Passive clamping single-phase single-grade bridge type power factor correcting convertor and control method thereof
A power factor correction and converter technology, applied in the direction of AC power input conversion to DC power output, output power conversion device, high-efficiency power electronic conversion, etc., can solve the problem of slow circuit response speed, transformer voltage peak, output side power frequency, etc. Ripple and other problems, to eliminate voltage spikes, reduce the capacity level, to achieve the effect of power factor correction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
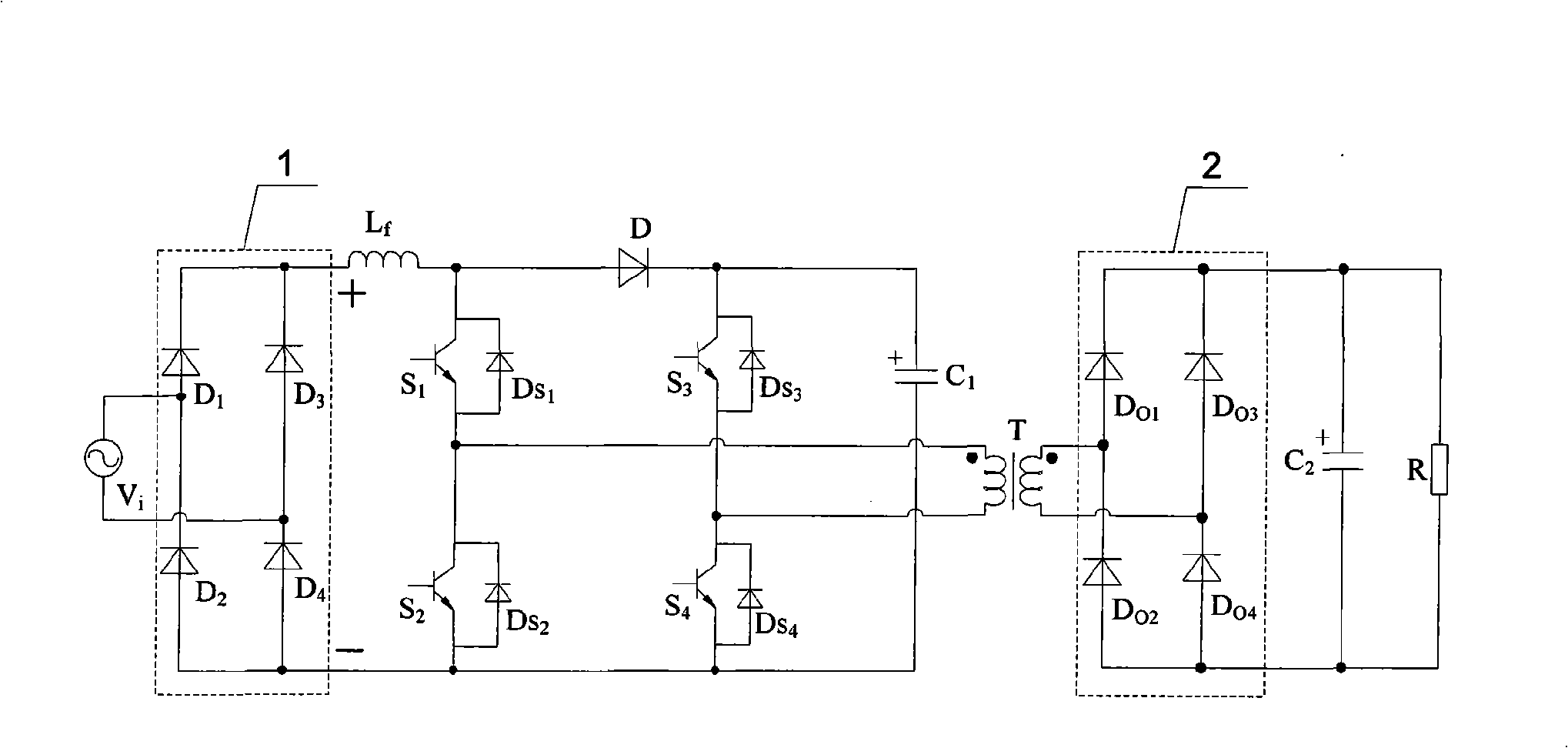
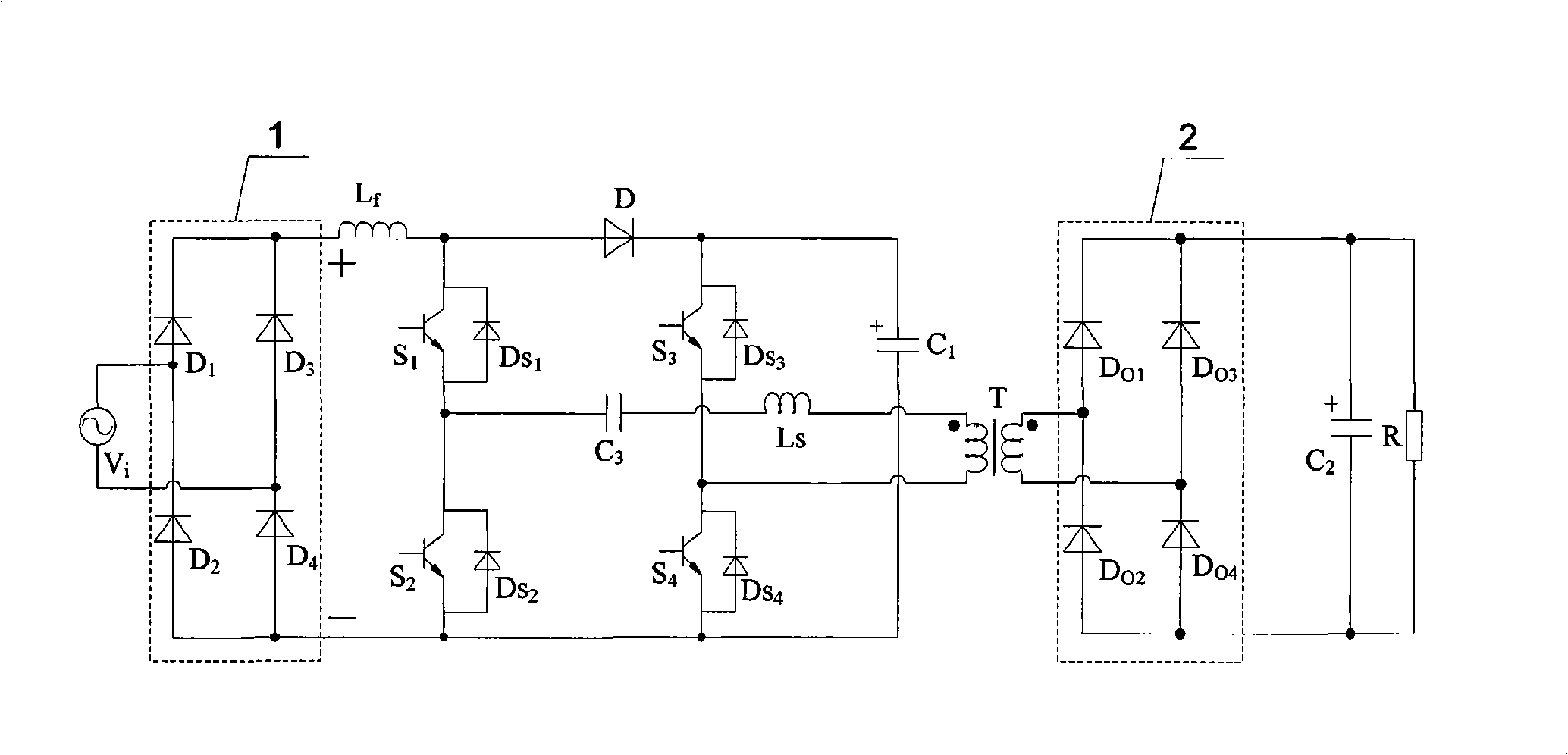
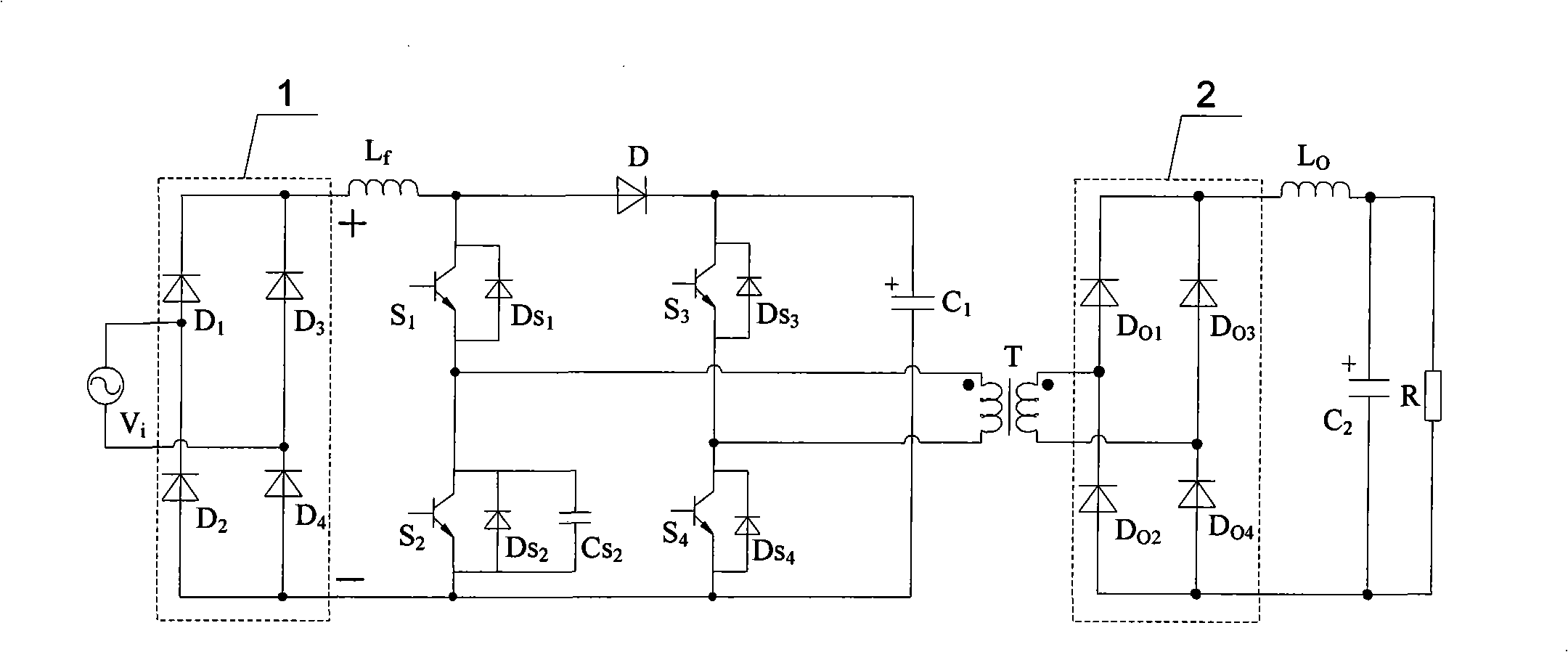
[0018] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 and Figure 5 Describe this embodiment, the single-phase single-stage bridge power factor correction converter with passive clamping described in this embodiment includes a single-phase input rectifier circuit 1, a boost inductor L f , the first switch tube S 1 , the second switch tube S 2 , the third switch tube S 3 , the fourth switch tube S 4 , diode D, clamp capacitor C 1 , high-frequency transformer T, single-phase output rectifier circuit 2, output filter capacitor C 2 and load R,
[0019] The positive output terminal of the single-phase input rectifier circuit 1 and the boost inductor L f Connected to one end of the boost inductor L f The other end of the diode is connected to the anode of the diode D, and the cathode of the diode D is connected to the clamping capacitor C 1 Connected to one end of the clamp capacitor C 1 The other end of is connected with the negative output end of th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Specific Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the first switching tube S 1 , the second switch tube S 2 , the third switch tube S 3 and the fourth switching tube S 4 An IGBT power tube with a body diode or a MOSFET switch tube with a body diode are used, and other components and connections are the same as those in the first embodiment.
[0025] The first switch tube S 1 , the second switch tube S 2 , the third switch tube S 3 and the fourth switching tube S 4 The built-in body diodes are D S1 、D S2 、D S3 and D S4 .
[0026] body diode (D S1 、D S2 、D S3 or D S4 ) are respectively connected in antiparallel to four switching tubes (the first switching tube S 1 , the second switch tube S 2 , the third switch tube S 3 or the fourth switch tube S 4 ), when the four switch tubes use IGBT power tubes, the anode of the body diode is connected to the emitter of the IGBT power tube, and the cathode of the body diode is conn...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0027] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination Figure 1 to Figure 8 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that the single-phase input rectifier circuit 1 adopts a full-bridge rectifier circuit composed of four diodes, and other components and connections are the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0028] The single-phase input rectification circuit 1 is composed of four diodes, and the four diodes are D 1 、D 2 、D 3 and D 4 . Single-phase AC supply voltage V i (input current i i ) is rectified by a single-phase input rectifier circuit 1 to become direct current.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com