Self-starting, permanent-magnet synchronous
A technology of synchronous motors and electric motors, applied in the field of electric motors, can solve problems such as high production costs, and achieve the effects of simple manufacturing, protection from corrosion, and high synchronous torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
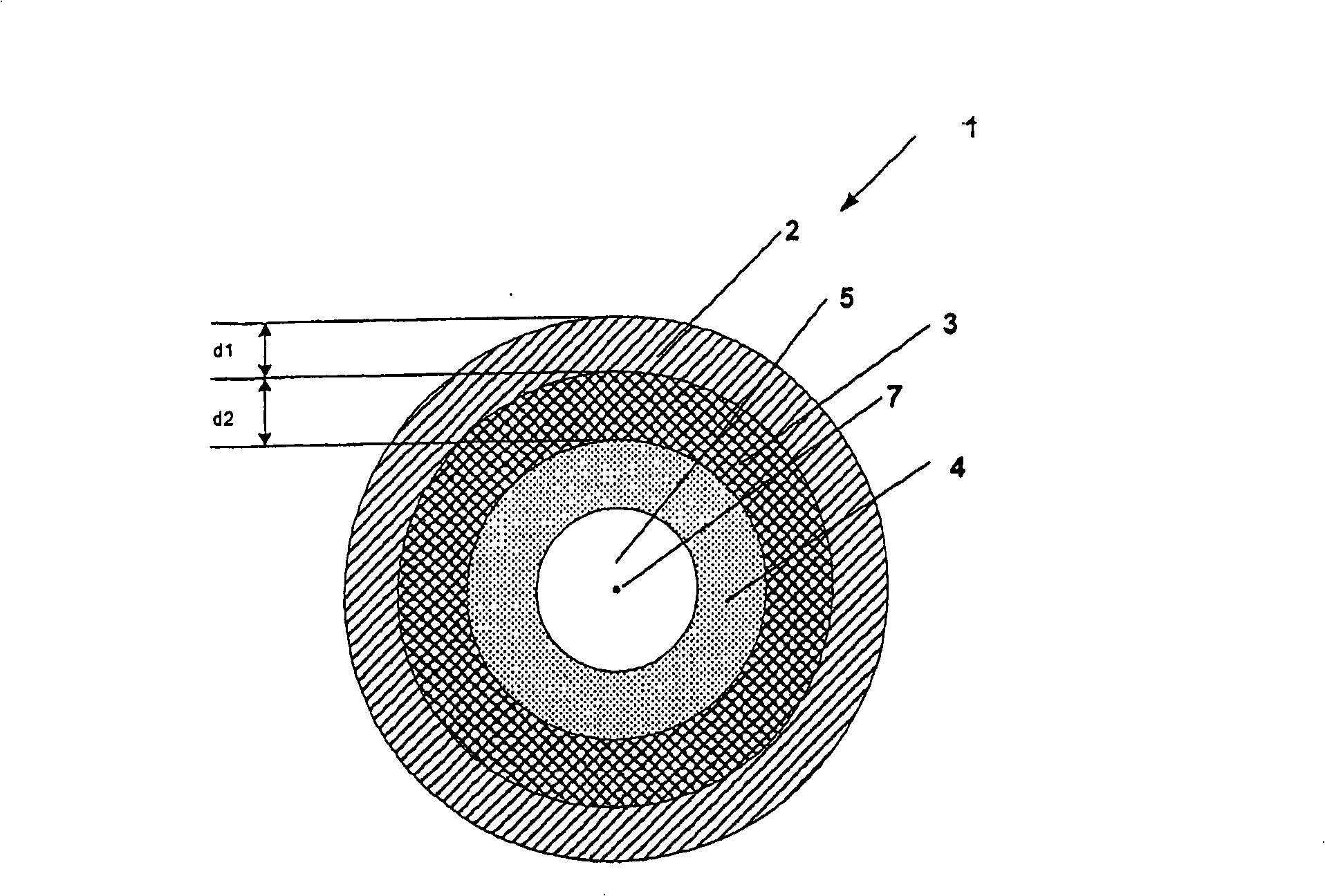
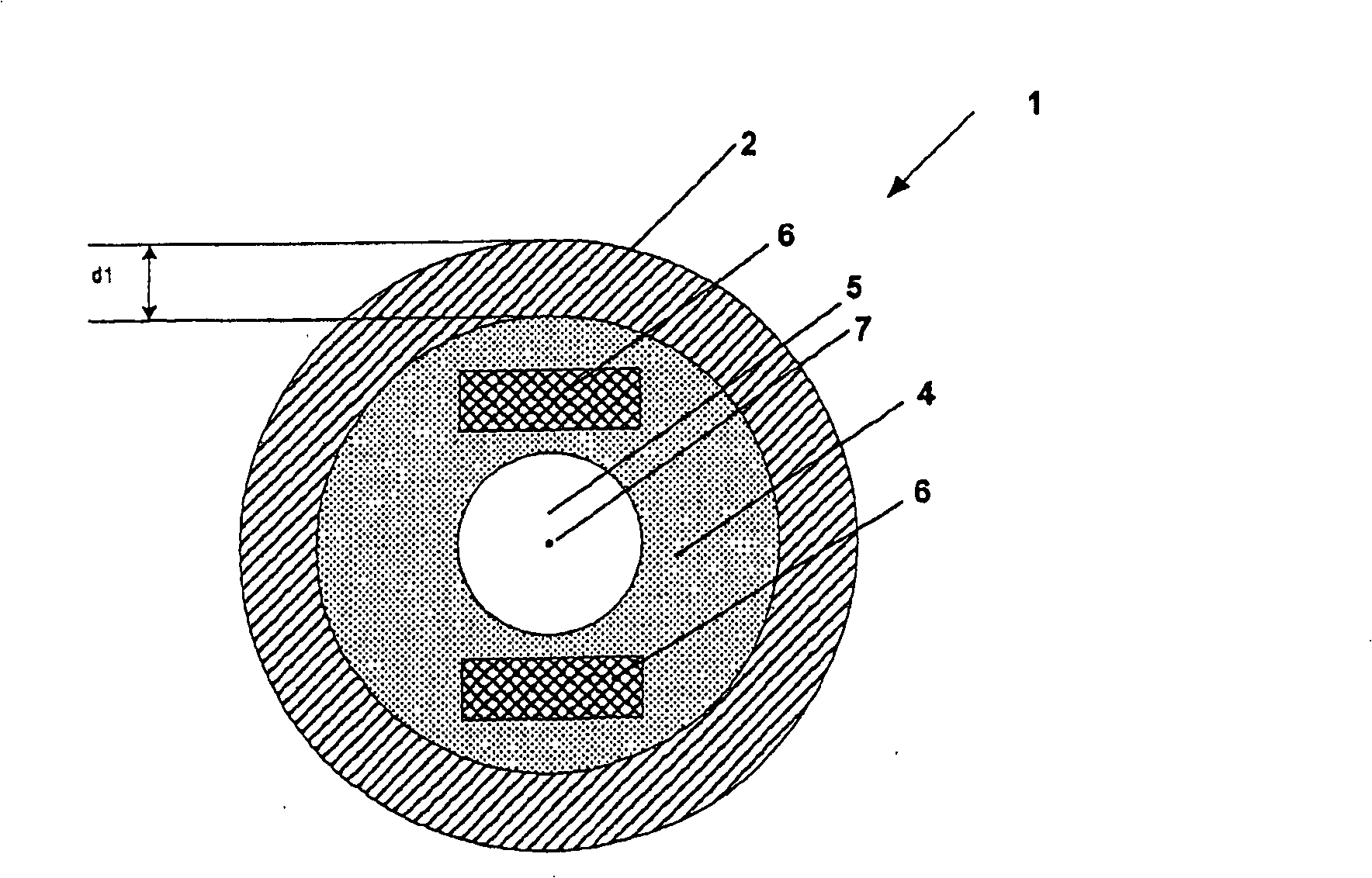
[0032] figure 1 A cross-sectional view of a rotor 1 according to the invention is shown. The rotor 1 has a rotor shaft 5 and an electrically conductive cage winding 2 arranged coaxially to the rotor axis 7 and designed as a solid hollow cylinder. Furthermore, the rotor 1 has a permanent magnet 3 which is likewise designed in the form of a solid hollow cylinder and extends coaxially along at least part of the cage winding 2 . The hollow cylindrical permanent magnet has a thickness d2.
[0033] The permanent magnet 3 is located inside the cage winding 2 and bears against the inner side of the cage winding 2 . The cage winding 2 has a thickness d1 which is preferably between 5% and 30%, in particular between 10% and 20%, of the total radius of the rotor 1 . In contrast, the permanent magnets 3 have an axial thickness d2 of between 10% and 40% of the total radius of the rotor 1 . Here, hollow cylindrical permanent magnets made of samarium-cobalt compounds or neodymium-iron-bor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com