Surface plasmon resonance sensor and chip used for the same
一种表面等离子体、共振传感器的技术,应用在用于传感的纳米技术、仪器、科学仪器等方向,能够解决不能实现低成本、制造生产能力低、难以做到批量生产等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0102] 9 is a schematic diagram showing a basic configuration of a localized surface plasmon resonance sensor (hereinafter referred to as a localized SPR sensor) 31 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The local presence SPR sensor 31 consists of a light source 32 like a halogen lamp, an optical fiber 33, a collimating lens 34, a collimating plate 35 with pinholes, a polarizing plate 36, a beam splitter 37 (also called a half mirror), an objective lens 38 , a flow chamber 48 , a beam splitter 40 , a photodetector 41 , a data processing device 42 and a syringe pump 43 are constituted.
[0103] The light source 32 is preferably a light source that irradiates white light like a halogen lamp, but may be any light source that includes light in the wavelength range used for measurement. The light L emitted from the light source 32 is guided to the collimator lens 34 through the optical fiber 33 . The collimator lens 34 collimates the light L emitted from the tip of t...
Embodiment approach 2
[0178] The sensor chip 39 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention will be described. The sensor chip 39 according to the second embodiment is characterized in that the center portion of the bottom surface of the recessed portion 57 swells toward the opening side.
[0179] Looking specifically at the electric field distribution generated inside the concave portion 57 shown in FIG. 17 , it can be seen that the electric field intensity is not so large near the bottom of the concave portion 57 . This is because the electric power lines in the recessed portion 57 are bulged on the opening side. Therefore, if the bottom surface of the recessed portion 57 is a flat surface as in the first embodiment, the Figure 32 As shown in (a), even if a specific substance such as protein is bound to the bottom surface of the recessed portion 57, since the specific substance is located in a region with a low electric field intensity, the change in refractive index due to the specific ...
Embodiment approach 3
[0191] Next, the concave structure of the sensor chip according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention will be described. In the sensor chip of the third embodiment, the recessed portion 57 is not extended from the end of the measurement region 44 in a groove shape to the end as in the first embodiment, but the recessed portion 57 is divided in the longitudinal direction as shown in FIG. 40 . multiple parts. As a result, the concave portions 57 have a substantially rectangular concave structure and are arranged in two directions orthogonal to each other.
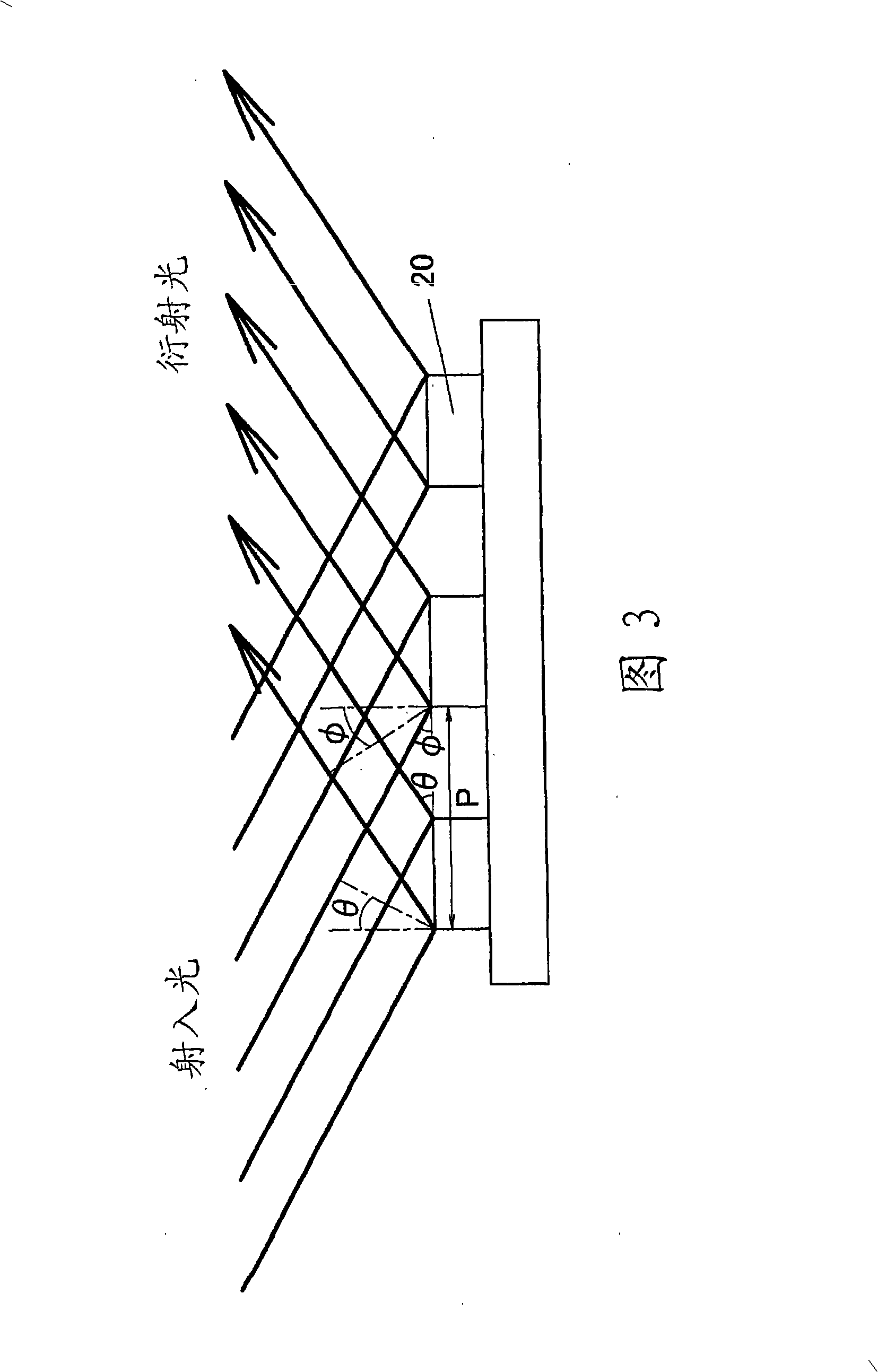
[0192] The arrangement method of the recesses 57 may be a rectangular arrangement (a lattice arrangement method) or a triangular (delta) arrangement (a staggered arrangement method as shown in FIG. 40(b) ). Here, the case of the delta arrangement will be described. The concave portions 57 are arranged at a constant pitch P in a direction parallel to the polarization plane of the incident light, as in the first embodiment,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com