Non-volatile memory and method for reduced erase/write cycling during trimming of initial programming voltage
A programming voltage, non-volatile technology, applied in the field of determining the optimal initial programming voltage of various memory cell groups, which can solve the problem of exhaustion of service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
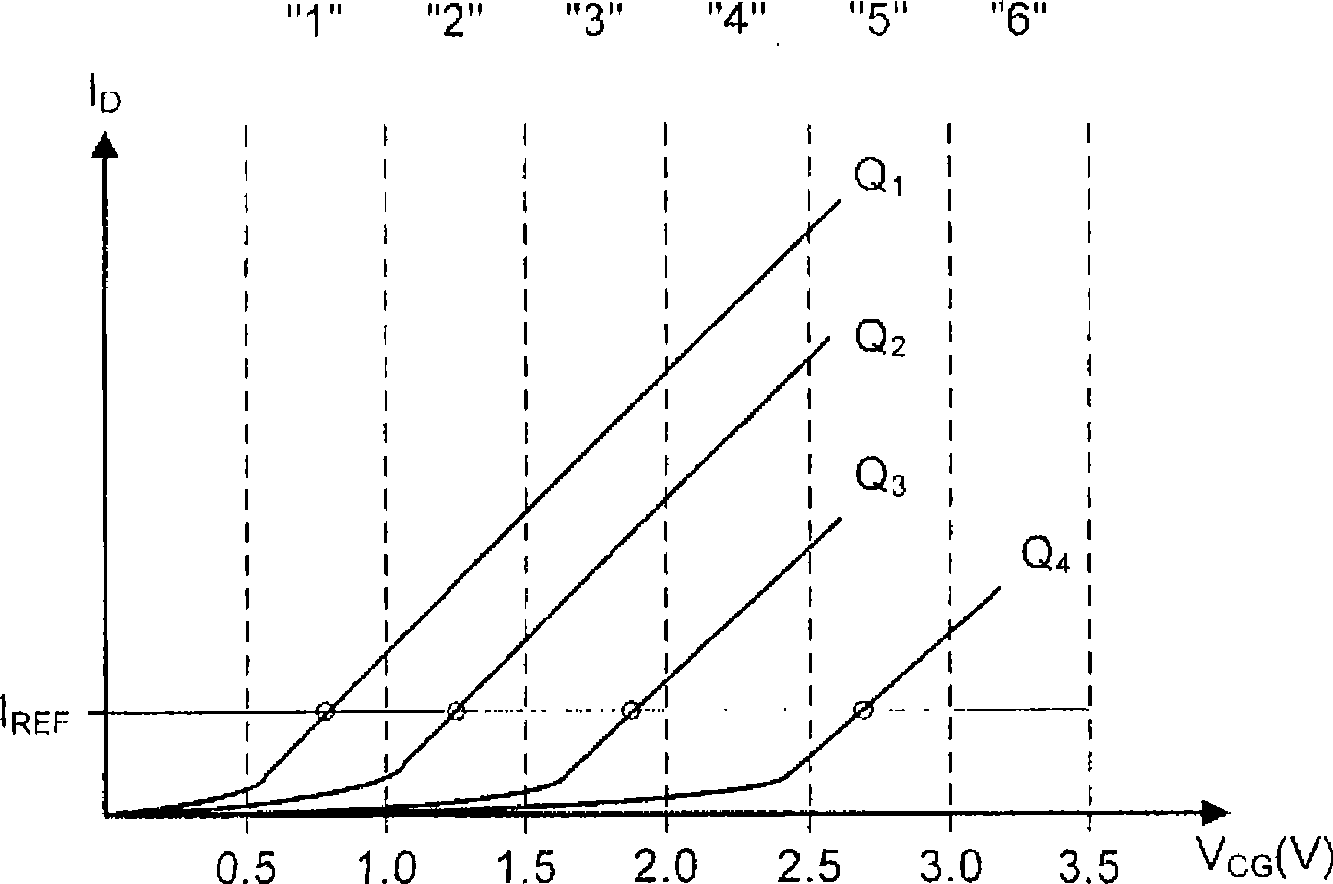
[0042] memory system
[0043] Figure 1 to Figure 7 An example memory system is illustrated in which various aspects of the invention may be implemented.
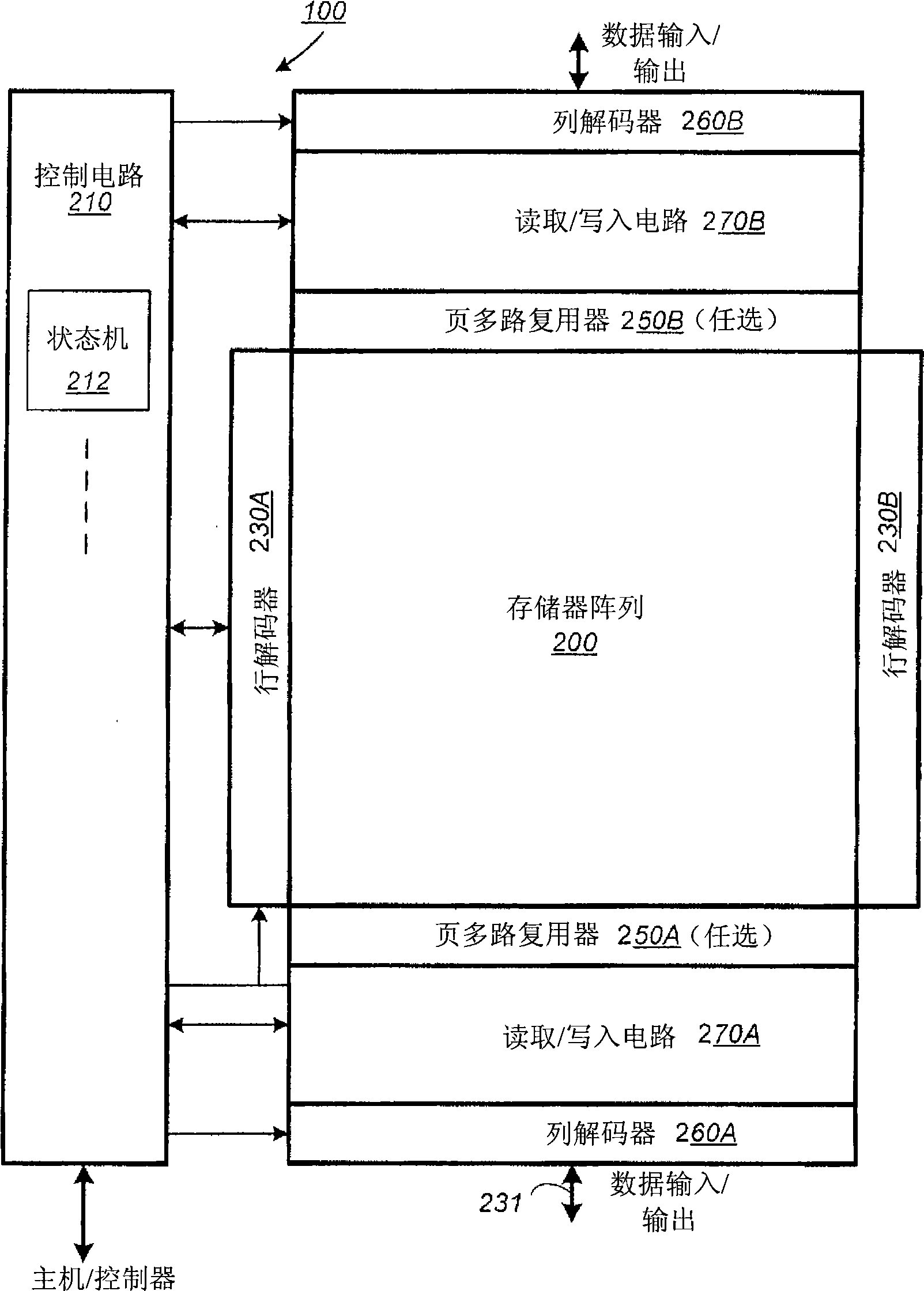
[0044] figure 1 The functional blocks of a non-volatile memory chip are schematically illustrated. The memory chip 100 includes a two-dimensional memory cell array 200, a control circuit 210, and peripheral circuits such as decoders, read / write circuits, and multiplexers. The memory array 200 can be composed of word lines (see figure 2 ) via row decoders 230A and 230B and can be addressed by bit lines (see figure 2 ) are addressed via column decoders 260A and 260B. Read / write circuits 270A and 270B allow pages of memory cells to be read or programmed in parallel. In a preferred embodiment, a page is made up of adjacent rows of memory cells sharing the same word line. In another embodiment, where a row of memory cells is divided into multiple pages, block multiplexers 250A and 250B are provided to multiplex read / wr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com