Method of preparing a carbonaceous material for an emitter of an electron emission device
An electron emission device, carbide technology, applied in the direction of the cold cathode of the discharge tube, the main electrode of the discharge tube, etc., can solve the problems of large field enhancement factor β, short life, poor uniformity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] First, 100 g of granular α-SiC with an average particle diameter of 0.7 μm was prepared as a carbon precursor in a high-temperature furnace composed of a graphite reaction chamber, a transformer, and the like. At a rate of 0.5L per minute, the Cl 2The gas was applied to a high temperature furnace maintained at 1000°C for 7 hours. Then, 30 g of carbide-derived carbon was prepared by extracting silicon from the carbon precursor using a thermochemical reaction.
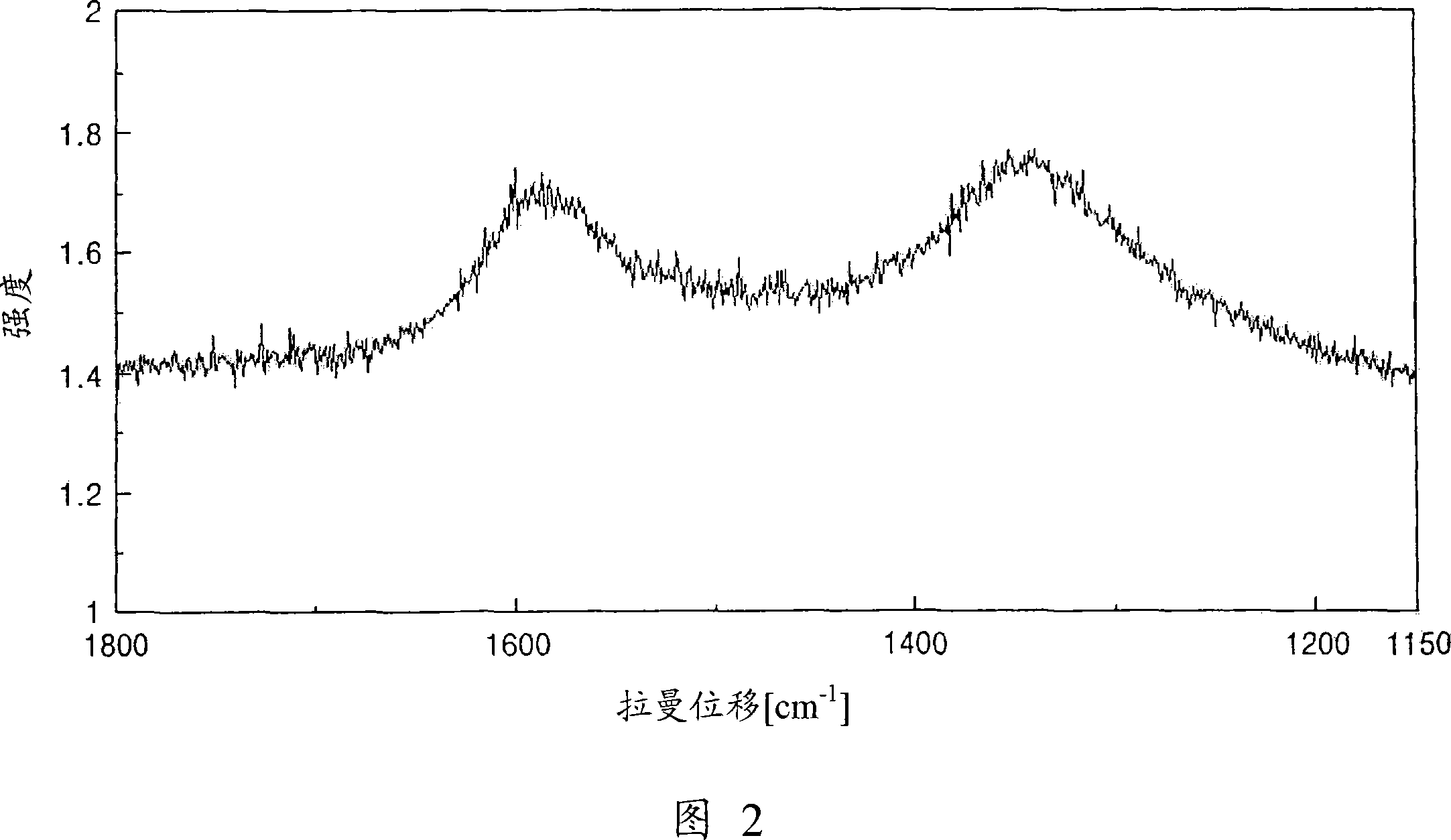
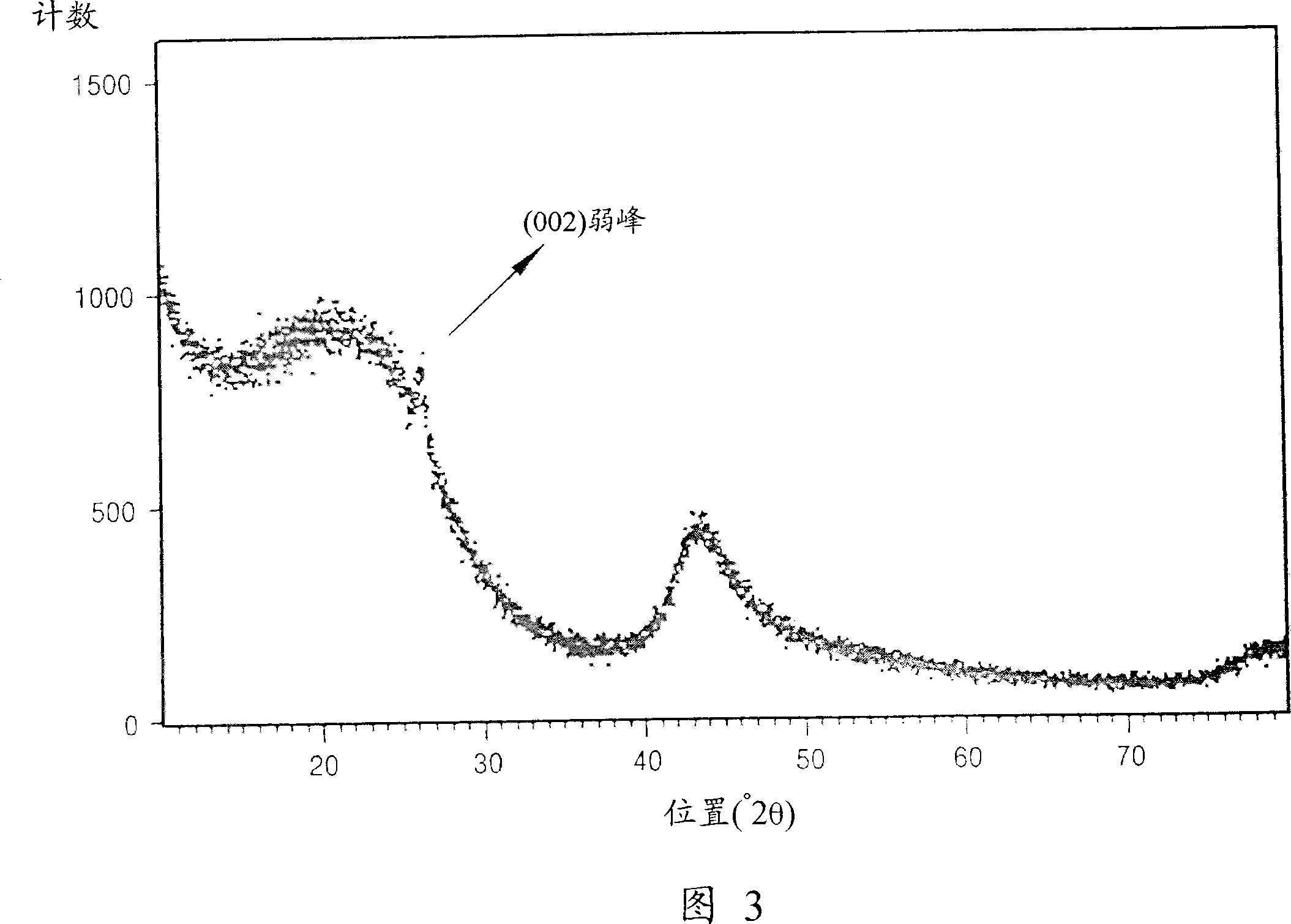
[0066] Carbon from carbides was analyzed using Raman peak analysis, X-ray diffraction and electron microscopy. I G / I D The ratio is 0.5 to 1. A weak peak of the graphite (002) plane can be observed at 2θ=25°. The electron diffraction pattern is a halo-pattern representing amorphous carbon. In addition, according to the method of Brunauer, Emmett and Teller (BET method), the specific surface area of the carbide-derived carbon synthesized by this method is 1000 to 1100 m 2 / g.
Embodiment 2
[0068] 13 g of carbide-derived carbon were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that 100 g of granular ZrC having an average particle diameter of 3 μm was used as a starting carbide compound, and heat-treated at 600° C. for 5 hours. Carbon derived from carbides was analyzed using Raman peak analysis. I G / I D The ratio is 1 to 1.3. Using the X-ray diffraction method, a weak single peak of the graphite (002) plane can be observed at 2θ=25°. In addition, according to the BET method, the specific surface area of the carbide-derived carbon synthesized by this method is 1200m 2 / g.
Embodiment 3
[0070] 25 g of carbide-derived carbon were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that 100 g of granular Al with an average particle size of 3 μm was used 4 C 3 , as the starting carbide compound, and heat-treated at 700°C for 5 hours. Carbon derived from carbides was analyzed using Raman peak analysis and X-ray diffraction. I G / I D The ratio is 1 to 3.2. A weak singlet of the graphite (002) plane was observed at 2Θ = 25°. Carbon from carbides was analyzed using high resolution TEM. Many graphite stripes can be observed, as shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11. In addition, according to the BET method, the specific surface area of carbide-derived carbon synthesized by this method is 1050 to 1100 m 2 / g.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com