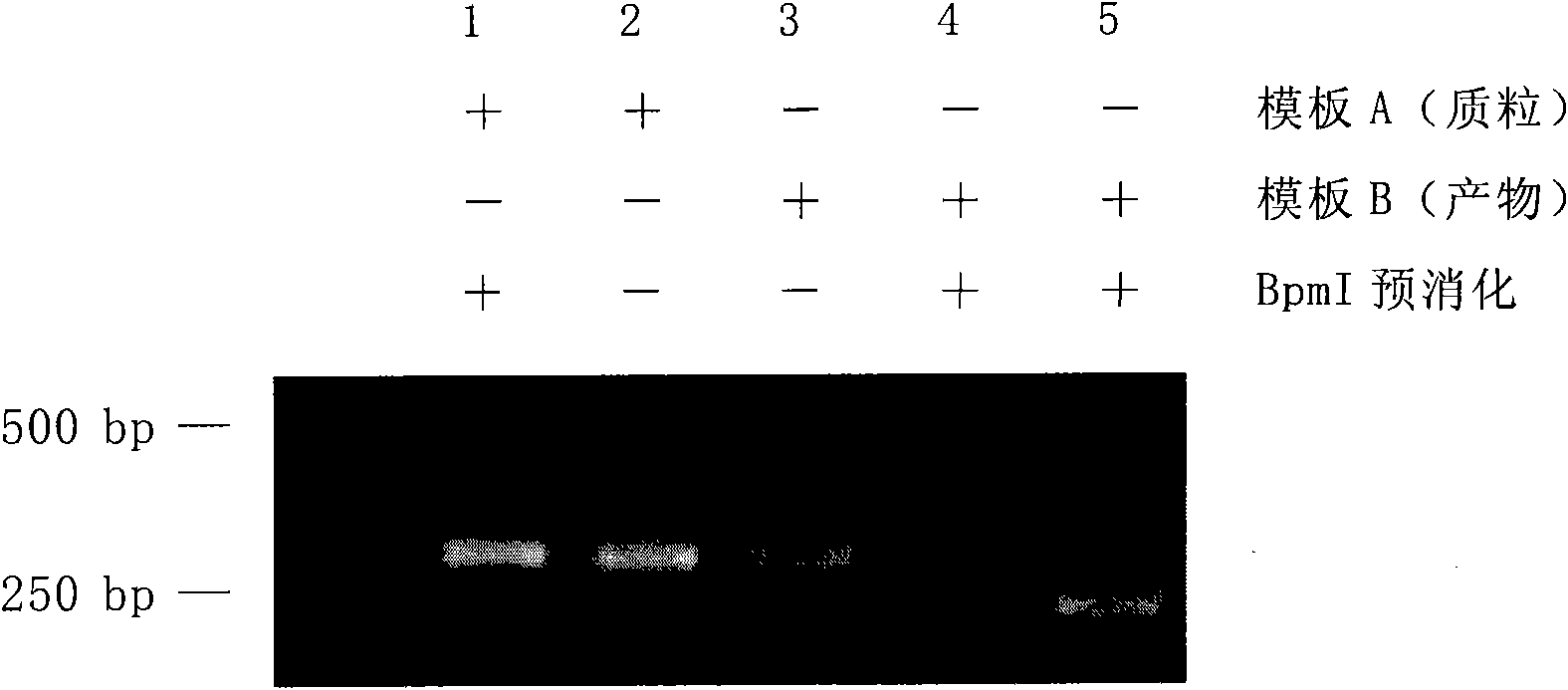Method for preventing PCR pollution by using restriction endonucleases
A technology of restriction endonucleases and polymerases, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the disadvantage of long fragment amplification, increase probe hybridization, molecular cloning downstream The difficulty and cumbersomeness of the experiment, the reduction of PCR efficiency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Amplification of exon-4 sequence of human p53 gene
[0090] The sequence of human p53 gene exon-4 is shown in SEQ ID NO:1.
[0091] tcccc gatgatttgatgctgtc cccggacgatattgaacaatggttcactgaagacccaggtccagatgaagctcccagaatgccagaggctgctccccgcgtggcccctgcaccagcagctcctacaccggcggcccctgcaccagccccctcctggcccctgtcatcttctgtcccttcccagaaactactaccagggcag ggtttccgtctgggcttct tgcattctggga g(SEQ ID NO: 1)
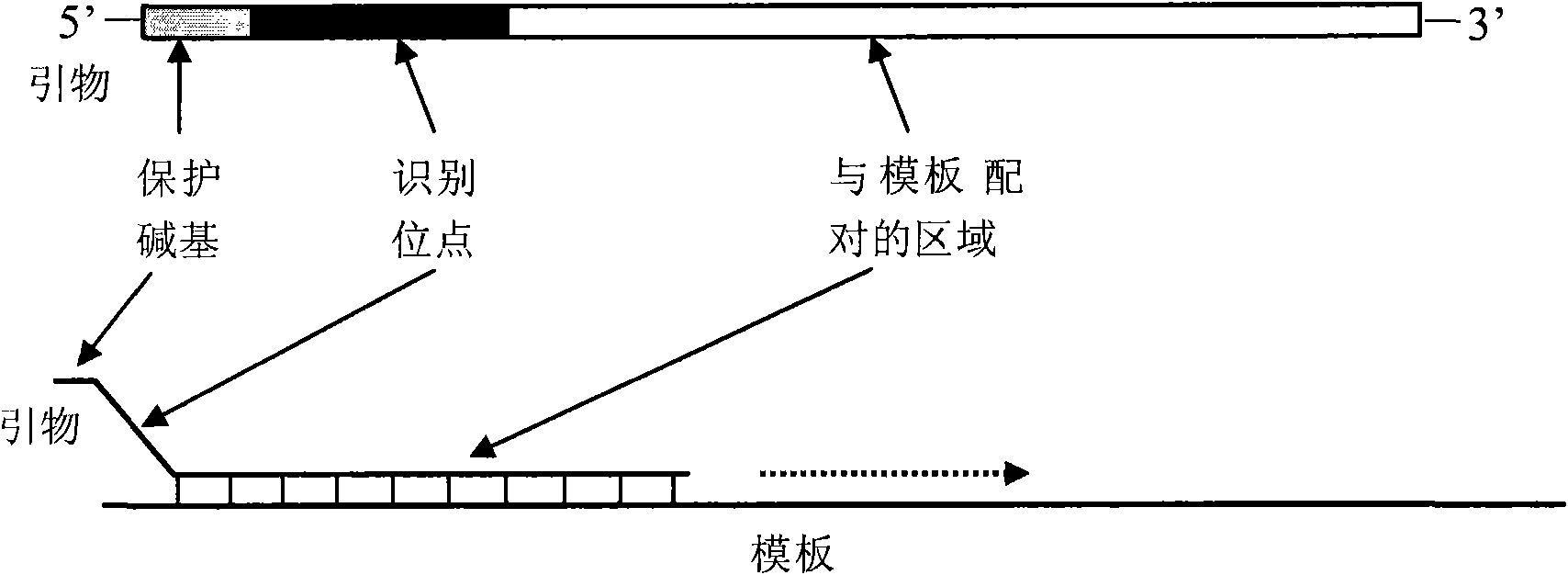
[0092] Note: The bold part is the outer primer binding position, and the underlined part is the inner primer binding position
[0093] In this embodiment, the detection purpose is to use human genomic DNA as a template to amplify the fragment of exon-4 of the human p53 gene.
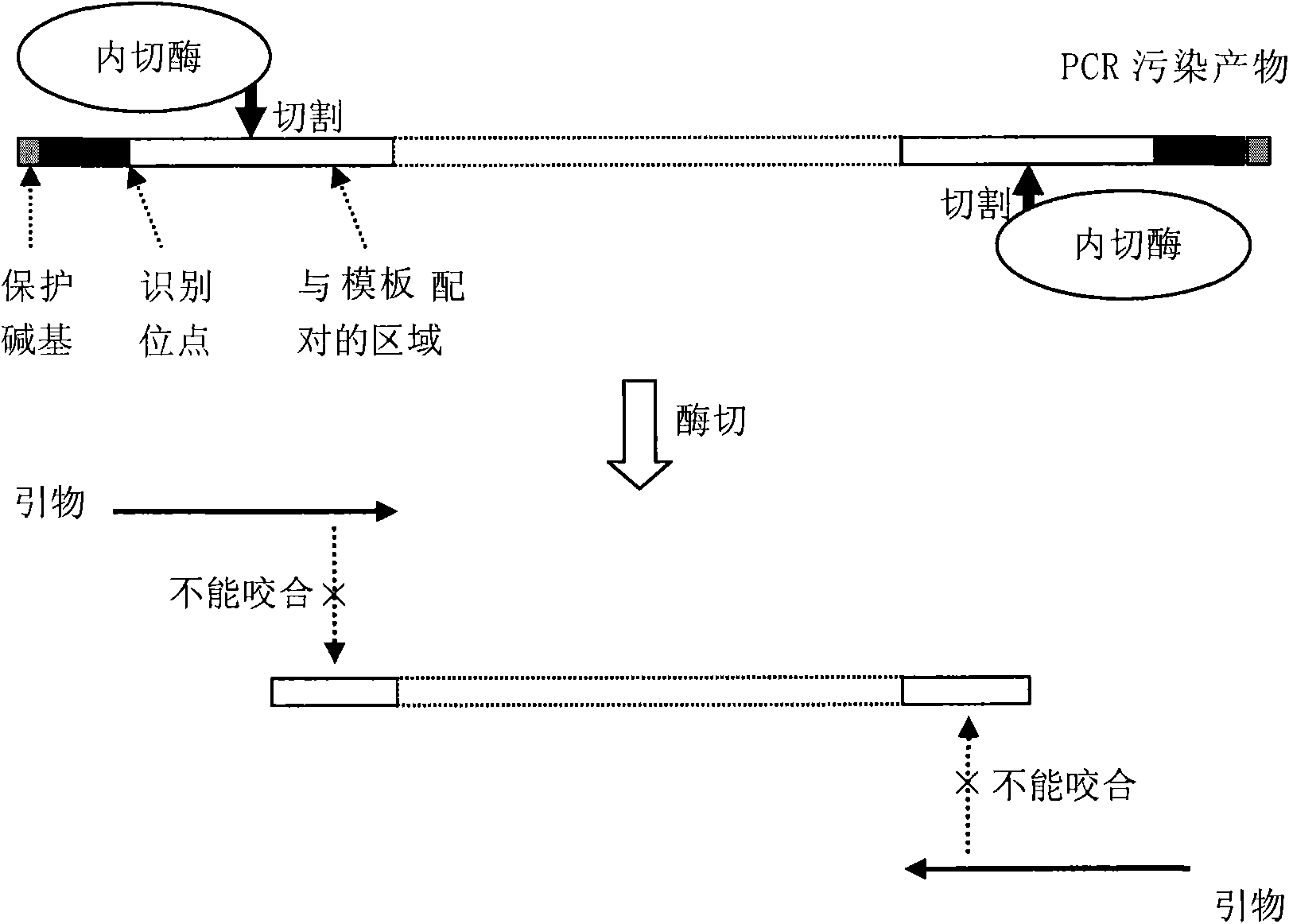
[0094] In this embodiment, since there is no Bpm I restriction site in SEQ ID NO:1, the type IIS restriction endonuclease Bpm I is selected to prevent PCR contamination (of course, for SEQ ID NO:1, it can also be Use IIS type restriction endonucleases Alw I, Bci VI, Bsa I, BsmA I, Hga I, Hph I, MmeI, etc.).
[0095] 1. D...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Amplification of exon-4 sequence of human p53 gene
[0135] Example 1 was repeated, the only difference was that the commercially available pSK-p53 plasmid (A) containing the exon-4 fragment of the human p53 gene in Example 1 was replaced with human genomic DNA extracted by conventional methods.
[0136] The results also showed that after digesting the previous PCR contaminants with IIS restriction endonuclease Bpm I, the false positives caused by PCR contaminants can be effectively reduced or even eliminated.
Embodiment 3
[0138] Amplification of human DAPK gene
[0139] Example 2 is repeated, the difference lies in: the detection object in this example is the human DAPK gene, and its length is 1707 bp. Therefore, the type IIS restriction endonuclease used is Fok I, and the primers used are as follows:
[0140] Forward primer: 5’-ATT GGATG AGGTTGCCACGCTCCACTA-3' (SEQ ID NO: 6)
[0141] Reverse primer: 5’-AAT GGATG CGCCTCACTGGGAGCAATC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 7)
[0142] The underlined part is the recognition site of Fok I enzyme
[0143] The restriction site of Fok I is 5’...GGATG(N) 9 …3’
[0144] 3’...CCTAC(N) 13 …5
[0145] Use the human genomic DNA extracted by conventional methods (A) or the previous PCR product (B) (contaminants) diluted 10000 times as templates, and add or not add IIS restriction endonuclease Fok I to the system for PCR reaction. Among them, the pH value of the PCR reaction system is 8.4.
[0146] The results showed that after digesting the previous PCR contaminants with IIS ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com