Vane type continuous rotating cylinder
A vane type and rotary cylinder technology, applied in the direction of rotary piston pumps, rotary piston machines, rotary piston engines, etc., can solve the problems of high processing difficulty, low energy conversion efficiency, non-continuous power output, etc. The effects of leakage loss, wide range of allowable working fluids, and wide torque output range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
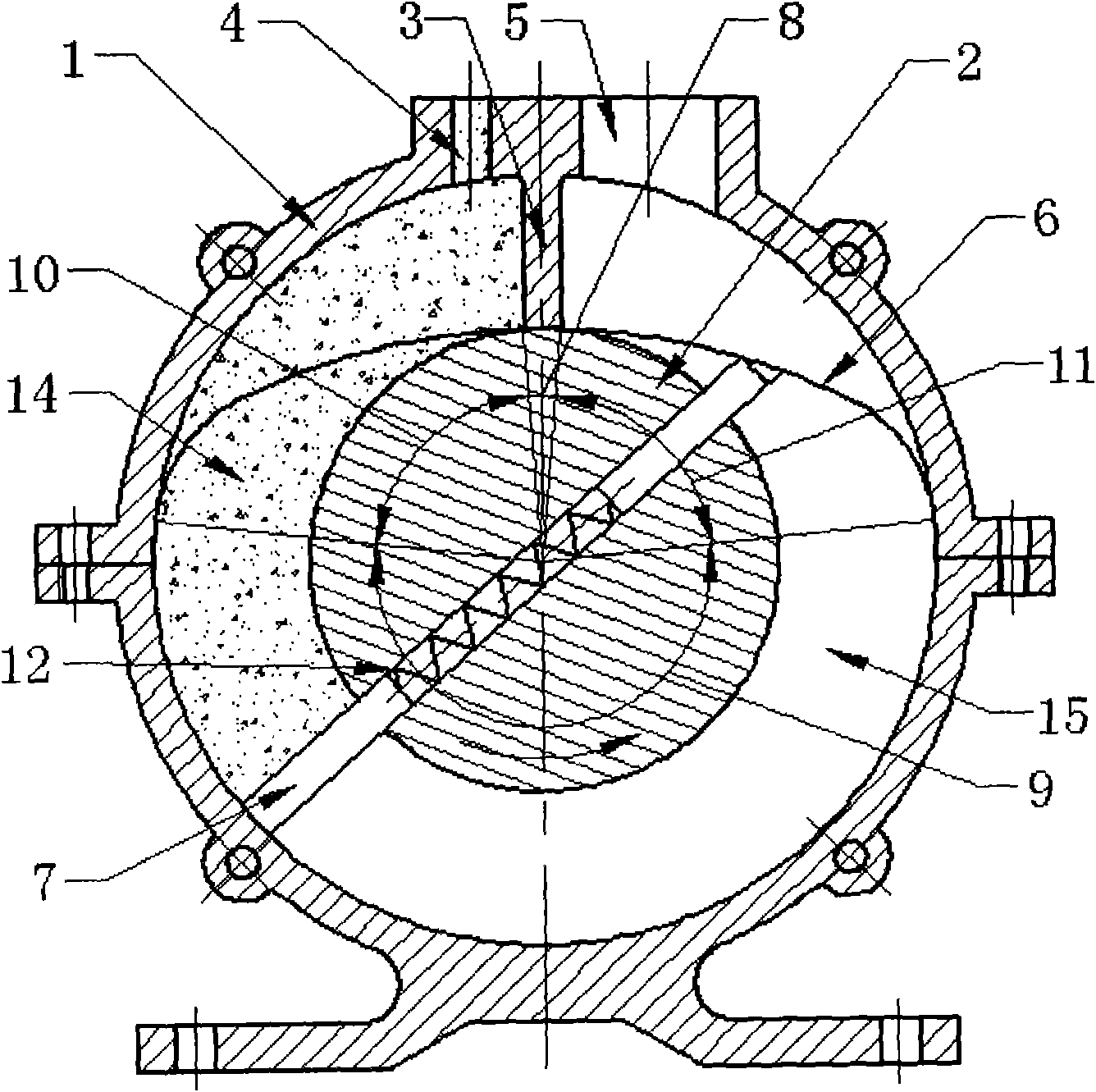
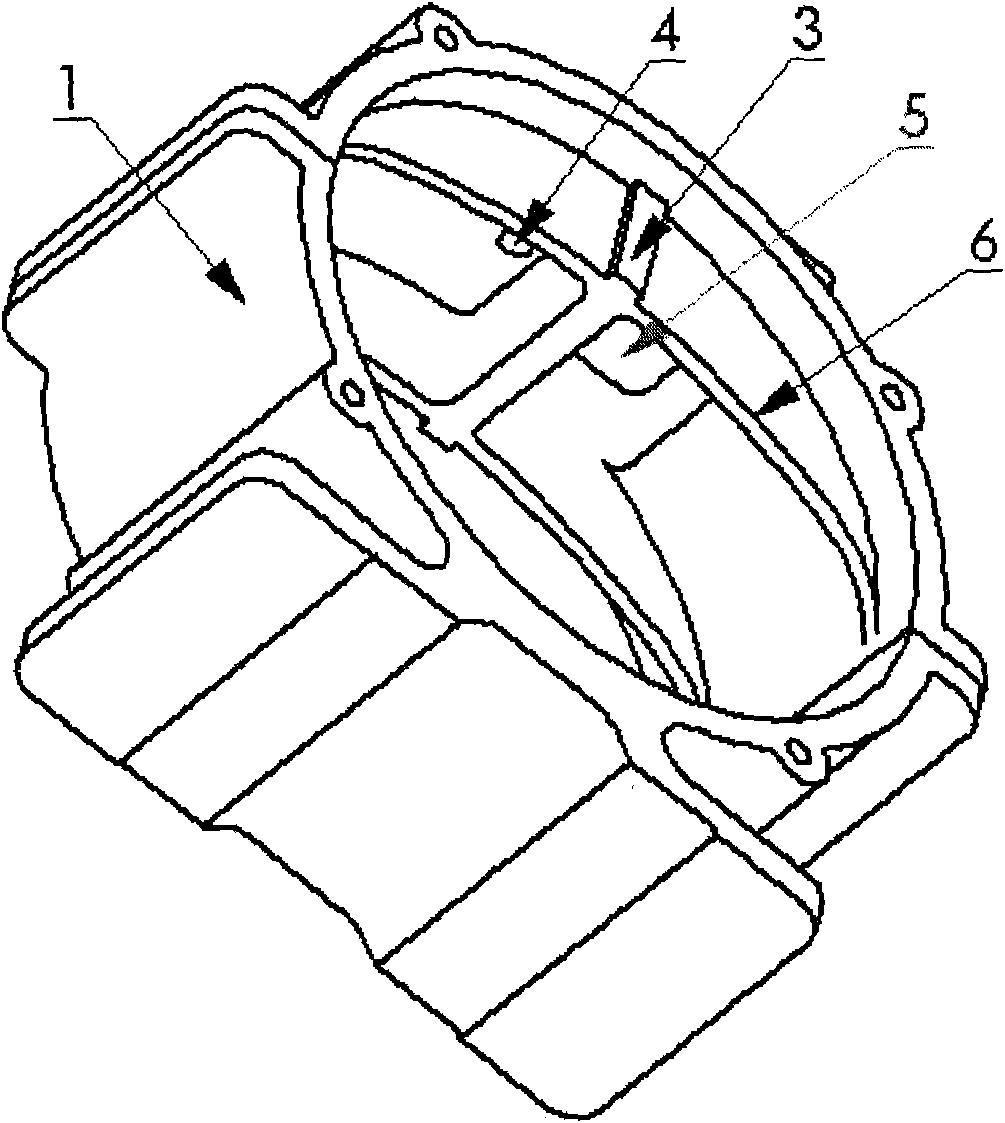
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the vane-type continuous rotary cylinder of the present invention is similar in structure to the vane-type swing cylinder, including a cylinder body 1, a rotor 2, a partition 3, a working medium inlet 4, a working medium outlet 5, a cam 6, and a vane 7. Compared with the existing vane-type swing cylinder, there are more cams 6. The function of the cams 6 is to make the working vanes 7 displace in a plane parallel to or passing through the axis of the cylinder body, so that they can cross the partition plate 3 and perform work in a cycle, so as to realize single To the continuous circular motion mode. exist figure 1 The middle rotor 2, the cam 6 and the blades 7 form a concentric cam mechanism.
[0048] In the case of applying fluid pressure energy to mechanical energy, such as figure 1 As shown, an annular chamber is provided by the cylinder body 1 and the rotor 2, a partition 3 is arranged in the chamber, the working medium inlet 4 and ...
no. 2 example
[0055] The difference from the first embodiment is that when the cam 6 is a disk-type male cam, the follower, that is, the blade 7, moves outside the cam and is located on the rotor 2 with the partition 3, as Figure 5 As shown, the vane 7 is arranged on the cylinder body 1. In the above-mentioned content, the near angle of repose 8 is interchanged with the far angle of repose 9, and the thrust motion angle 10 is interchanged with the return motion angle 11. In the annular chamber of the foregoing embodiment In this embodiment, the outer wall becomes the inner wall of the annular chamber, and other contents remain unchanged.
no. 3 example
[0057] Such as Figure 6 and Figure 7 As shown, the difference from the first embodiment is that the cam 6 is a cylindrical cam and is located in the cylinder body 1, and its working principle can be understood with reference to the description of the first embodiment. In addition, as shown in the second embodiment, a cylindrical cam can also be arranged on the rotor 2, and its working principle can be understood with reference to the description of the first embodiment and the second embodiment.
[0058] In addition, the cams in the foregoing embodiments can be appropriately deformed in combination with various technologies related to cam mechanisms in modern mechanical technology, typically including:
[0059] a. Design of the movement law of the follower
[0060] The blade 7 is used as a follower. When its mass is large, the momentum has a great influence on its motion, and the primary consideration is to reduce its maximum speed; when the requirement for its inertial fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com