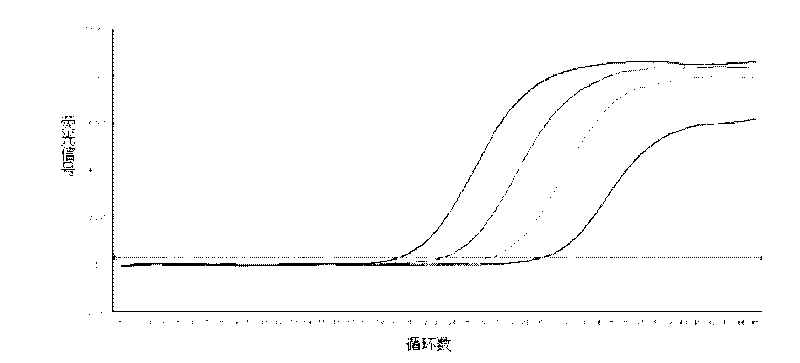
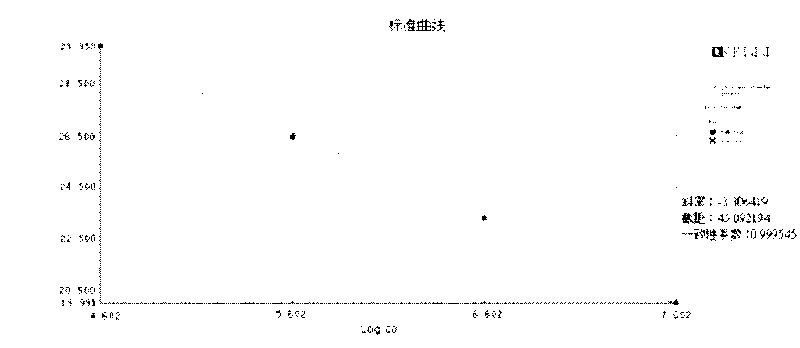
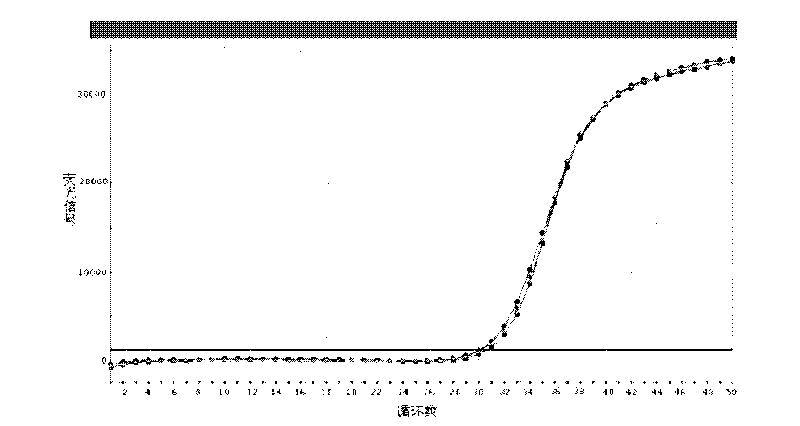
Reagent and method for quick release of nucleic acid
A nucleic acid release and reagent technology, which is applied in the field of rapid nucleic acid release reagents, can solve the problems of high price and limited wide application, and achieve the effects of simple operation, avoiding differences and errors, and stable experimental results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Example 1 Fluorescence quantitative PCR detection example for HBV DNA
[0019] Preparation of nucleic acid release reagent: 0.1 mM / L surface active peptide is dissolved in 80 mM / L KCl sterile aqueous solution, and 0.1% (mass to volume ratio) SDS and 0.5% (volume) ethanol are added. The percentage is calculated based on the volume of sterile water (the same below).
[0020] HBV DNA fluorescence quantitative PCR detection: suck 5 microliters of the nucleic acid release reagent and 5 microliters of the test sample (standard, negative, positive control, unknown concentration of HBV DNA-positive serum or plasma) with a filter tip, Add to the PCR reaction tube, pipette the tip 5 times, mix well, let stand for about 5 minutes, use the filter nozzle to suck 40 microliters of the prepared PCR reaction solution, in Stratagene Mx3000P or ABI7300 / 7500 series PCR Perform real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification on the instrument.
[0021] The concentration and ratio of each ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2 Fluorescence quantitative PCR detection for HCV RNA
[0028] Preparation of nucleic acid release reagent: 0.05mM / L surface active peptide is dissolved in 100mM / L KCl sterile aqueous solution, and 0.01% (mass to volume ratio) LLS and 0.05% (volume) ethanol are added.
[0029] Use a suction nozzle with a filter element to suck up 5 microliters of the nucleic acid release reagent and 5 microliters of the sample to be tested (standard, negative and positive control, known HCV RNA positive serum or plasma), and add it to the PCR reaction tube with a pipette tip Pipette 8 times, mix well, and after standing for about 5 minutes, use a filter nozzle to suck 40 microliters of the prepared PCR reaction solution, and perform real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR amplification on the Stratagene Mx3000P or ABI7300 / 7500 series PCR instrument.
[0030] The HCV PCR reaction solution is composed of primers, probes, dNTPs, 5×PCR buffer, sterilized purified water, ROX solution, enzym...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3 Fluorescence quantitative PCR detection for DNA of pathogens of STD series
[0037] Preparation of nucleic acid release reagent: prepare the nucleic acid release reagent according to the ratio of Example 1, and dilute the nucleic acid release reagent with water in a ratio of 2:3 before use.
[0038] Fluorescence quantitative PCR detection of pathogen DNA of STD series: Wipe the urethral opening with a cotton test piece, then insert another cotton test piece into the urethra and gently rotate it and take it out. Place the test piece in an EP tube containing 0.5ml of saline and stir and squeeze it. After drying, discard the swab, use a suction nozzle with a filter to suck 5μl of the above-mentioned secretion-containing sample, add it to the nucleic acid release reagent, pipette 10 times with a pipette tip, mix well, and let it stand for about 5 minutes. The suction nozzle with filter element sucks 40μl of the prepared PCR reaction solution, and performs real-time flu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com