Inhibitor for acetylcoenzyme A synthetase in human pathogen clostridium difficile
A technology of Clostridium difficile and acetyl coenzyme, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as death, growth inhibition, and failure of Clostridium to perform normal energy and material metabolism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
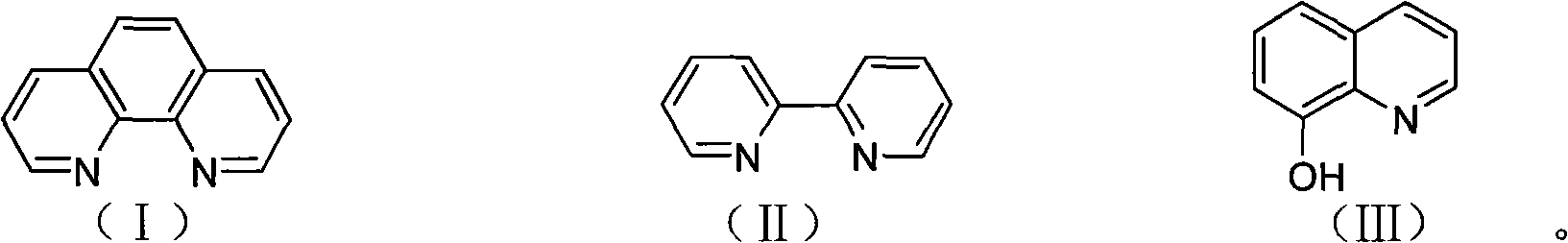
[0016] Taking 8-hydroxyquinoline as an example, the specific operation process is as follows:
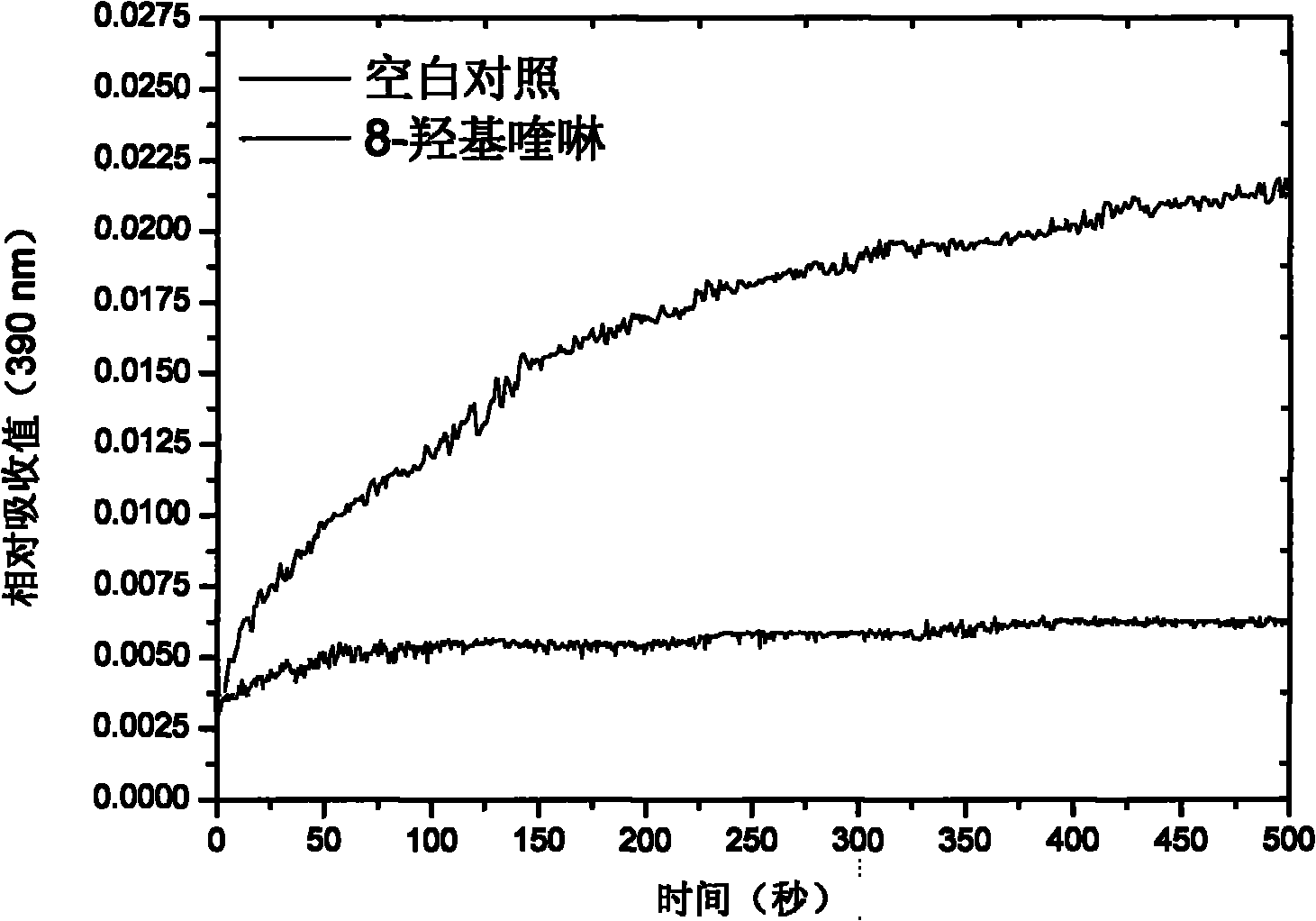
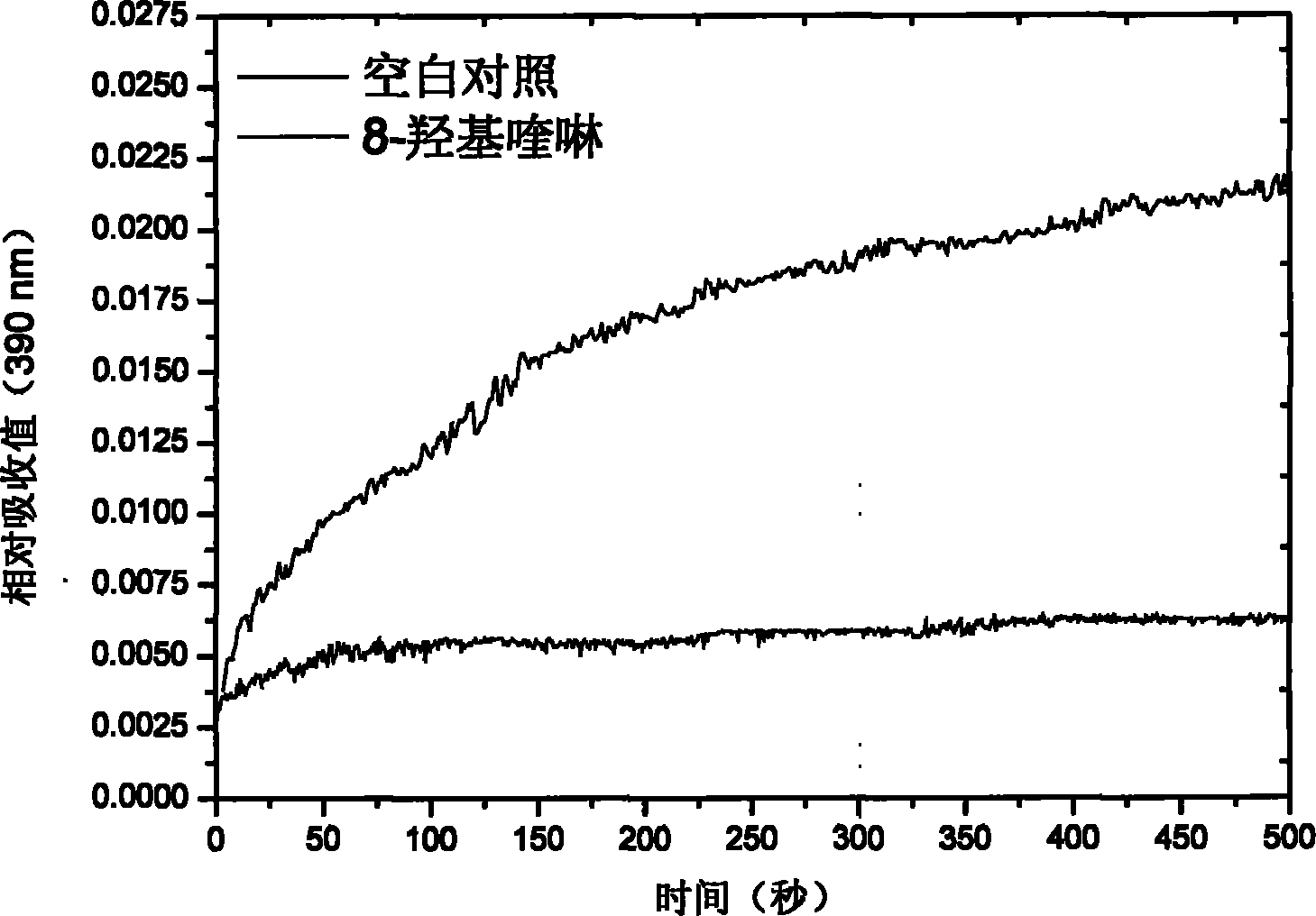
[0017] First prepare a titanium citrate solution, and use potassium ferricyanide to calibrate its precise concentration to 15.8mM. Weigh 145 mg of 8-hydroxyquinoline and dissolve it with 1 mL of absolute ethanol. The extracted methyl cobalt iron sulfur protein (CoFeSP) has a concentration of 40μM, ACS cd It is 198μM. Prepare 1.2mL reaction solution A, which contains 20μM ACS cd , 1mM titanium citrate, and 50mM tris buffer solution (pH=8.0), after half an hour of combination, add 1μL of 1M 8-hydroxyquinoline for more than 1 hour; prepare 1.2mL reaction solution B, which contains 10μM CoFeSP, 1mM titanium citrate And 50mM tris buffer solution (pH=8.0).
[0018] Use a 2.5mL disposable syringe to transfer the reaction solutions A and B to the intercepting spectrophotometer, and monitor the curve of the absorbance at 390nm over time after the two are mixed. This curve reflects the ACS cd Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com