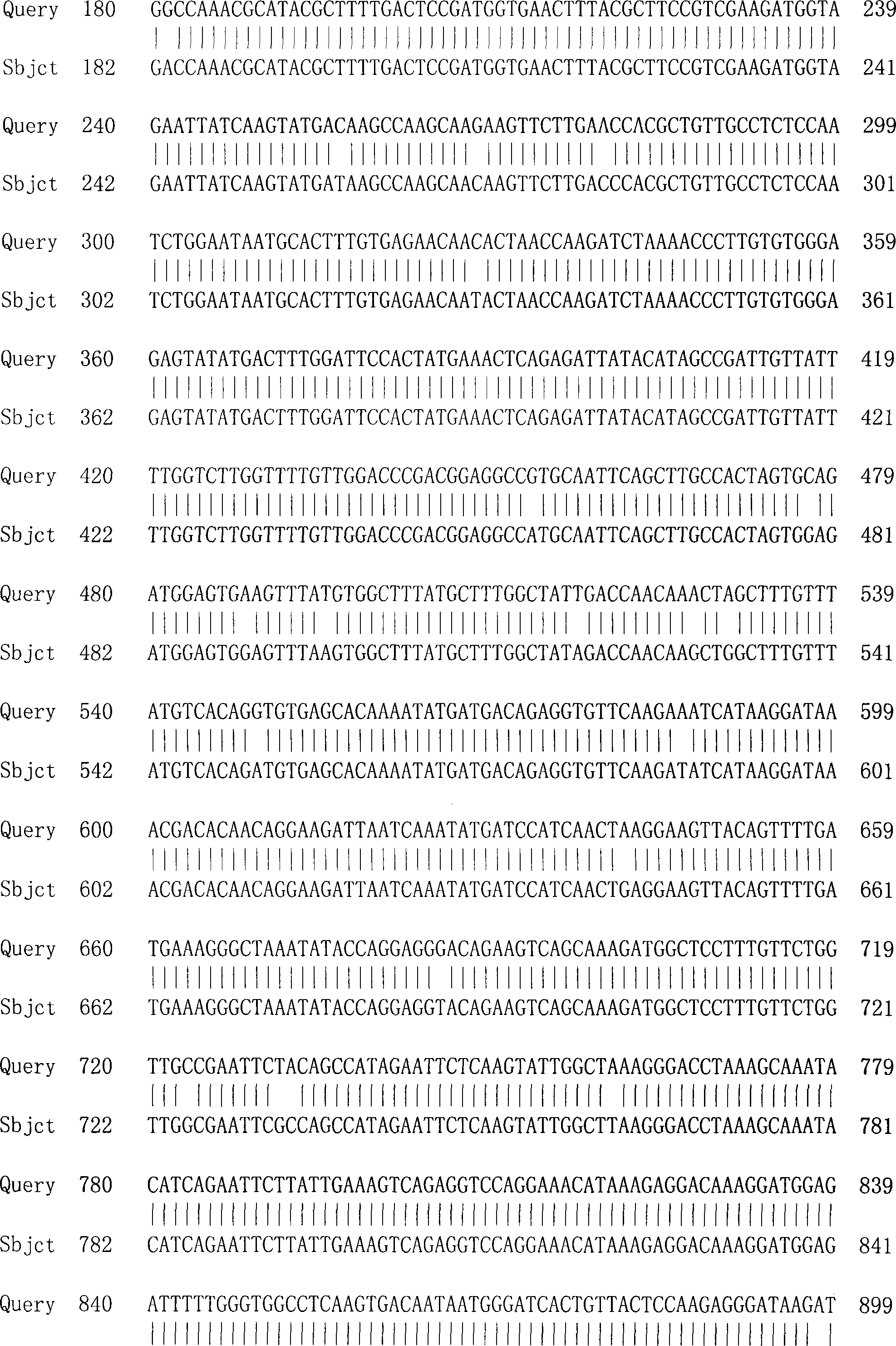Japan snakeroot strictosidine synthase gene and its coding protein and application
A technology of isosidine and snakeroot, applied to the isosidine synthase gene and its encoded protein and its application field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The experimental methods without specific conditions in the following examples usually follow conventional conditions, such as the conditions described in Sambrook and other molecular cloning: Laboratory Manual (New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989), or as recommended by the manufacturer conditions of. Example 1 (Cloning of the isocarin synthase gene of Snakegrass japonica)
[0035] 1. Organization separation (isolation)
[0036] The Snakeroot plant originated from Fujian, and the young roots were taken and immediately placed in liquid nitrogen for cryopreservation.
[0037] 2. RNA isolation (RNA isolation)
[0038] Take part of the tissue and grind it with a mortar, add it to a 1.5mL EP tube containing lysate, shake it enough, and then move it into a glass homogenizer. After homogenization, transfer to a 1.5mL EP tube to extract total RNA (TRIzol Reagents, GIBCO BRL, USA). Use formaldehyde denaturing gel electrophoresis to identify the total RNA quality, and...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 (Sequence information and homology analysis of Japanese snakeroot isocarin synthase gene)
[0049] The length of the full-length cDNA of the new snakeroot isocarin synthase of the present invention is 1258 bp, and the detailed sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, wherein the open reading frame is located at nucleotides 65-1126. According to the full-length cDNA, the amino acid sequence of Snakegrass isoflavin synthase was deduced, with a total of 353 amino acid residues, a molecular weight of 39.3KD, and a pI of 5.7. The detailed sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2.
[0050] The full-length cDNA sequence and its encoded protein of Snakegrass isoflavin synthase and its encoded protein were carried out in the Non-redundant GenBank+EMBL+DDBJ+PDB and Non-redundant GenBank CDStranslations+PDB+SwissProt+Superdate+PIR database using BLAST program Nucleotide and protein homology search revealed that it has 95% homology with the snakeroot STR gene (GenBank Accession No.AB060341...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Results: In the comparison of 353 amino acids, the two have 94% identity and 96% similarity, respectively. Example 3 (Prokaryotic expression and purification of Japanese snakeroot isocarin synthase or polypeptide in Escherichia coli)
[0062] In this example, a full-length Japanese snakeroot OjSTR coding sequence or fragment was constructed into a commercial protein fusion expression vector to express and purify the recombinant protein.
[0063] 1. Construction of prokaryotic expression vector and transformation of Escherichia coli
[0064] According to the nucleotide sequence of Snakeroot OjSTR, design primers to amplify the protein coding region, and introduce restriction endonuclease sites on the positive and negative primers (this depends on the selected pET32a(+) vector) , In order to construct an expression vector. Using the amplified product obtained in Example 1 as a template, after PCR amplification, the Japanese snakeroot OjSTR gene was cloned into the pET32a(+) v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com