Application of Lambda interferon in resisting human immunodeficiency virus
A technology of human immunodeficiency and interferon, which is applied in the application field of a new type of interferon - interferon λ in anti-human immunodeficiency virus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
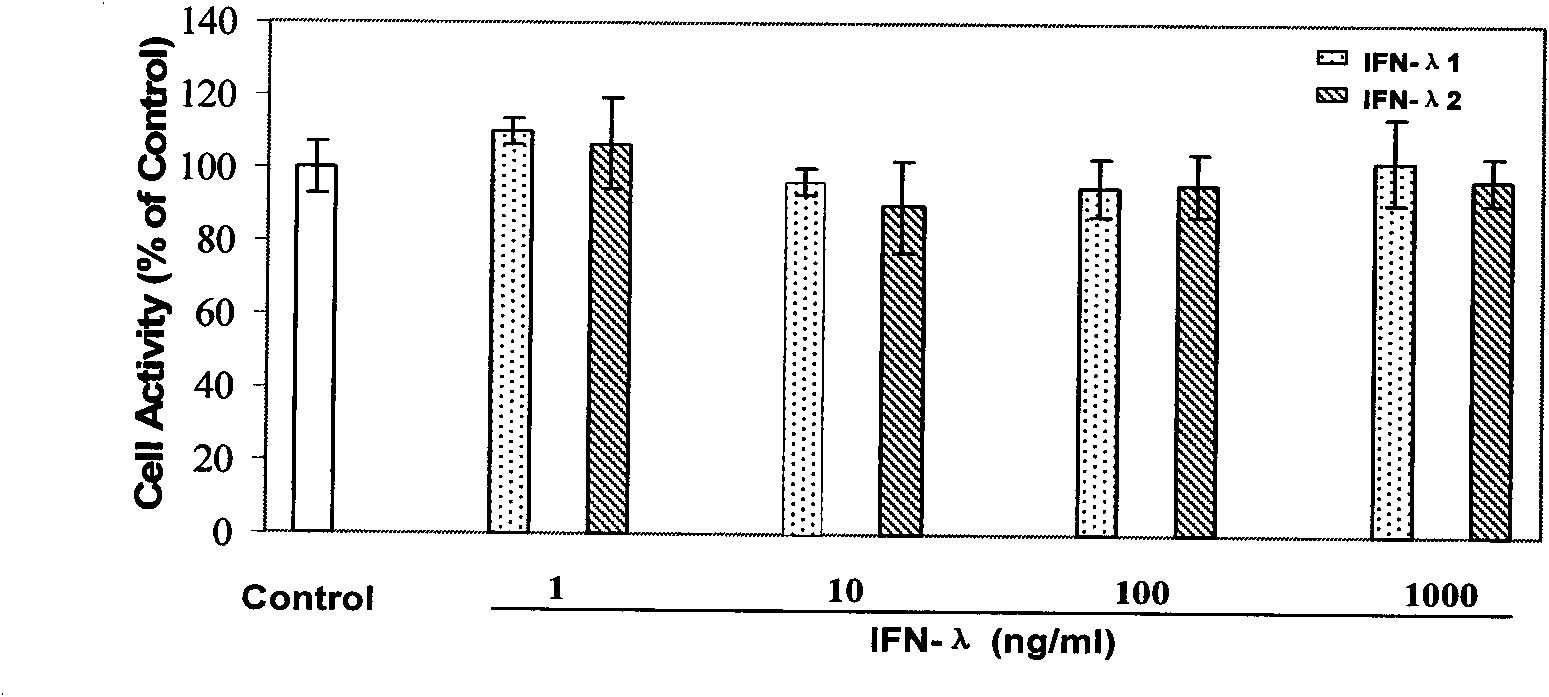
[0021] Example 1: Toxic effect of IFN-λ on human macrophages
[0022] Differentiated mature human macrophages were added with different concentrations of IFN-λ1 / λ2 and cultured for 72 hours. The cytotoxic effect of IFN-λ1 / λ2 was detected by MTS method. The results showed that the concentration of IFN-λ1 / λ2 ranged from 1ng / ml to 1000ng / ml is less than 10% for human macrophage toxicity, and there is no significant difference in statistical analysis, so it can be considered that IFN-λ1 / λ2 has no toxicity to human macrophages ( figure 1) .
Embodiment 2
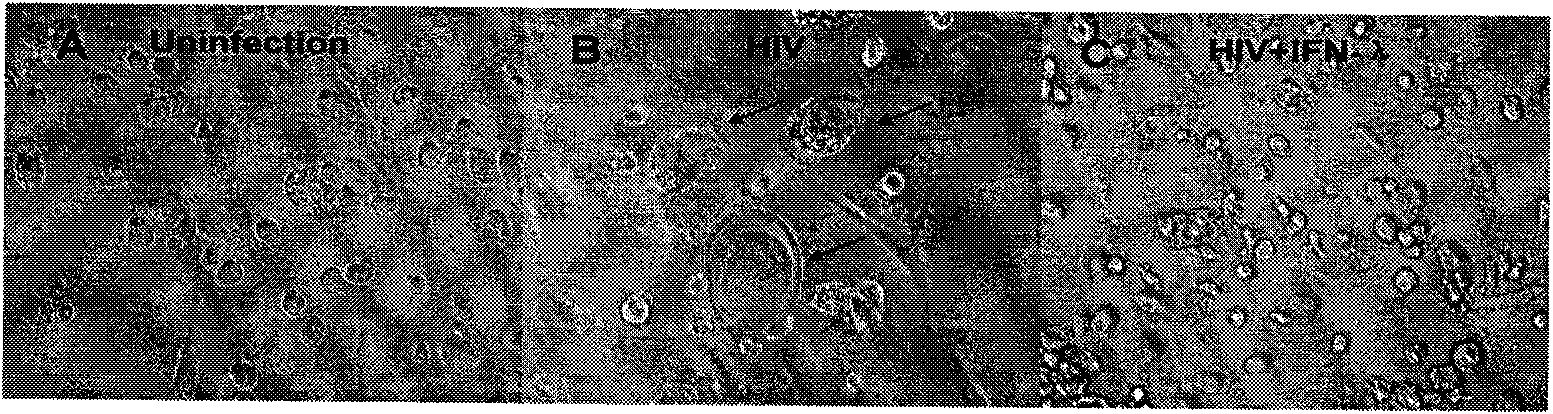
[0023] Embodiment 2: IFN-λ anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in vitro
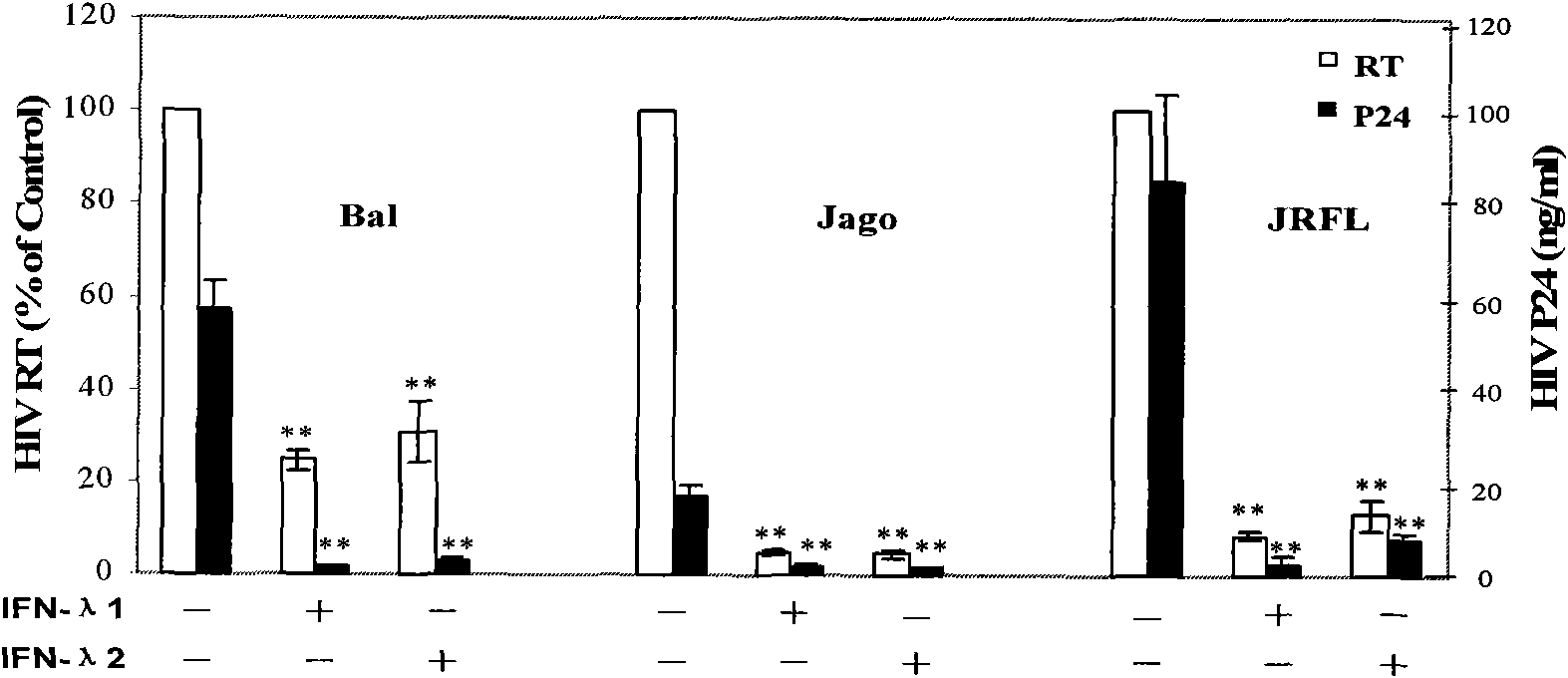
[0024] IFN-λ1 / λ2 (100ng / ml) pretreated differentiated mature human macrophages for 24 hours, HIV-1R5 strains Bal, Jago and JRFL (P24 protein content were all 30ng / 10 6 cells) were infected for 2 hours, washed three times with DMEM medium, then added DMEM (V / V) medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 37 ° C, 5% CO 2 (V / V) culture; on the 8th day after infection, observed under the light microscope, the macrophages in the HIV-1 infection group presented a typical multinucleated giant cell morphology, and the multinucleated giant cells in the IFN-λ treatment group were significantly less than the virus control group ( figure 2) .
[0025] Cell supernatants were collected on day 8 post-infection and isotopic 32 P-labeled HIV reverse transcriptase method and ELISA method were used to detect HIV-1 viral reverse transcriptase (RT) and P24 protein. The content of P24 was significantly lower...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3: IFN-λ anti-HIV-1 infection in vitro has a time effect:
[0027] IFN-λ1 / λ2 (100ng / ml) pretreated differentiated mature human macrophages for 24 hours, infected with HIV-1 Bal strain for 2 hours, washed three times with DMEM medium, and then added DMEM containing 10% fetal bovine serum (V / V) Medium, 37°C, 5% CO 2 (V / V) culture; cell supernatants were collected on the 4th day, 8th day and 12th day of infection respectively, and isotope was applied 32 P marker HIV reverse transcriptase method to detect RT. The results showed that on the 8th day after infection, the effect of inhibiting HIV-1 infection was obvious ( Figure 4, P Figure 4, P<0.05). It shows that IFN-λ inhibits the replication and infection of HIV-1 in human macrophages and presents a time relationship.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com