Alpha-glucose-based new hesperidin dihydrochalcone as well as preparation method and application thereof
A hesperidin dihydrochalcone and glucose-based technology, which is applied in the field of food additives and its preparation, can solve problems such as limited effects, and achieve the effect of broadening the scope of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
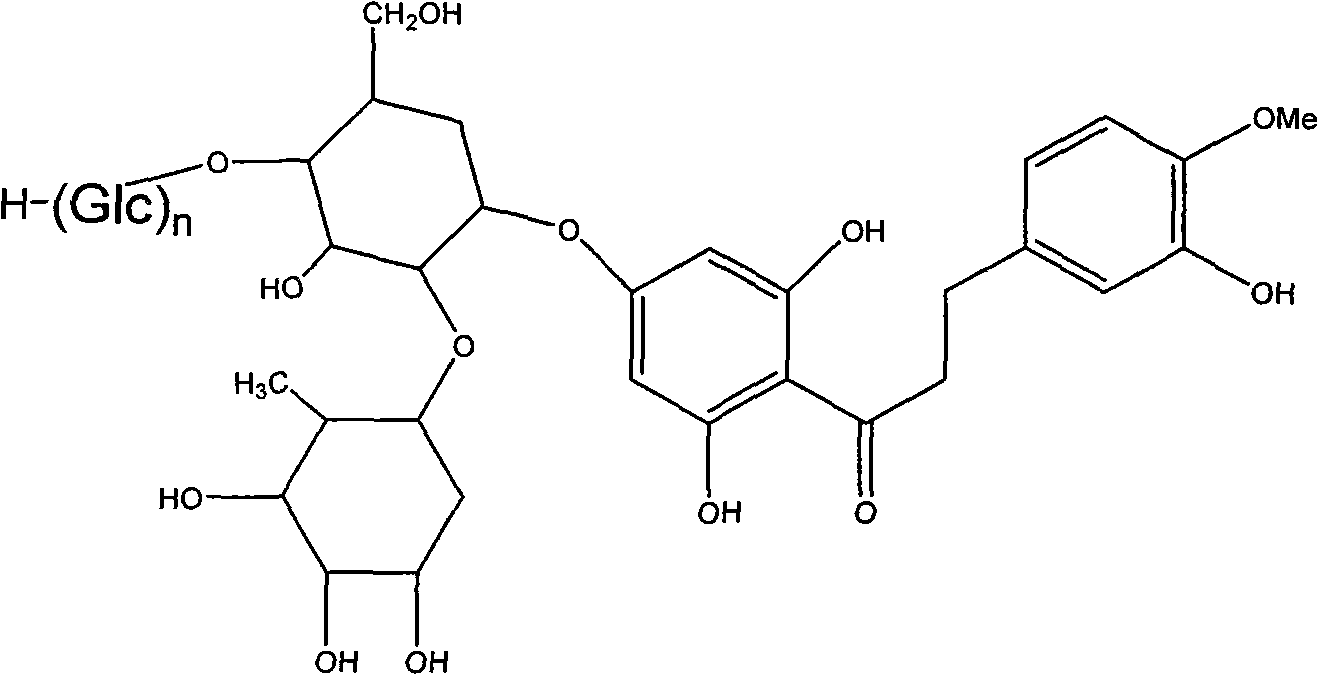
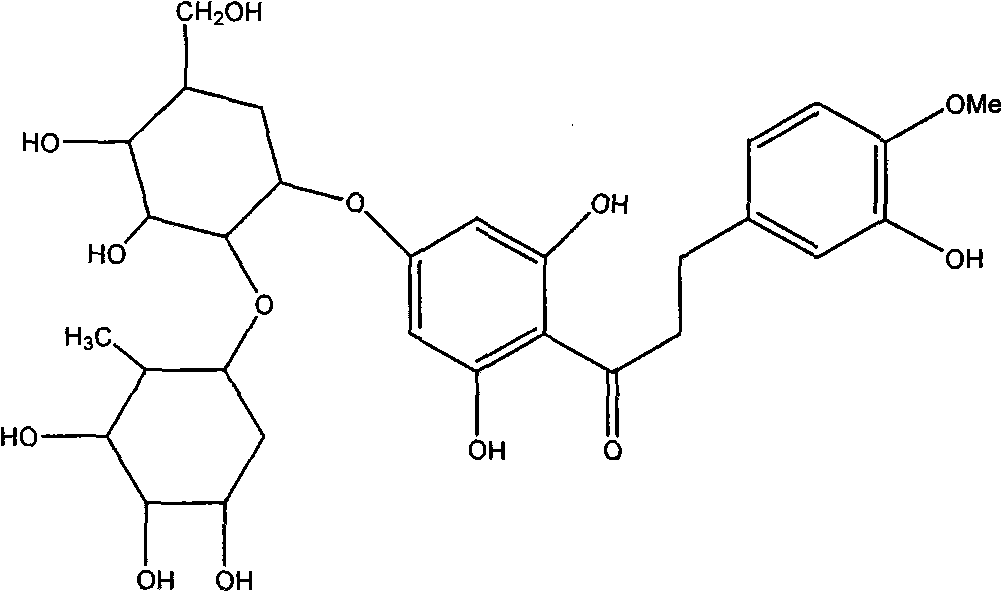
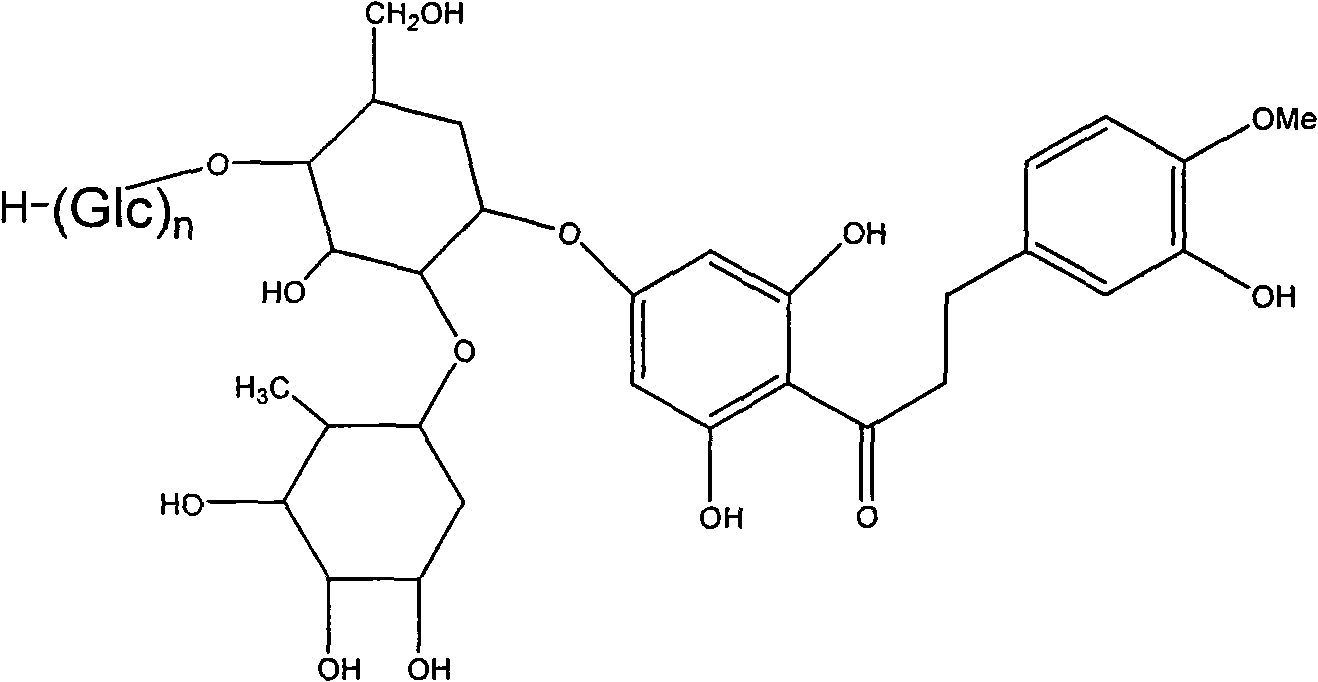
[0034] Add 1 part of quality neohesperidin dihydrochalcone and 4 parts of quality cyclodextrin (DE 8) into 20 parts of 20% ethanol solution, then add cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase enzyme solution to adjust When the pH value reaches about 6.0, react at 60°C for 48h. Paper chromatographic analysis showed partial conversion of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone to α-glucosyl neohesperidin dihydrochalcone. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was heated to 80°C to inactivate the enzyme, then the solvent was spin-dried and 50ml of distilled water was added, left overnight and then filtered to obtain the supernatant. Pass the supernatant through a HP-20 macroporous resin column, wash the column with distilled water to remove sugar and inorganic salts, then wash the column with 40% ethanol solution, concentrate and spin dry to obtain the product, namely α-glucosyl neohesperidin dihydrogen chalcone.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Add 1 part of quality neohesperidin dihydrochalcone and 7 parts of quality cyclodextrin (DE 15) into 15 parts of 30% ethanol solution, then add cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase enzyme solution, adjust When the pH value reaches about 6.0, react at 60°C for 48h. Paper chromatographic analysis showed partial conversion of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone to α-glucosyl neohesperidin dihydrochalcone. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was heated to 80°C to inactivate the enzyme, then the solvent was spin-dried and 50ml of distilled water was added, left overnight and then filtered to obtain the supernatant. Pass the supernatant through a HP-20 macroporous resin column, wash the column with distilled water to remove sugar and inorganic salts, and then wash the column with 30% ethanol solution, concentrate and spin dry to obtain the product, namely α-glucosyl neohesperidin dihydrogen chalcone.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Add 1 part of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone and 8 parts of cyclodextrin (DE 6) to 20 parts of water, adjust the pH to about 9.8 to dissolve, and then add cyclodextrin glucosyl Transferase enzyme solution, react at 65°C for 50h. Paper chromatographic analysis showed partial conversion of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone to α-glucosyl neohesperidin dihydrochalcone. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was heated to 80° C. to inactivate the enzyme, and after cooling, the solution was adjusted to neutrality, and the supernatant was collected by filtration after standing overnight. Pass the supernatant through a HP-20 macroporous resin column, wash the column with distilled water to remove sugar and inorganic salts, then wash the column with 40% ethanol solution, concentrate and spin dry to obtain the product, namely α-glucosyl neohesperidin dihydrogen chalcone.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com