Method for analyzing contents and valence states of metals inside and outside doped mesoporous molecular sieve framework
A mesoporous molecular sieve and molecular sieve technology, which is applied in the field of analyzing the content and valence of metal elements inside and outside the framework of doped mesoporous molecular sieves, can solve the problems of inaccurate, inaccurate description of content, inability to determine metal valence and position, etc. simple method effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
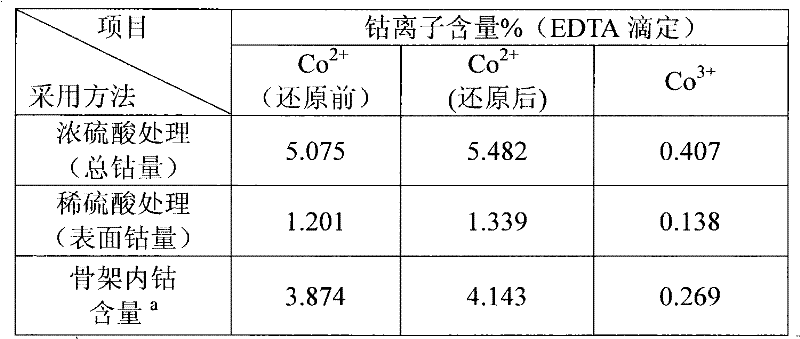
[0022] Example 1: Analysis of cobalt-containing MCM-41. Take 0.1g of the sample and soak it in 2mL of 18mol / L concentrated sulfuric acid at 100°C for 12h, and dissolve it in 20mL of 0.5mol / L dilute sulfuric acid at 15°C for 10min. The mixture was centrifugally filtered with deionized water, no metal ions were detected in the residue, and the metal ion clear liquid was obtained with a volumetric flask to constant volume. =5-6 in the hexamethylenetetraammonium buffer system, use EDTA to directly titrate divalent cobalt ions, and trivalent cobalt ions can be reduced by KI and then titrated with EDTA.
[0023] The specific results are shown in Table 1, and the data is the mass percentage of cobalt in the material.
[0024] Table 1
[0025]
[0026] a: total cobalt content - surface cobalt content.
Embodiment 2
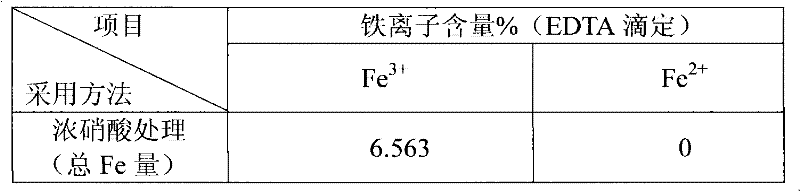
[0027] Example 2: Analysis of Iron-Containing MCM-41. Take 0.1g of the sample and soak in 4mL of 16mol / L concentrated nitric acid at 100°C for 12h, and dissolve and stir in 20mL of 0.5mol / L dilute nitric acid at 20°C for 10min. The mixture was centrifugally filtered with deionized water, no metal ions could be detected in the residue, and the obtained clear liquid was constant volume, using sulfosalicylic acid as an indicator, and using hydrochloric acid to control the pH=1.5-2, and directly titrated ferric ions with EDTA. Since the synthesized sample uses ferric nitrate as the iron source and is roasted at 550°C, there is no divalent iron ion in the sample. The specific results are shown in Table 2, and the data is the mass percentage of iron in the material.
[0028] Table 2
[0029]
[0030]
[0031] b: total iron content - surface iron content.
example 3
[0032] Example 3: Analysis of vanadium-containing MCM-41. Take 0.1g of the sample and soak it in 5mL of 6mol / L sodium hydroxide at 60°C for 6h, and dissolve it in 40mL of 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide at 20°C for 10min. The mixture was centrifugally filtered with deionized water, no metal ions could be detected in the residue, the obtained clear liquid was constant volume, and N-phenyl anthranilic acid was used as an indicator, and pentavalent vanadium was directly titrated with ammonium ferrous sulfate under strong acidic conditions. The tetravalent vanadium can be oxidized to pentavalent by potassium permanganate and then analyzed. The specific results are shown in Table 3, and the data is the mass percentage of vanadium in the material.
[0033] table 3
[0034]
[0035] c: total vanadium content - surface vanadium content.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap