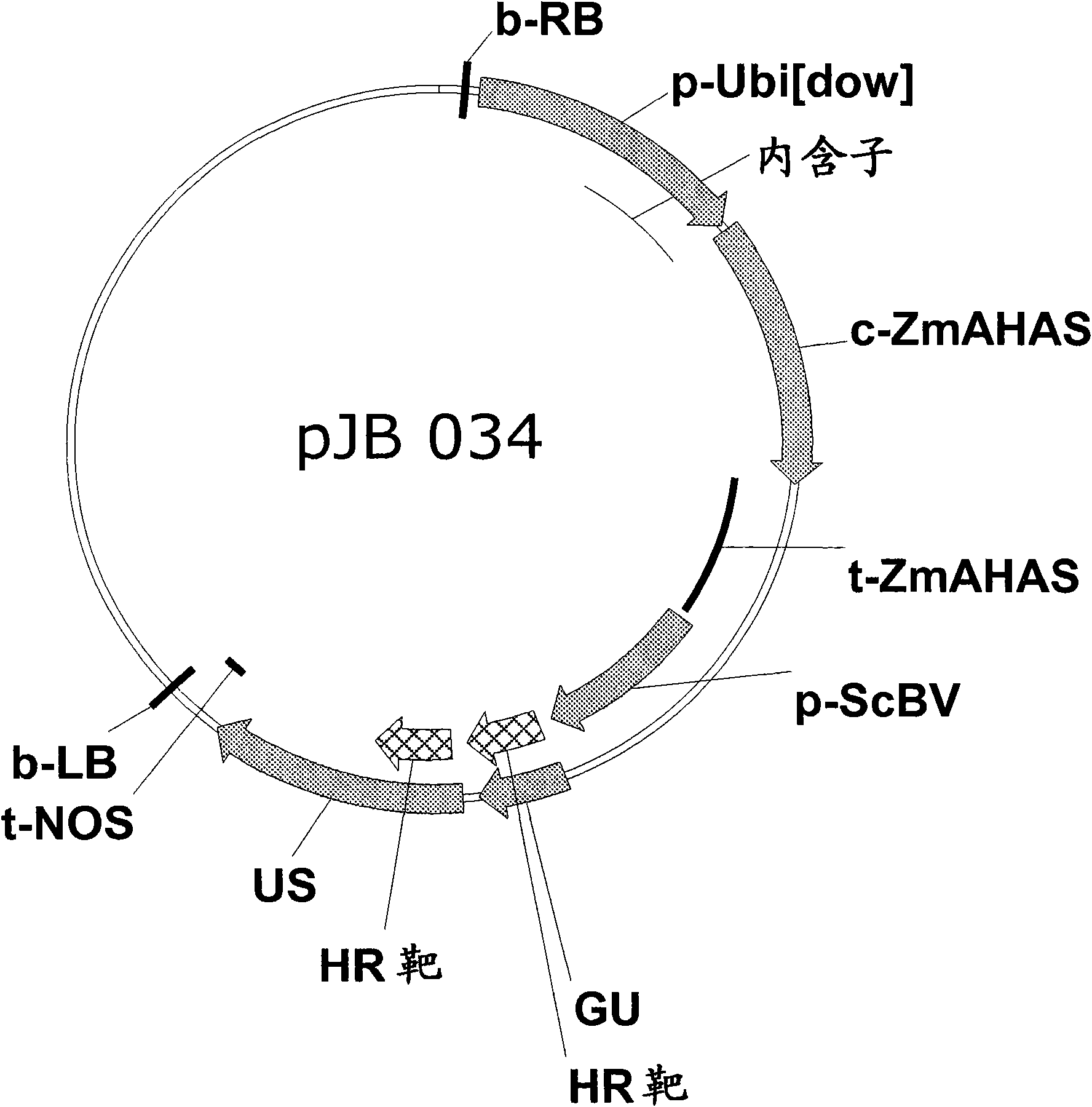
Method of excising a nucleic acid sequence from a plant genome
A nucleic acid sequence and genome technology, applied in the fields of botany equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, plant products, etc., can solve problems such as deletion and chromosome rearrangement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0282] Materials and General Methods
[0283] Unless otherwise stated, chemicals and reagents in the examples were obtained from Sigma Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO), restriction endonucleases were from New England Biolabs (Beverly, MA) or Roche (Indianapolis, IN), oligonucleases were obtained from Nucleotides were synthesized by MWG Biotech Inc. (High Point, NC), and other modifying enzymes or kits for biochemical and molecular bioassays were from Clontech (Palo Alto, CA), Pharmacia Biotech (Piscataway, NJ), Promega Corporation (Madison, WI) or Stratagene (La Jolla, CA). Materials for cell culture media were obtained from Gibco / BRL (Gaithersburg, MD) or DIFCO (Detroit, MI). Cloning steps performed for the purpose of the present invention such as restriction cutting, agarose gel electrophoresis, purification of DNA fragments, transfer of nucleic acids to nitrocellulose and nylon membranes, ligation of DNA fragments, transformation of E. coli cells, cultivation of bacteria, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com