Method for removing larva toxin of masson pine caterpillar
A technology of masson pine and larvae, applied in the fields of application, food preparation, food science, etc., to achieve the effect of low cost, easy operation, and simple removal process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
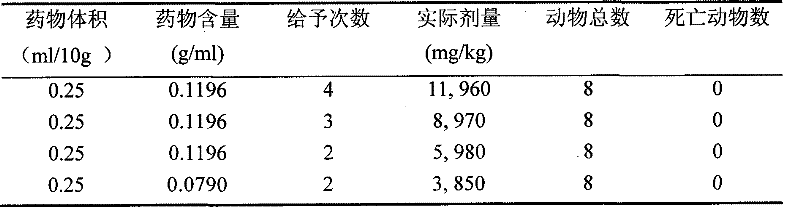
[0012] Take 5kg masson pine larvae and freeze them at -10°C for 5 hours, take them out, add 30L of 0.8% dilute salt solution, and soak them at room temperature (25-30°C) for 4 hours. The soaked larvae are obtained by filtration, and the filtrate can be used to develop insect toxin drugs. The soaked larvae are further fully treated at 70°C for 7 hours. Detection of toxin toxicity: using the conventional mouse acute toxicity test method, the LD was measured by oral administration of drugs to mice several times within 1 day 50 It is 11,960mg / kg (see Table 1), which belongs to the non-toxic standard.
[0013] Table 1 Acute toxicity test results of treated pine caterpillar larvae in mice
[0014]
[0015] (The actual maximum dosage is 11,960mg / kg)
Embodiment 2
[0017] Take 5kg masson pine larvae and freeze them at -10°C for 5 hours, take them out, add 35L of 1.0% dilute salt solution, and soak them at room temperature (25-30°C) for 5 hours. The soaked larvae are obtained by filtration, and the filtrate can be used to develop insect toxin drugs. The soaked larvae are further fully treated at 75°C for 7 hours. Detection of toxin toxicity: using the conventional mouse acute toxicity test method, the LD was measured by oral administration of drugs to mice several times within 1 day 50 It is 11,960mg / kg (see Table 1), which belongs to the non-toxic standard.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Take 5 kg of masson pine larvae and place them in a closed container, inject ether to kill them, take them out, add 40 L of 1.2% dilute salt solution, and soak them at room temperature (25-30° C.) for 4 hours. The soaked larvae are obtained by filtration, and the filtrate can be used to develop insect toxin drugs. The soaked larvae can be further fully treated at 80° C. for 7 hours. Detection of toxin toxicity: using the conventional mouse acute toxicity test method, the LD was measured by oral administration of drugs to mice several times within 1 day 50 It is 11,960mg / kg (see Table 1), which belongs to the non-toxic standard.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com