Method for screening disease marker
A technology for markers and diseases, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, library screening, microbial determination/testing, etc., to achieve the effect of overcoming difficult separation and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
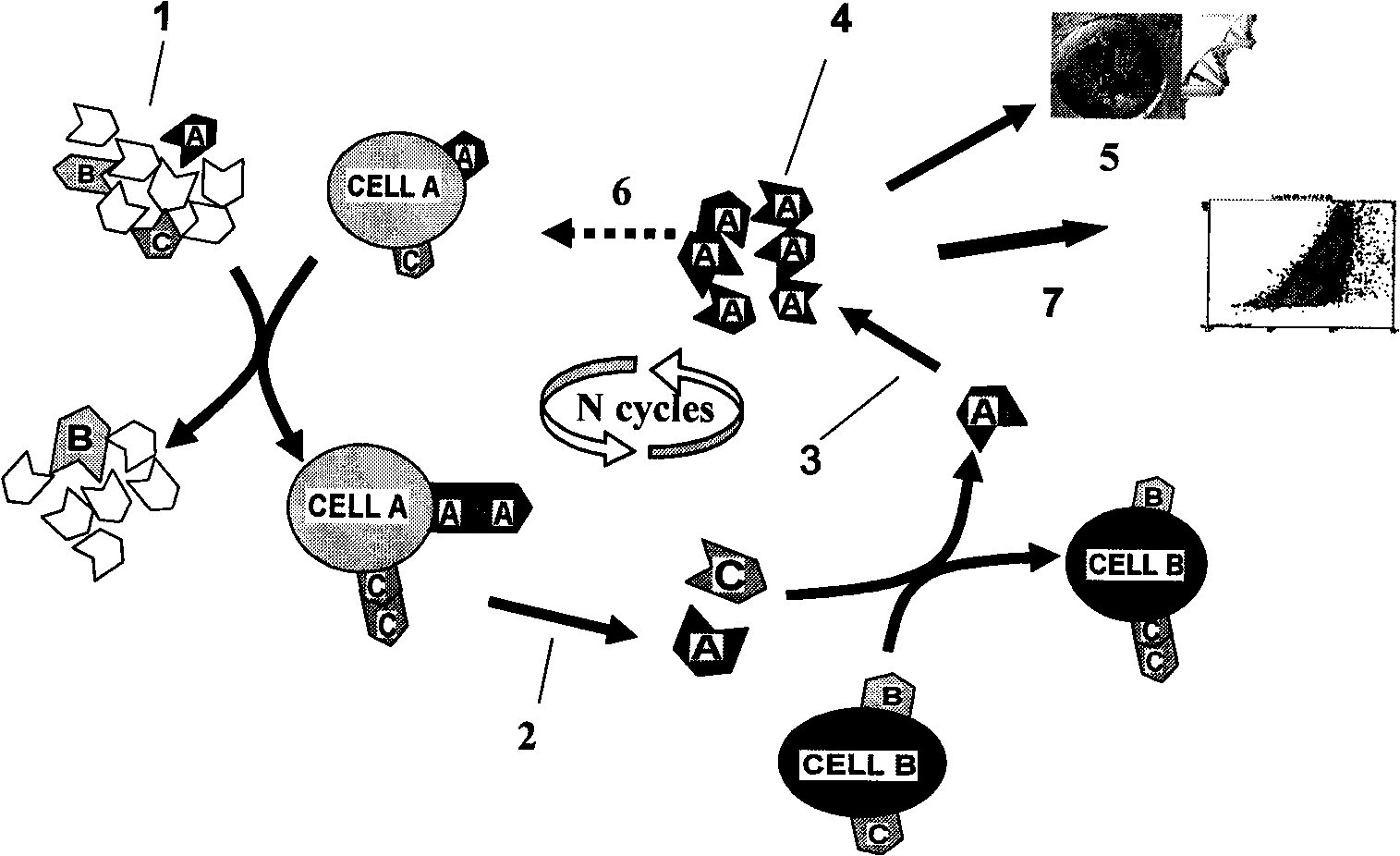
[0029] Example 1. Preparation of molecular probes related to leukemia
[0030] (1) Screening of nucleic acid aptamers related to leukemia
[0031] 1. Synthesis of random nucleic acid library
[0032] According to the literature (Jayasena S D. Aptamers: an emerging class of molecules thatrival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45: 1628-1650), the following random nucleic acid library was designed and synthesized: 5'-ATA CCA GCT TAT TCA ATT-52-nt-AGA TAG TAAGTG CAATCT-3'.
[0033] 2. Screening of nucleic acid aptamers related to leukemia
[0034] Binding buffer: containing 4.5g / L glucose, 5mM MgCl 2 , 1mM CaCl 2 , 2.67mM KCl, 1.47mM potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 137.93mM sodium chloride, 8.06mM disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1mg / mL tRNA (R8759 Sigma, Ribonucleic acid, transfer from baker's yeast (S.cerevisiae)) and 1mg / mL Bovine serum albumin (Fisher), pH 7.4.
[0035] CCRF-CEM cells (CCL-119) and Ramos cells (CRL-1596) were purchased from ATCC (American Type ...
Embodiment 2
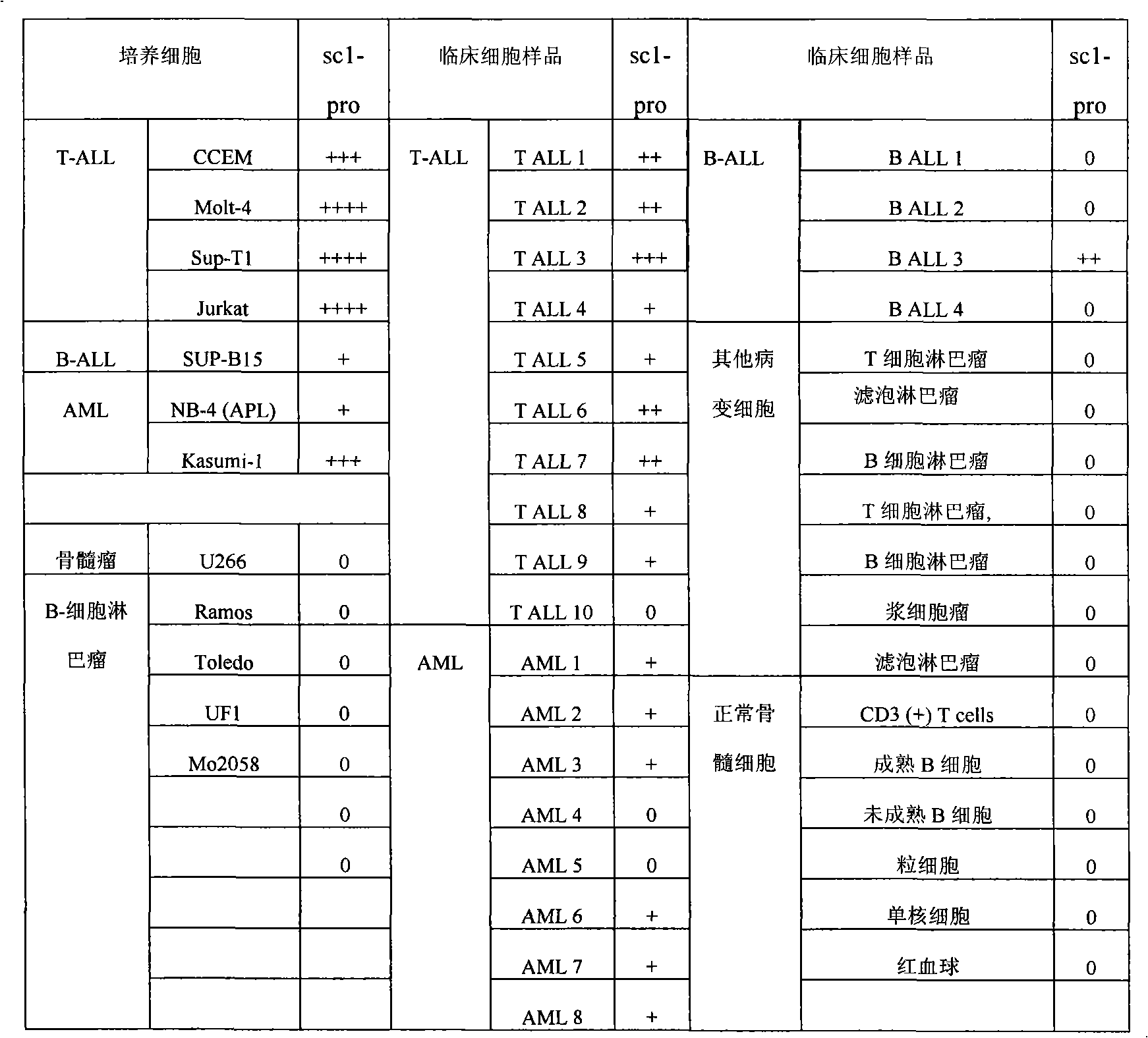
[0059] Example 2. Preparation of leukemia markers using leukemia-associated nucleic acid aptamers
[0060] 1. Preparation of markers
[0061] The nucleic acid aptamer molecule sc1 is labeled with biotin to make a molecular probe sc1-pro-bio.
[0062] Take 10×10 8 CCEM cells were lysed on ice with 50mM Tris-hydrochloric acid buffer for 20 minutes, centrifuged to remove the supernatant, and the pellet was lysed with phosphate buffer containing 0.3% Triton-100 for 1 hour on ice, and the supernatant was obtained by centrifugation.
[0063] After the supernatant was incubated with 1 nmol of molecular probe sc1-pro-bio on ice for 30 minutes, 200 μL of streptavidin-labeled magnetic particles (1 micron, Dynal Biotech ASA, Oslo, Norway) were added and incubated for 5 minutes, Adsorb the magnetic particles with a magnet, remove the supernatant; wash the magnetic particles three times with phosphate buffer, add the magnetic particles to 30 μL of polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dissociation constant | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com