Improved immunoassay methods
A technology of subjects and antibodies, applied in the field of detection of antibodies and biomarkers, can solve problems such as intolerant changes in the amount of antibodies
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0136] Example 1 - General Protocol for Titrating Antigens in Autoantibody Assays
[0137] Samples of (biotinylated) tumor marker antigens can be prepared by recombinant expression, following a method similar to that described in WO99 / 58978.
[0138] Briefly, the cDNA encoding the marker antigen of interest was cloned into the pET21 vector (Invitrogen) that had been modified to encode a biotin tag and a 6x histidine tag to aid in the purification of the expressed protein. The resulting clones were cultured (in inclusion bodies) in suitable bacterial host cells, the bacteria were lysed and denatured, and the expressed antigen was recovered by passage through a nickel chelate affinity column (Hi-trap, available from Amersham, following the manufacturer's protocol). The expressed antigen was refolded by dialysis in an appropriate buffer and the yield of expressed antigen was assessed by SDS-PAGE, western blot and ELISA and quantified before storage.
[0139] Negative control VO...
Embodiment 2
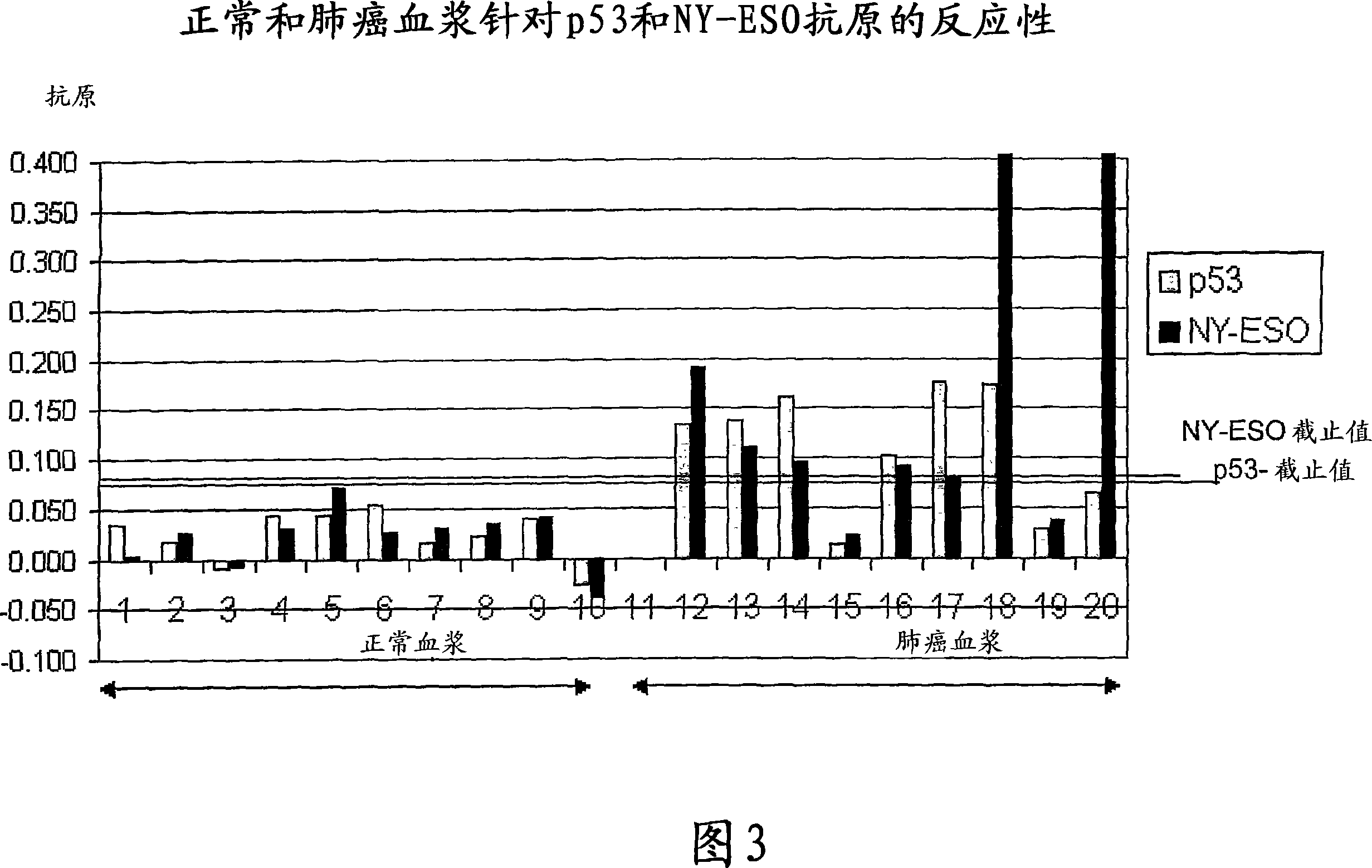
[0162] Example 2, detection of autoantibodies in primary breast cancer
[0163] The following data were obtained from a pilot study evaluating the sensitivity and reproducibility of a titrated autoantibody assay in primary breast cancer (PBC). The study included serum samples from 17 women with no evidence of cancer as well as preoperative serum samples from 20 women with primary breast cancer. Normal and cancer samples were age-matched. One normal sample and three cancer samples could only be removed because they showed evidence of an anti-biotin antibody response and therefore could not be assessed using the current assay format. Approximately 10% of the population is thought to develop an immune response against biotin.
[0164] The assay was carried out according to the procedure given in Example 1 using the antigens p53, c-myc, NY-ESO-1 and BRCA2.
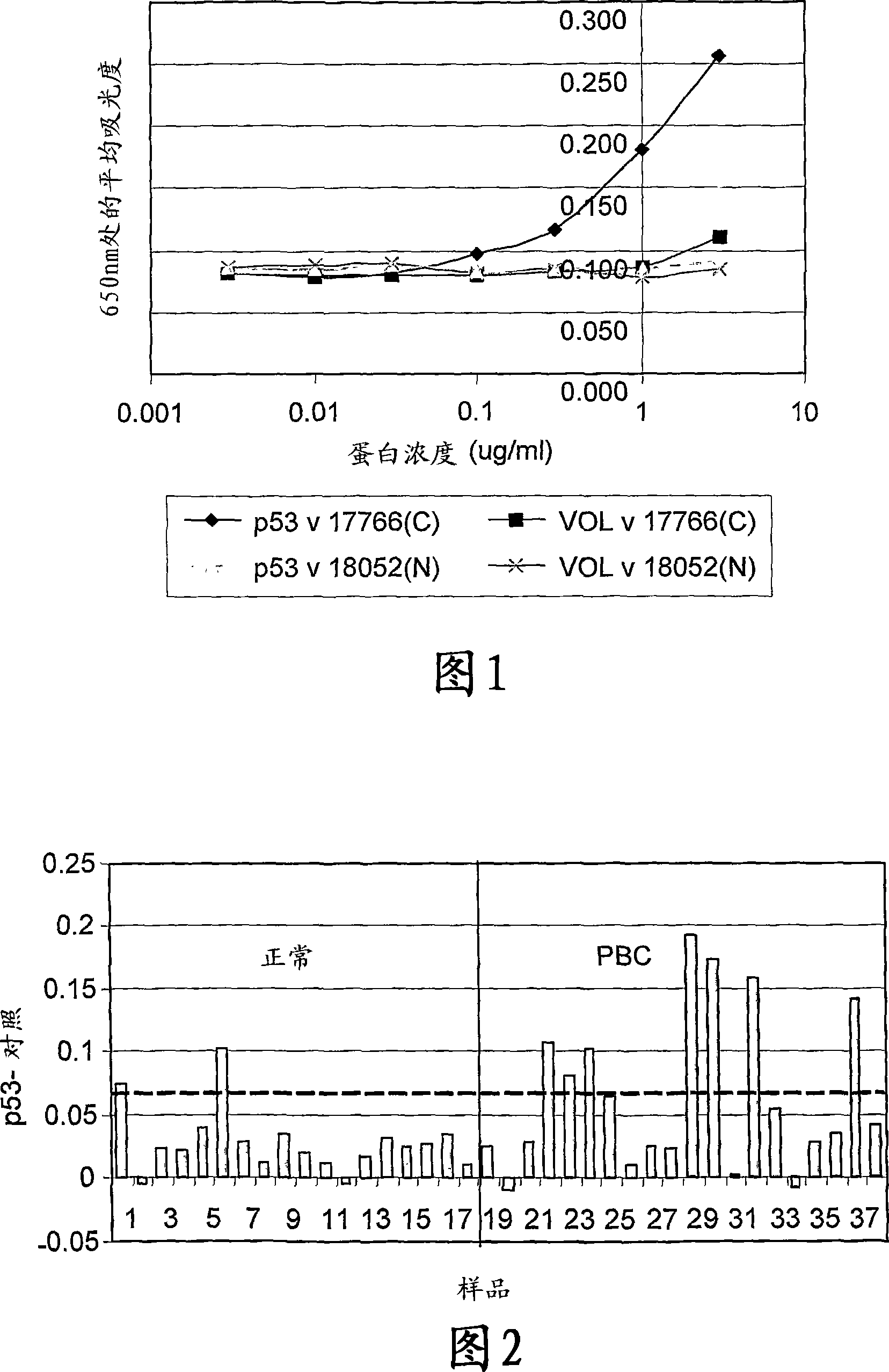
[0165] Figure 1 gives an example of the curve obtained when this antigen titration assay was used to measure p53 autoan...
Embodiment 3
[0173] Example 3, Determination of Autoantibodies in Lung Cancer
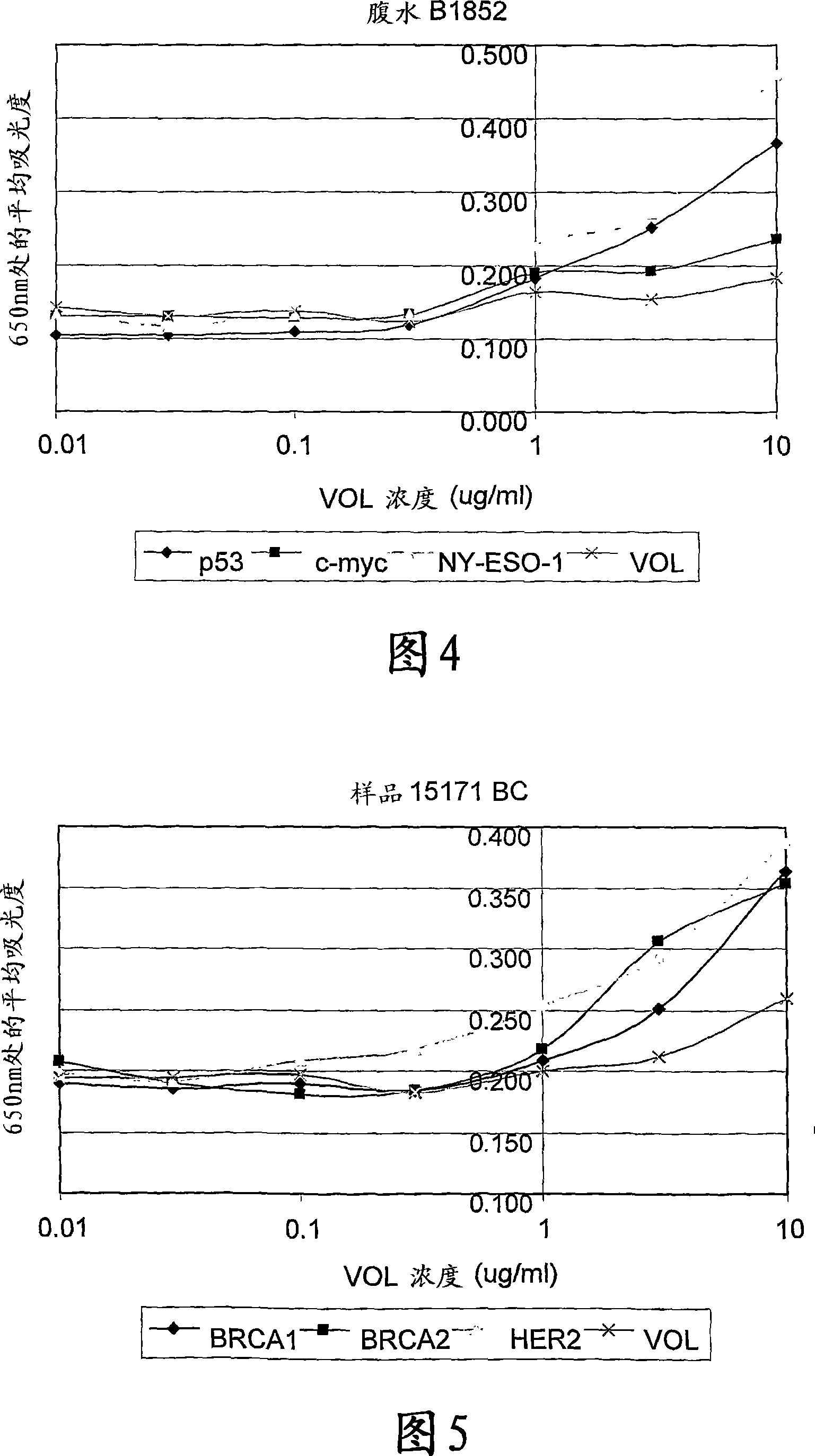
[0174] Analysis of autoantibody responses to 2 antigens (p53 and NY-ESO) in a pilot lung cancer study (10 normal and 9 lung cancer plasma) showed a detection rate of 78% (Figure 3).
[0175] The assay was performed according to the general protocol in Example 1 except that plasma samples were used instead of serum.
[0176] Positive patient samples exhibited a reverse sigmoid titration curve similar to that shown in Figure 1. Figure 3 shows a comparison of p53 and NY-ESO autoantibody levels in normal individuals and lung cancer patients measured using an antigen titration assay. The normal cutoff was calculated as the mean plus 2 standard deviations for the normal population.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com