Method for determining initial position angle of rotor of permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, rotor initial position technology, applied in the control of generators, electronic commutators, motor generator control and other directions, can solve the problems of easy detection failure, complex logic judgment, etc., to improve reliability and clear logic , the effect of enhancing noise immunity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
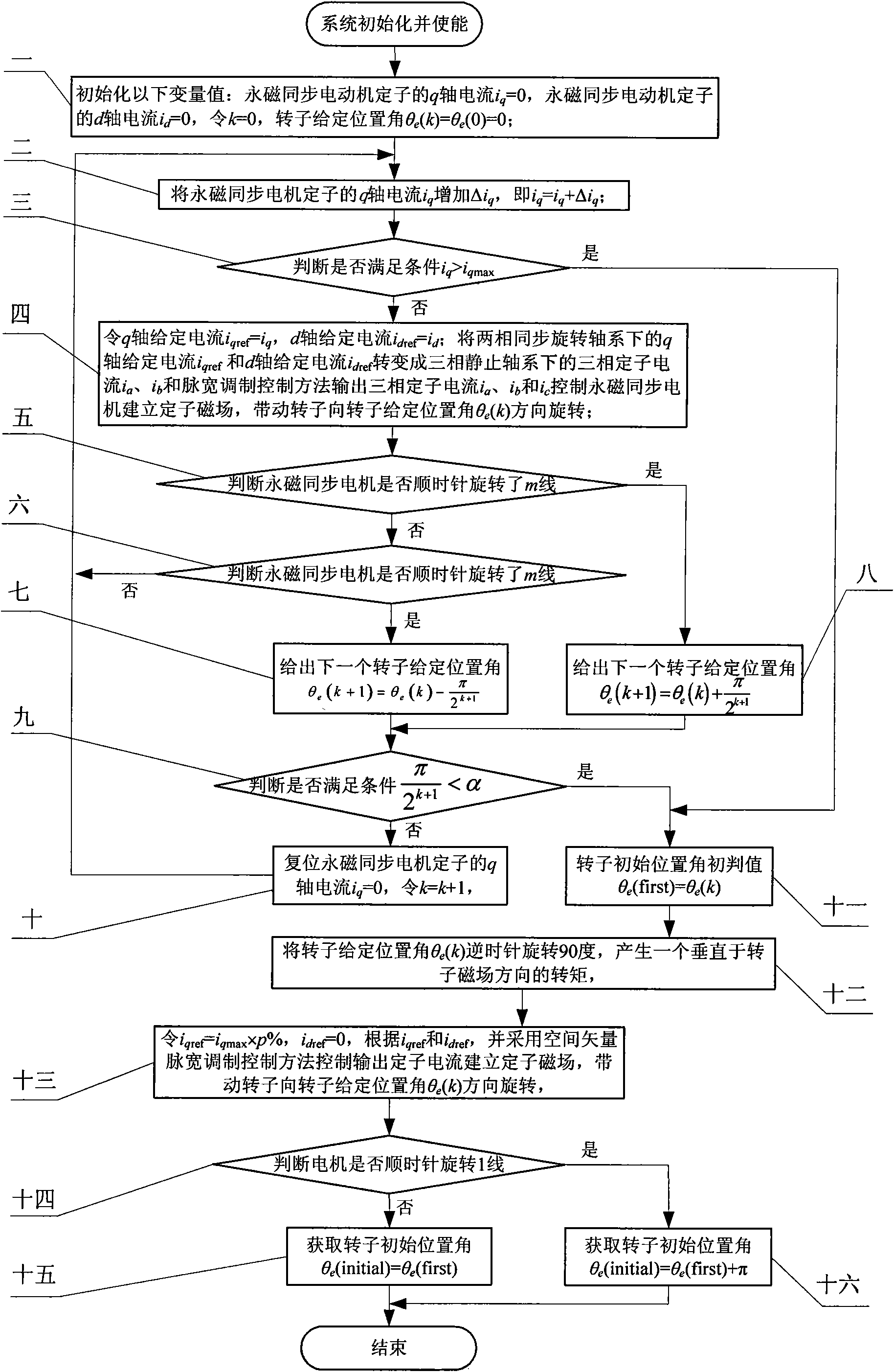
[0038] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 4 Describe this embodiment, the method of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1. Initialize the following variable values:
[0040] The q-axis current i of the permanent magnet synchronous motor stator q = 0, the d-axis current i of the permanent magnet synchronous motor stator d =0, let k=0, the rotor given position angle θ e (k) = θ e (0)=0,
[0041] Step 2: The q-axis current i of the permanent magnet synchronous motor stator q Increase Δi q , namely i q = i q +Δi q , Δi q is the incremental value of the q-axis current, Δi q Take the q-axis current limit value i of the permanent magnet synchronous motor stator q max 1% to 5% of
[0042] Step 3: Determine whether condition i is met q ≥i q max ,
[0043] If the judgment result is yes, go to step 11, if the judgment result is no, go to step 4,
[0044] Step 4: Let the q-axis set the current i qref = ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
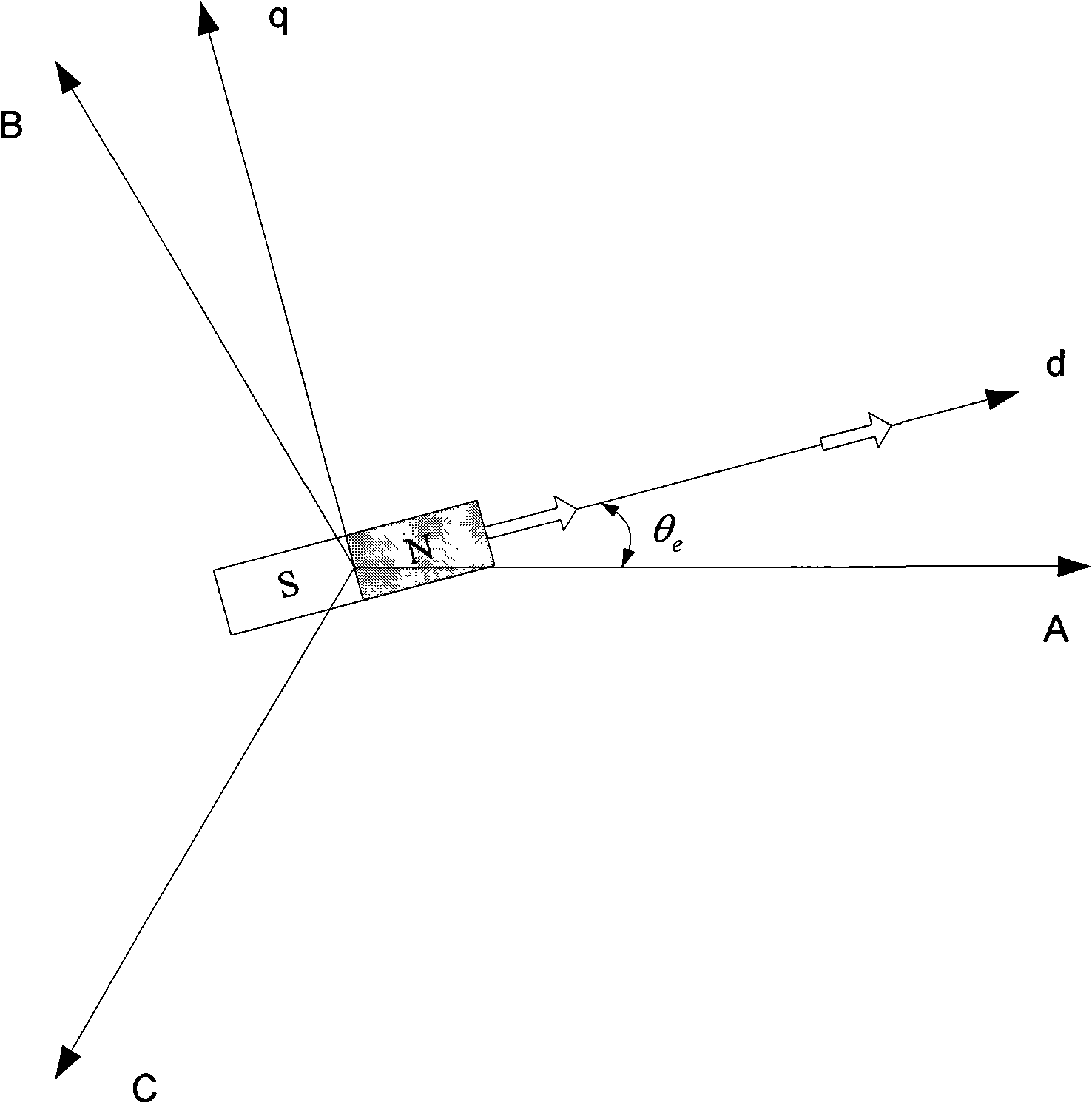
[0092] Specific implementation mode two, the following combination figure 1 , image 3 and Figure 4 Describe this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the method for judging whether the motor has rotated m lines clockwise in step 5 is:
[0093] An incremental encoder is used to measure the position information of the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. When the incremental encoder outputs m pulses and the output A pulse lags the B pulse by 90 degrees, the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotates clockwise Line m.
[0094] In step 6, the method of judging whether the motor has rotated the m line counterclockwise is as follows:
[0095] An incremental encoder is used to measure the position information of the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotor. When the incremental encoder outputs m pulses and the output A pulse is 90 degrees ahead of the B pulse, the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotates counterclockwise Line...
Embodiment approach 1
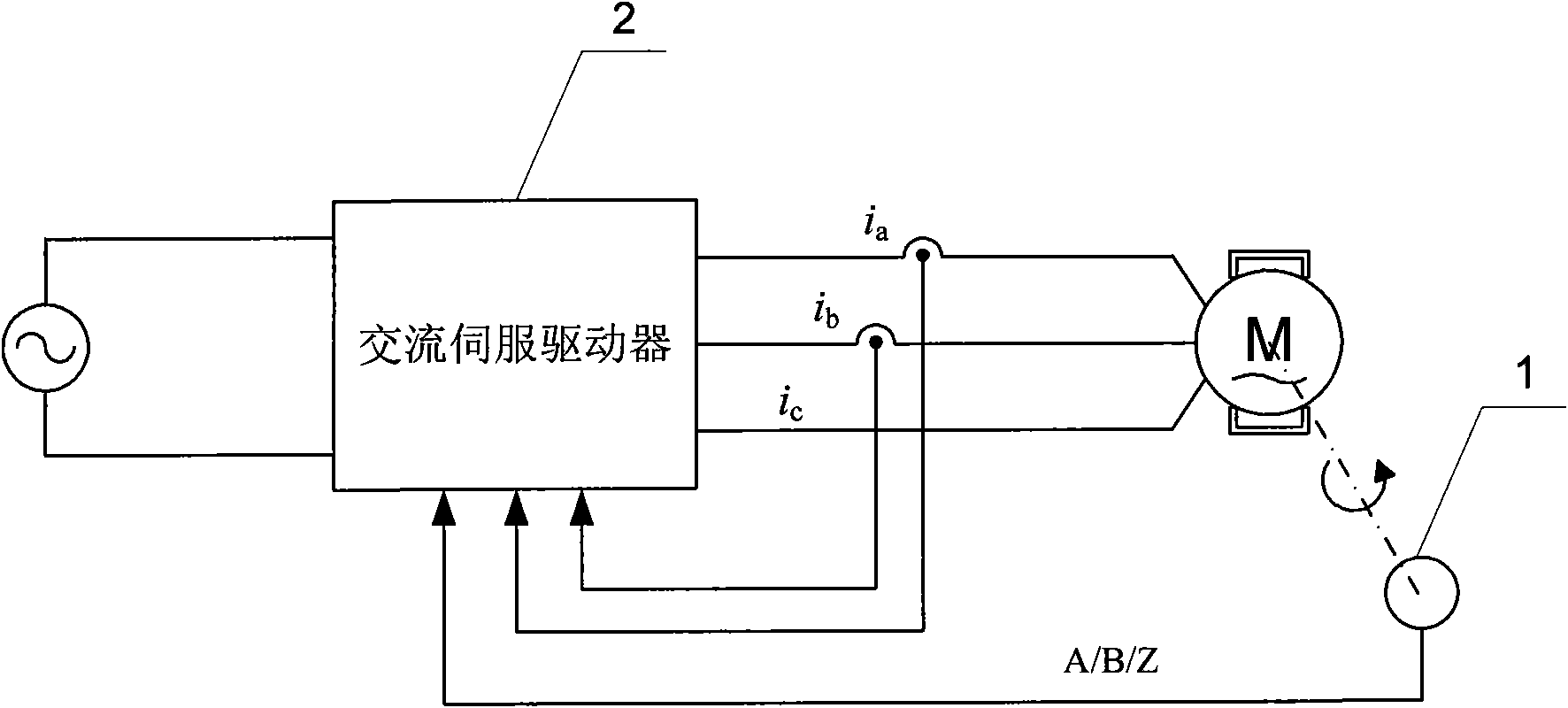
[0098] The method for determining the rotor initial position angle of the permanent magnet synchronous motor described in Embodiment 1 is compiled into a rotor initial position detection program, which is set in a digital signal processor (DSP), and the AC servo drive 2 uses the digital signal processor (DSP) as the The core is to use the incremental encoder 1 to measure the position information of the rotor of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, that is, the A / B / Z signal, and the A / B / Z signal is output to the digital signal processor after being processed by the conditioning circuit.
[0099]The characteristic of incremental encoder 1 is that it only outputs three pulse signals of A, B, and Z, wherein the A and B signals are orthogonal. When the permanent magnet synchronous motor rotates forward, the phase of the A pulse is 90 degrees ahead of the B pulse. When the permanent magnet synchronous motor reverses, the A pulse phase lags behind the B pulse by 90 degrees, and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com