Method for improving zero-valent iron dechromisation catalytic reduction liveness in neutrality condition
A zero-valent iron and ferrous sulfate technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, reduced water/sewage treatment, photography technology, etc., can solve problems such as unsatisfactory and low catalytic reduction activity, and achieve convenient operation and good application prospects. , the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
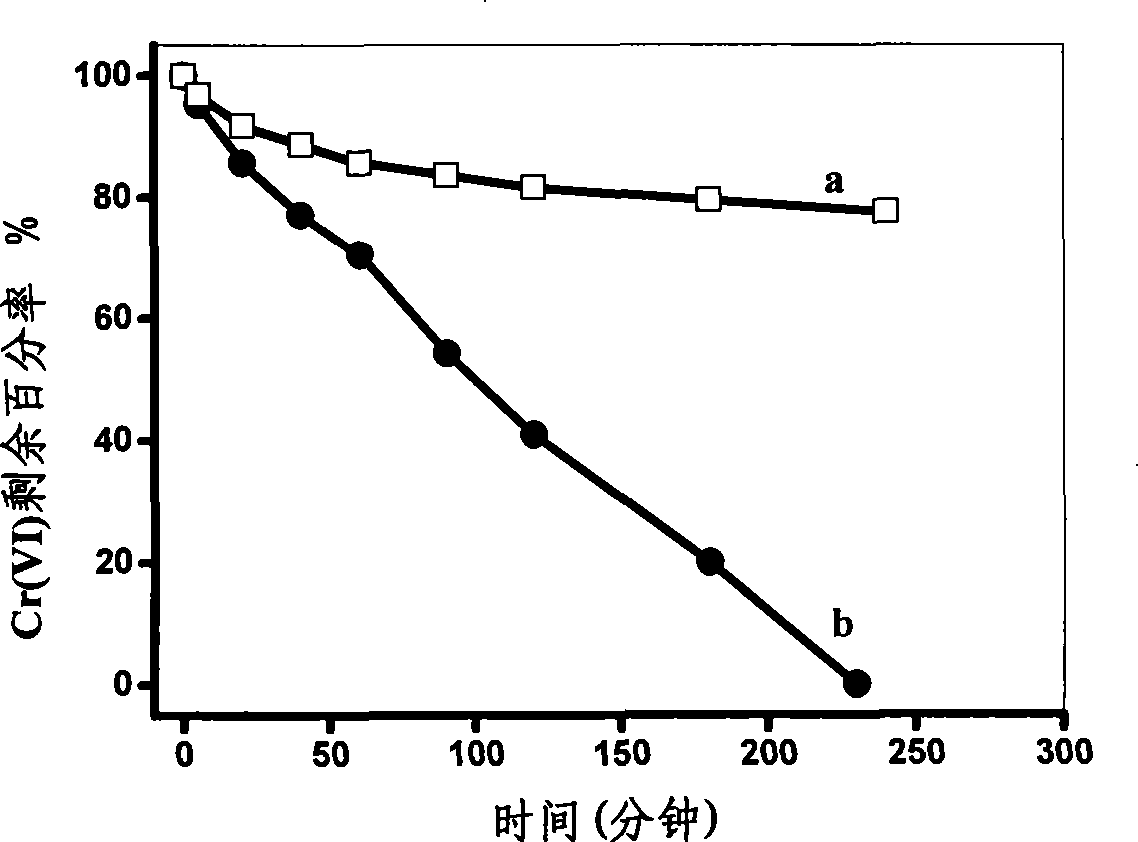
[0021] Prepare the electrolyte containing 0.1mol / L ferrous sulfate, 0.3mol / L boric acid, 0.4mol / L ammonium sulfate, 0.003mol / L ascorbic acid, 0.003mol / L saccharin, 0.002mol / L sodium lauryl sulfate, The pretreated titanium sheet was used as the working electrode, using 10mA / cm 2 current electrodeposition for 60 min. Add 20 mg of the zero-valent iron obtained into a solution with a Cr(VI) concentration of 10 mg / L, adjust the pH of the solution to 7.0, analyze the catalytic reduction activity of the zero-valent iron, and do not add ascorbic acid, saccharin and lauryl sulfate with other conditions the same The zero-valent iron obtained by electrodeposition in the electrolyte of sodium was used for comparison, and the results are shown in figure 1 .
Embodiment 2
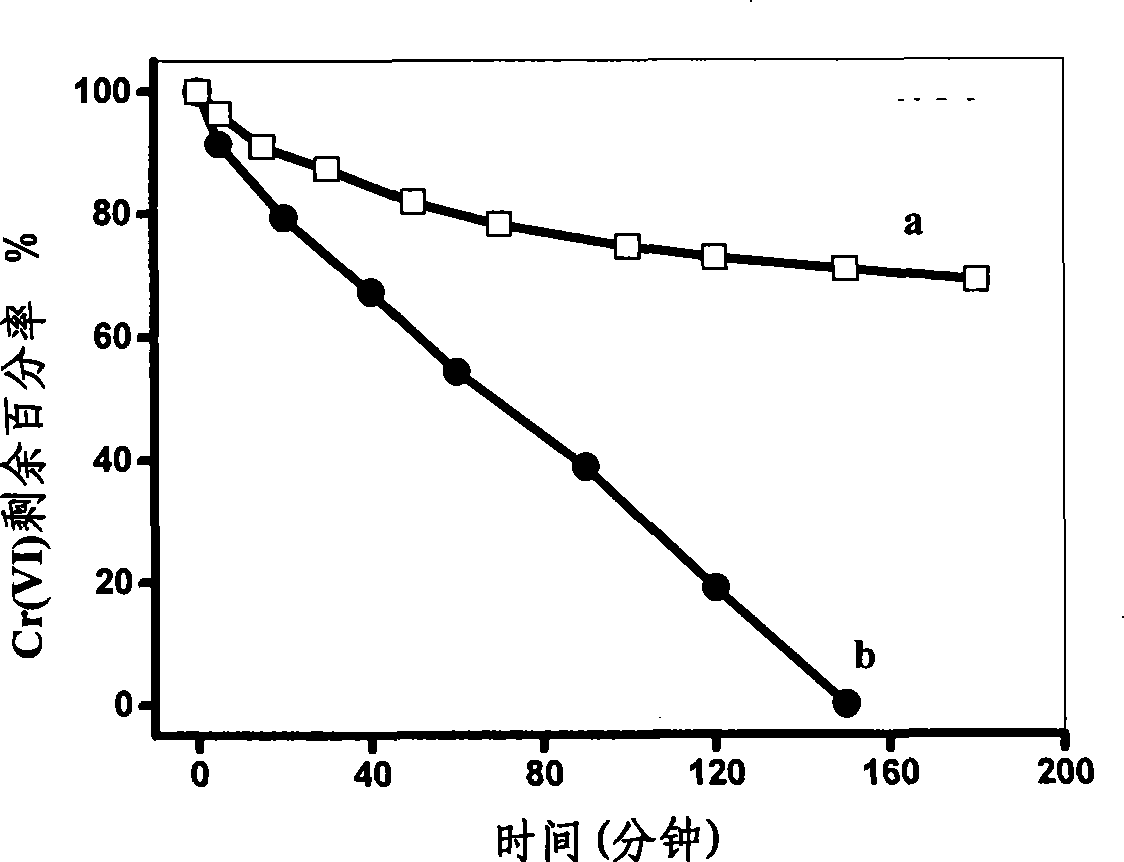
[0023] Prepare the electrolyte containing 0.1mol / L ferrous sulfate, 0.3mol / L boric acid, 0.4mol / L ammonium sulfate, 0.003mol / L ascorbic acid, 0.003mol / L saccharin, 0.002mol / L sodium lauryl sulfate, The pretreated titanium sheet was used as the working electrode, using 20mA / cm 2 current electrodeposition for 30 min. Add 20 mg of the obtained zero-valent iron into a solution with a Cr(VI) concentration of 5 mg / L, adjust the pH of the solution to 8.0, analyze the catalytic reduction activity of the zero-valent iron, and do not add ascorbic acid, saccharin and lauryl sulfate with other conditions the same The zero-valent iron obtained by electrodeposition in the electrolyte of sodium was used for comparison, and the results are shown in figure 2 .
Embodiment 3
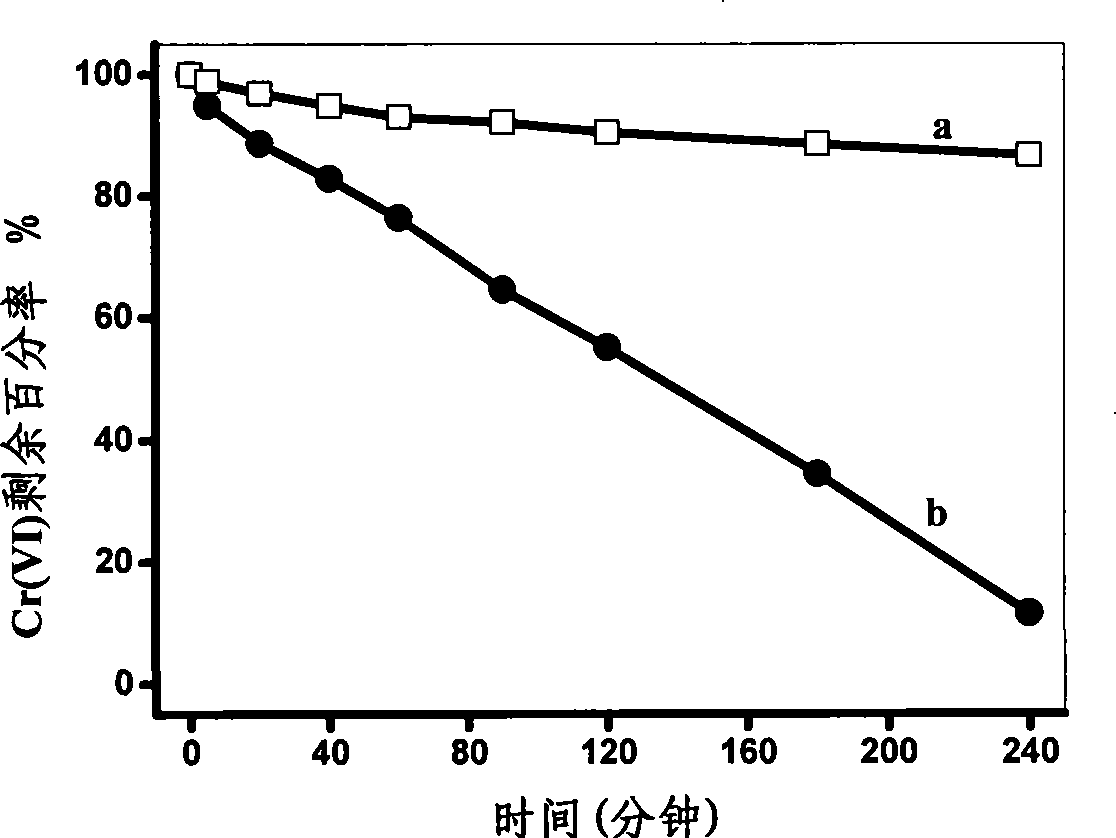
[0025] Prepare an electrolyte containing 0.2mol / L ferrous sulfate, 0.4mol / L boric acid, 0.5mol / L ammonium sulfate, 0.004mol / L ascorbic acid, 0.004mo / L saccharin, and 0.003mol / L sodium lauryl sulfate , with the pretreated titanium sheet as the working electrode, using 10mA / cm 2 current electrodeposition for 60 min. Add 30 mg of zero-valent iron obtained into a solution with a Cr(VI) concentration of 20 mg / L, adjust the pH of the solution to 6.5, analyze the catalytic reduction activity of zero-valent iron, and do not add ascorbic acid, saccharin and dodecylsulfuric acid with other conditions the same The zero-valent iron obtained by electrodeposition in the electrolyte of sodium was used for comparison, and the results are shown in image 3 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com