Projecting zoom lens and projection display device
A technology of zoom lens and lens, which is applied in projection devices, TVs, color TVs, etc., can solve the problem of image quality degradation of reproduced images, and achieve the effect of correcting the tilt of the image plane
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
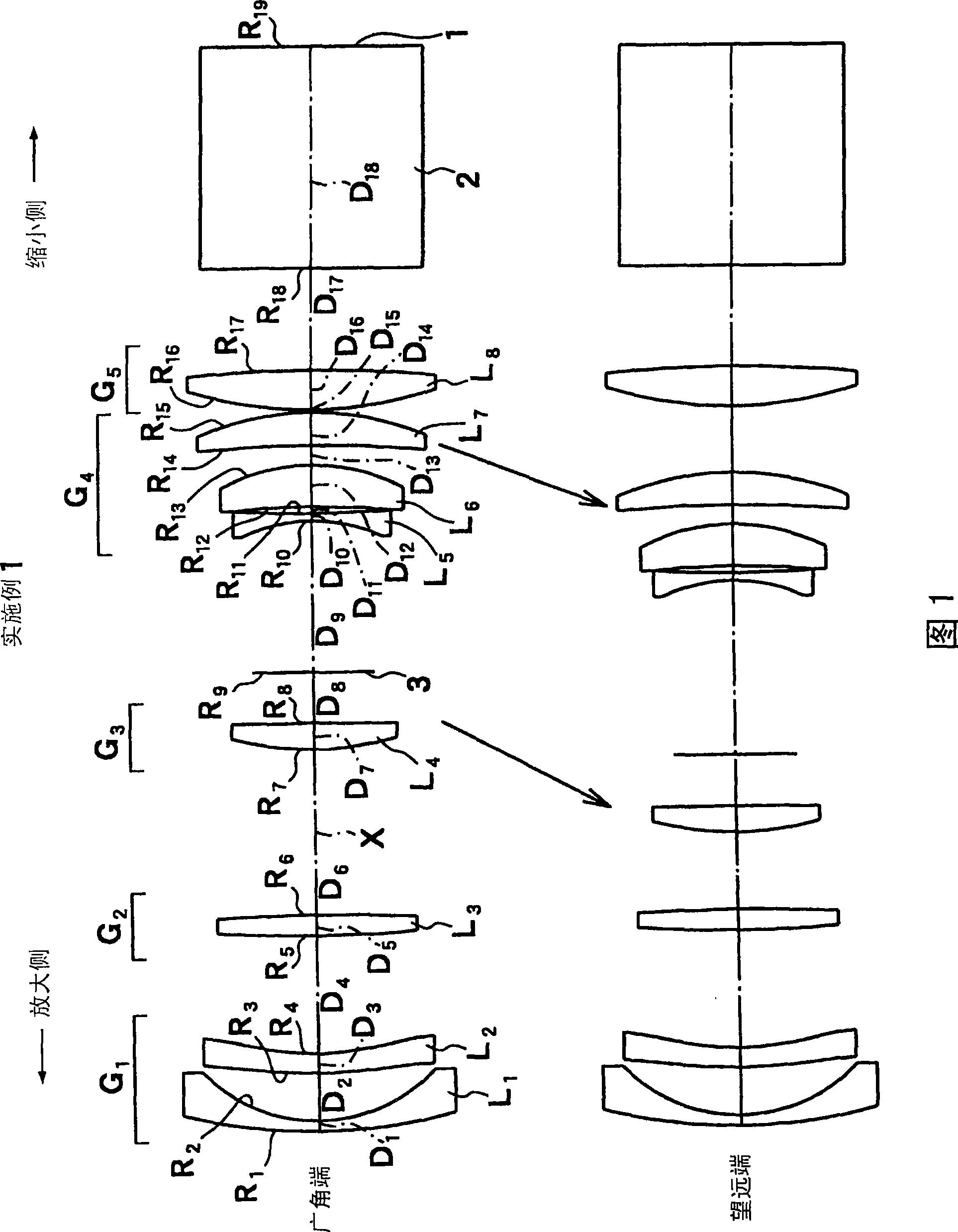
[0102] The projection zoom lens according to the first embodiment is configured as shown in FIG. 1 above. That is, this projection type zoom lens includes in order from the magnification side: the first lens group G 1 The first lens L is a negative meniscus lens whose concave surface faces the reduction side 1 And the second lens L made of aspheric lens with aspheric surface on both sides 2 constitute. Furthermore, the second lens group G 2 3rd lens L made only of biconvex lenses 3 constitute. Furthermore, the third lens group G 3 4th lens L consisting only of biconvex lenses 4 constitute. Furthermore, the fourth lens group G 4 5th lens L made of biconcave lens 5 , by following with the 5th lens L 5 The sixth lens L is a positive meniscus lens whose convex surface faces the reduction side and is arranged such that a negative air lens is formed therebetween. 6 , and the seventh lens L consisting of a positive meniscus lens whose convex surface faces the reduction sid...
Embodiment 2
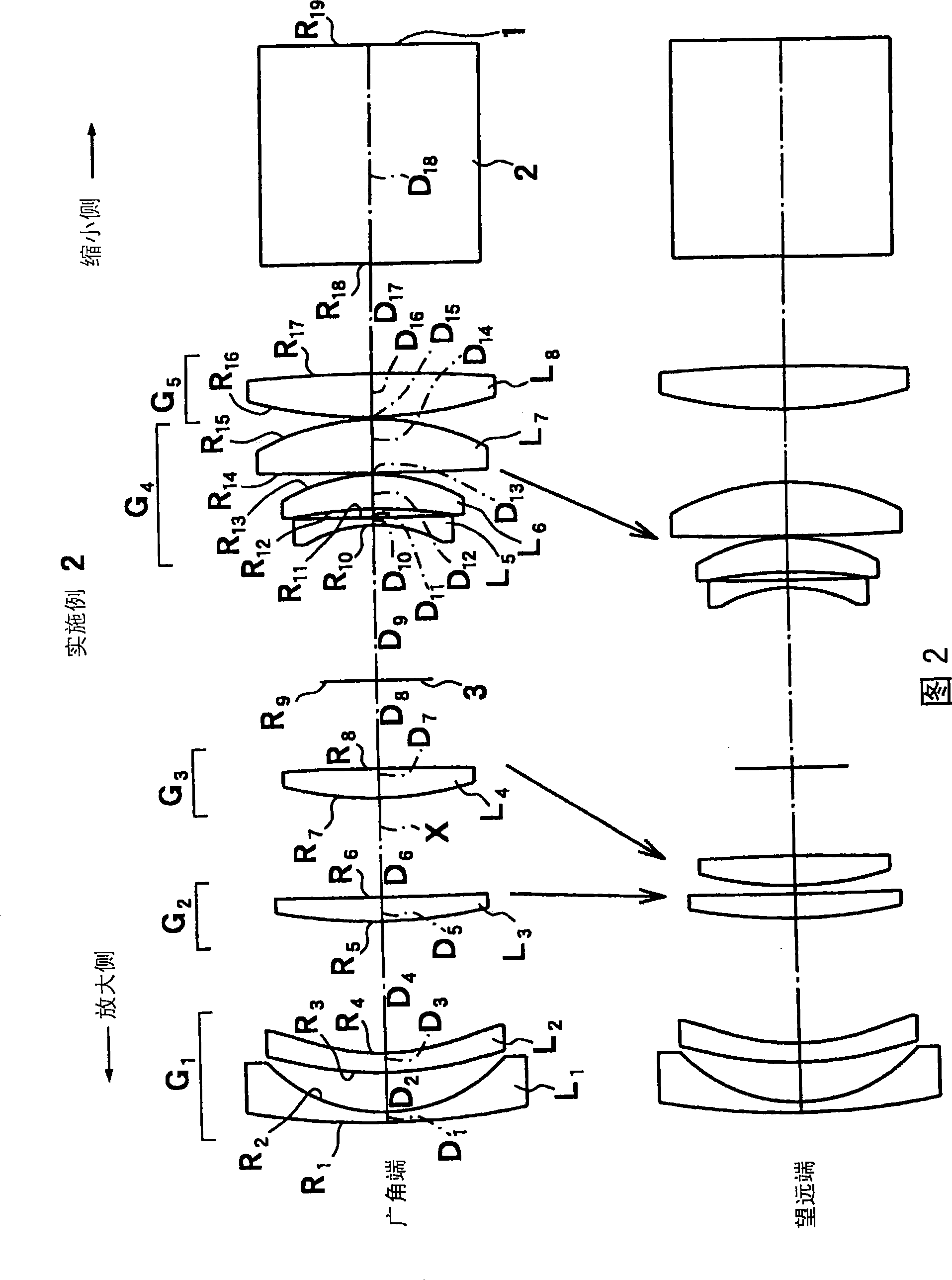
[0147] FIG. 2 shows a schematic configuration of a projection zoom lens according to the second embodiment. Although the projection type zoom lens according to the second embodiment has substantially the same structure as that of the first embodiment, the main difference is that the second lens group G is formed. 2 3rd lens L 3 Consists of a positive meniscus lens with the convex surface facing the magnification side; constitutes the 4th lens group G 4 7th lens L 7 It is made of biconvex lenses; furthermore, when zooming, the second lens group G moves from the wide-angle end to the telephoto end. 2 , the third lens group G 3 and the 4th lens group G 4 Move to the enlarged side independently of each other.
[0148] Table 2 shows the radius of curvature R of each lens surface, the center thickness of each lens, the air space D between each lens, the refractive index Nd and the Abbe number vd of each lens with respect to the d-line in Example 2.
[0149] Moreover, in the mi...
Embodiment 3
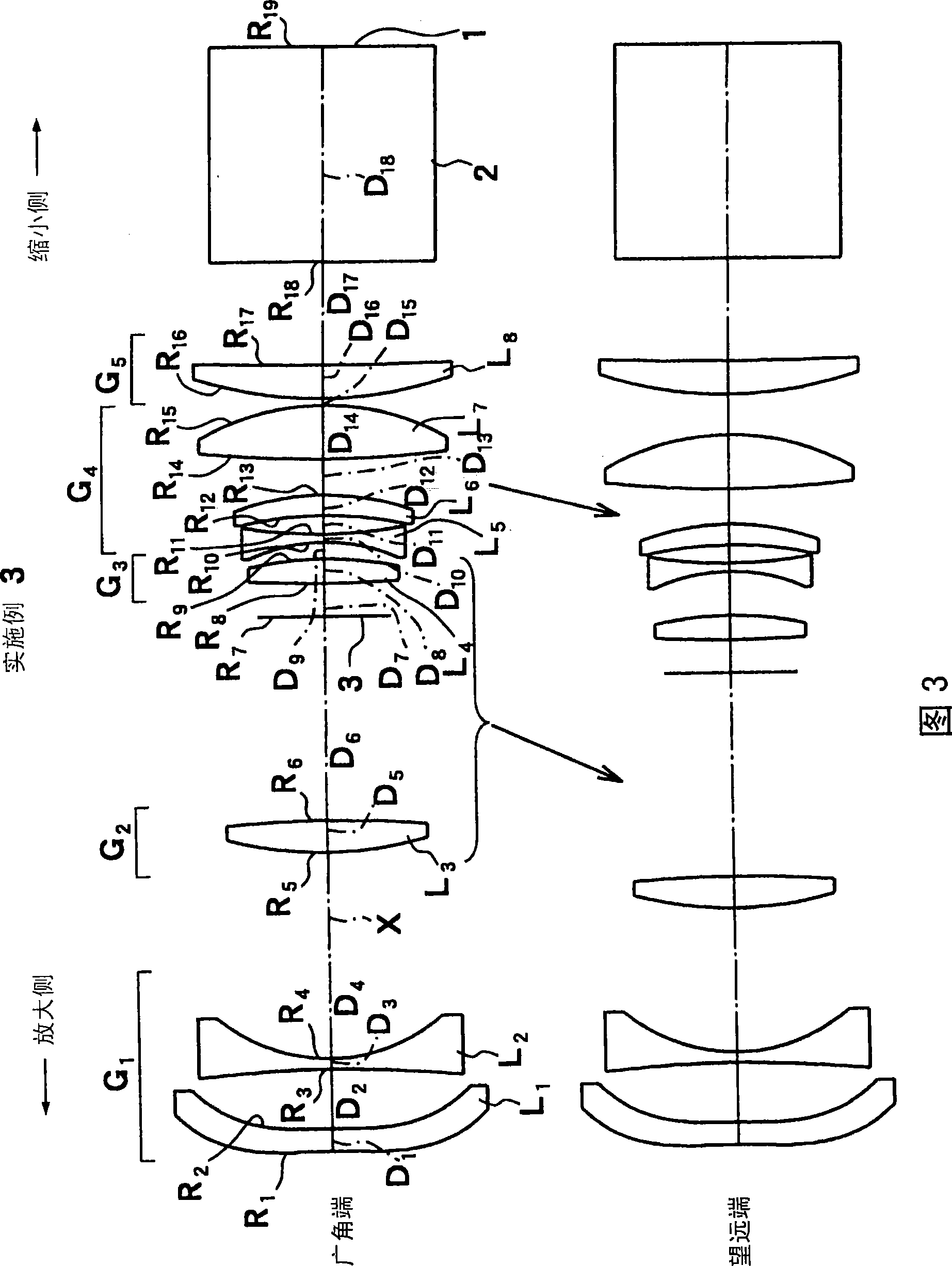
[0191] FIG. 3 shows a schematic configuration of a projection zoom lens according to the third embodiment. The projection type zoom lens according to the third embodiment has substantially the same configuration as that of the first embodiment, but the main difference is that the first lens group G 1 The first lens L made of a plastic aspheric lens with aspheric surfaces on both sides 1 With the second lens L made of biconcave lens 2 Composition; Composition of the 4th lens group G 4 7th lens L 7 Composed of biconvex lenses, constituting the 5th lens group G 5 The 8th lens L 8 Consists of a positive meniscus lens with a convex surface facing the magnification side. Further, although the aperture stop 3 is connected with the third lens group G 3 The configuration of the integral movement method is the same as that of Embodiment 1, but it is arranged in the third lens group G 3 and the second lens group G 2 are different between. Moreover, in the second lens group G 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com