Methods for treating pompe disease
A Pompe disease and fusion protein technology, applied in the field of treatment of Pompe disease, can solve problems such as no significant success, and achieve the effect of cost-effectiveness, potential and simple method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Example 1: Production of recombinant wild-type GAA and GILT-tagged GAA
[0092] plasmid
[0093] DNA encoding full-length wild-type human GAA was isolated and inserted into an expression vector for production of recombinant human GAA. The DNA cassette encoding amino acids 1-952 of fully human GAA (hereafter referred to as "cassette 635") was derived from IMAGE clone 4374238 (OpenBiosystems) and was derivatized using the following PCR primers:
[0094] GAA13: 5'-GGAATTCCAACCATGGGAGTGAGGCACCCGCCC (SEQ ID NO: 1) and
[0095] GAA27: 5'-GCTCTAGACTAACACCAGCTGACGAGAAACTGC (SEQ ID NO: 2).
[0096] Cassette 635 was digested with EcoRI and Xbal, inactivated by treatment with Klenow DNA polymerase, and ligated into the Klenow-treated HindIII site of the expression vector pCEP4 (Invitrogen), resulting in plasmid p635. Hereinafter, ZC-635 refers to wild-type untagged GAA protein.
[0097] A DNA cassette for the production of recombinant GILT-tagged GAA ZC-701 (hereinafter...
Embodiment 2
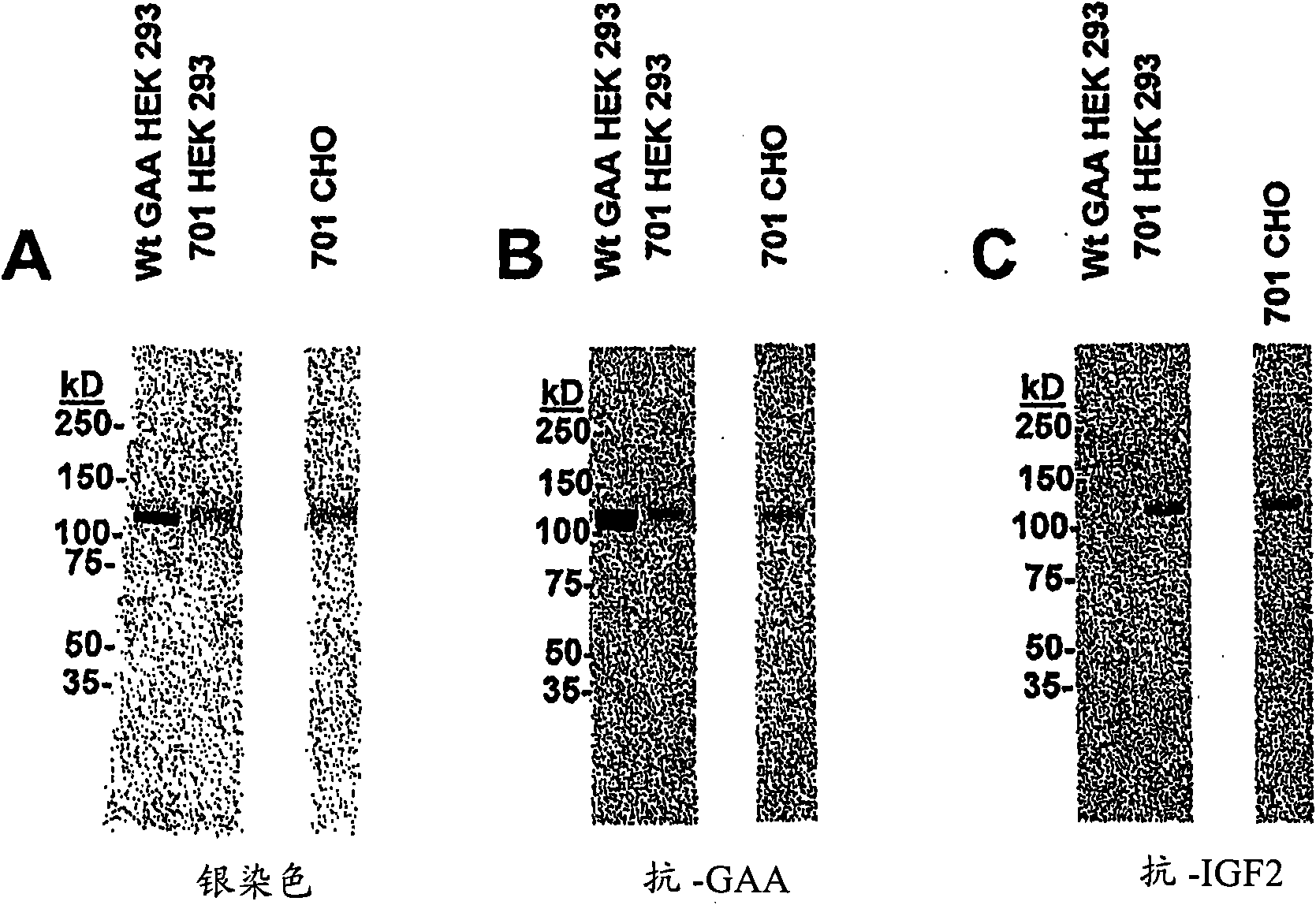
[0110] Example 2: Affinity of GILT-tagged GAA for CI-MPR
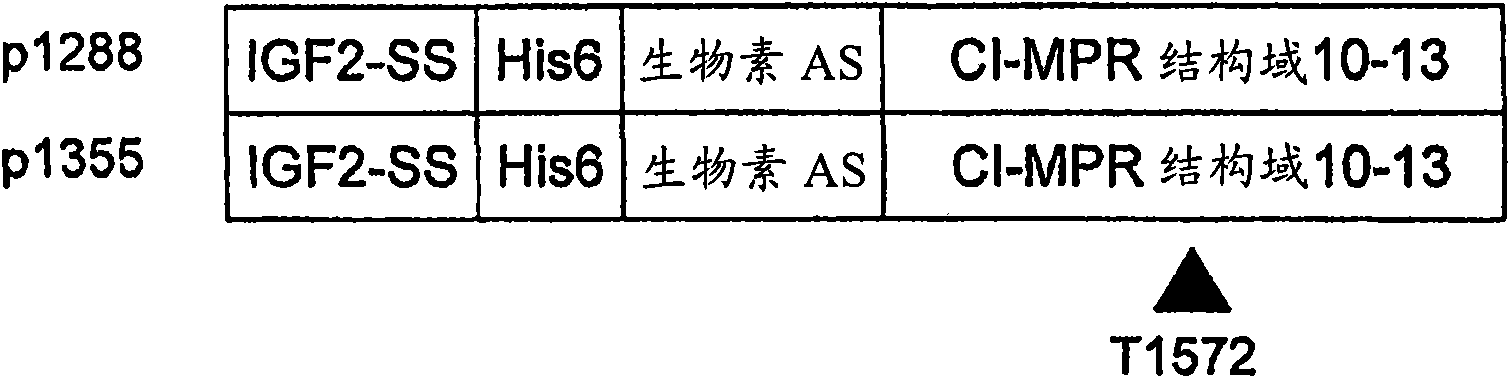
[0111] Binding affinity utilization of GILT-tagged GAA ZC-701 for CI-MPR Surface plasmon resonance assay (surface plasmon resonance assay) to determine. Two biotinylated and His-tagged recombinant proteins (containing wild-type CI-MPR domain 10-13 and one point mutation variant) were formed, respectively, according to standard molecular techniques. Schematic representation of the two recombinant proteins as Figure 3A shown. Plasmid p1288 contains the IGF-II signal peptide followed by: a poly-His (poly-His) tag; a biotin AS domain; and a sequence encoding wild-type CI-MPR domains 10-13. Plasmid p1355 contains the IGF-II signal peptide followed by: a poly-His (poly-His) tag; a biotin AS domain; and a CI-MPR encoding a point mutation I1572T that effectively reduces the affinity of the receptor for IGF-II Sequences of domains 10-13. The specific DNA and amino acid sequences associated with these two recombinant pr...
Embodiment 3
[0130] Example 3: Analysis of N-linked oligosaccharides shows that ZC-701 lacks M6P
[0131] N-linked oligosaccharide analysis was performed to determine the oligosaccharide profile of ZC-701 using PNGase deglycosylation followed by a combination of HPLC analysis with fluorescence detection (Blue Stream Laboratories).
[0132] Cleavage of N-linked sugars (carbohydrates) from glycoprotein samples was performed by N-glycanase at a ratio of 1:100 (enzyme to substrate) using approximately 100 μg of protein per sample. Once released, glycans were extracted using cold ethanol and dried by centrifugation. The recovered oligosaccharides were labeled with 2-aminobenzamide (2-AB) under acidic conditions in the presence of sodium cyanoborohydride. After the derivatization step, by The S sample filter catheter (Prozyme) removes excess dye and other reactive reagents remaining in the sample.
[0133] Analysis of N-linked oligosaccharides by HPLC-FLD used the following conditions: mob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com