Process for concentrated biomass saccharification
A technology for biomass and pretreatment of biomass, which is used in the field of saccharification for concentrated biomass, and can solve the problems of difficulty in completing saccharification of biomass.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
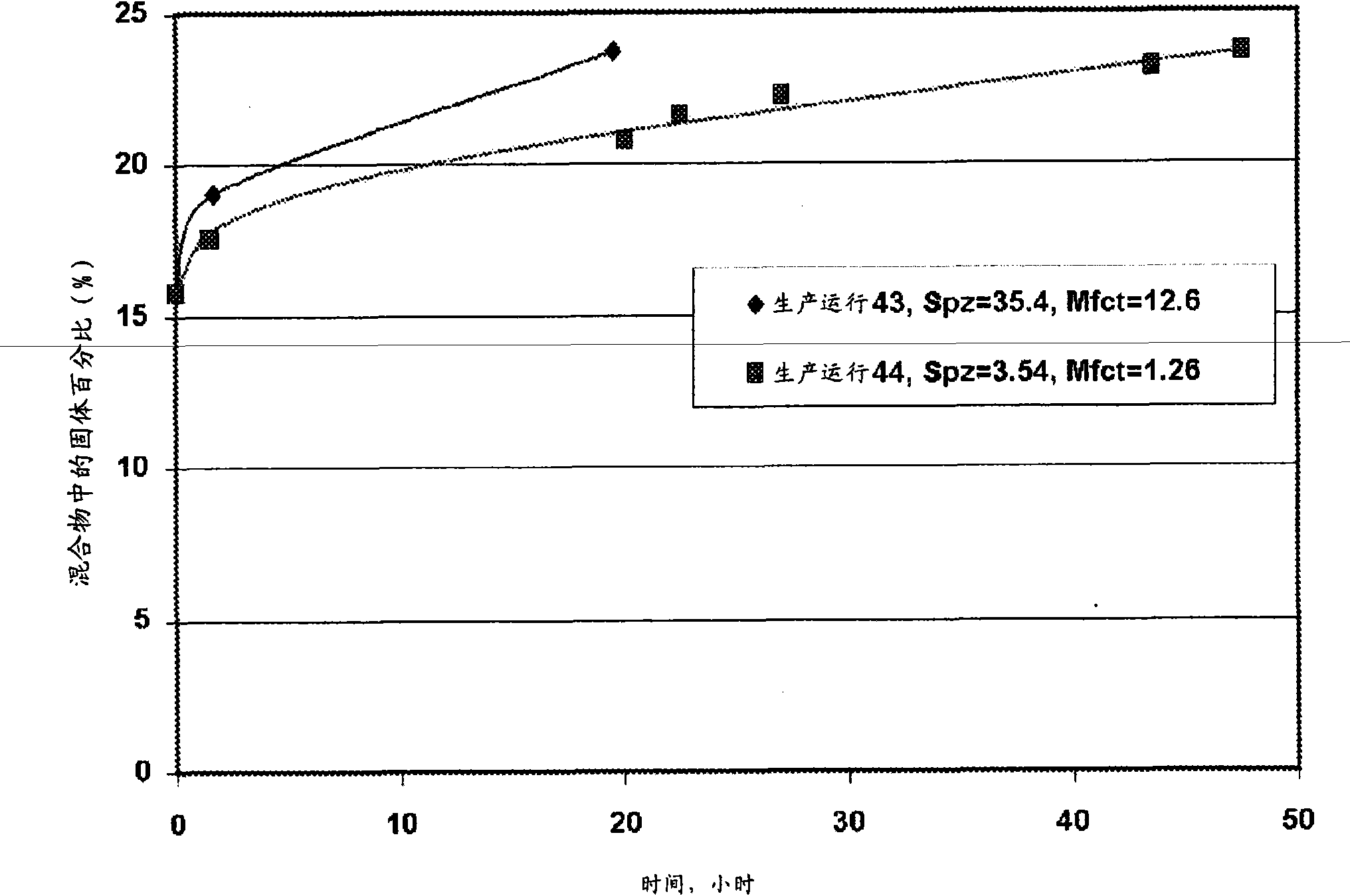
[0131] Saccharification of pretreated biomass with and without stirring
[0132] Two productions (#25 and 26) were carried out with ground pretreated biomass at 50°C, pH = 5.5, with a feed of about 20% DWB (dry weight of biomass). The biomass used in these production runs was a blend of three batches of pretreated corncobs reduced in particle size to about 1 mm. In the steam injection reactor as described above, by using 4g NH 3 A batch labeled HT-4 was prepared by treating broken cobs with steam at 145°C for 20 minutes per 100 g dry weight of biomass. Two additional batches were prepared by treating corn cobs with 6 g NH3 per 100 g dry weight of biomass and steam at 145 °C for 10 min in a barrel piston reactor as described above. The blend of these three batches of pretreated biomass was ground in a Waring commercial blender and sieved through a 1.1 mm sieve before being used in the saccharification experiments.
[0133] Production was performed in a 500 mL glass-jackete...
Embodiment 2
[0143] Saccharification of pretreated biomass with different initial sizes
[0144] Production runs 50 to 52 and 64 to 65 were performed with pretreated biomass ground to different sizes. Pretreated biomass was prepared from ground corncobs that were hammer milled and sieved through a 1 / 2 inch screen. They were in a Jaygo reactor as described in General Methods with 4 g NH 3 Steam treatment at 145 °C for 20 min per 100 g dry weight of biomass. This pretreated corncob biomass was labeled Jaygo-10. Prior to saccharification, the pretreated cobs are further ground and screened through appropriately sized screens in multiple steps to prepare the biomass for each saccharification production run. The screen sizes used to prepare the samples for each production run are shown in Table 2 below.
[0145] Production runs 50 and 51 were performed in 2-L reactors, and production runs 52, 64 and 65 were performed in 0.5-L reactors. In all cases, deionized water was used as the reacti...
Embodiment 3
[0156] Biomass liquefaction during enzymatic saccharification
[0157] As noted above, production run 52 may be used to measure changes in particle size distribution and liquefaction of biomass as the saccharification process continues. After 6 hours and 72 hours, the particle size distribution of the corncob biomass and hydrolyzate subjected to the initial grinding pretreatment was measured.
[0158] Table 4: Particle size distribution reduction during saccharification-production run 52
[0159]
[0160] The results clearly indicate that enzyme-catalyzed saccharification reduces the particle size distribution of the solids, thus causing liquefaction of the solids, allowing additional solids to be added to the hydrolyzate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com