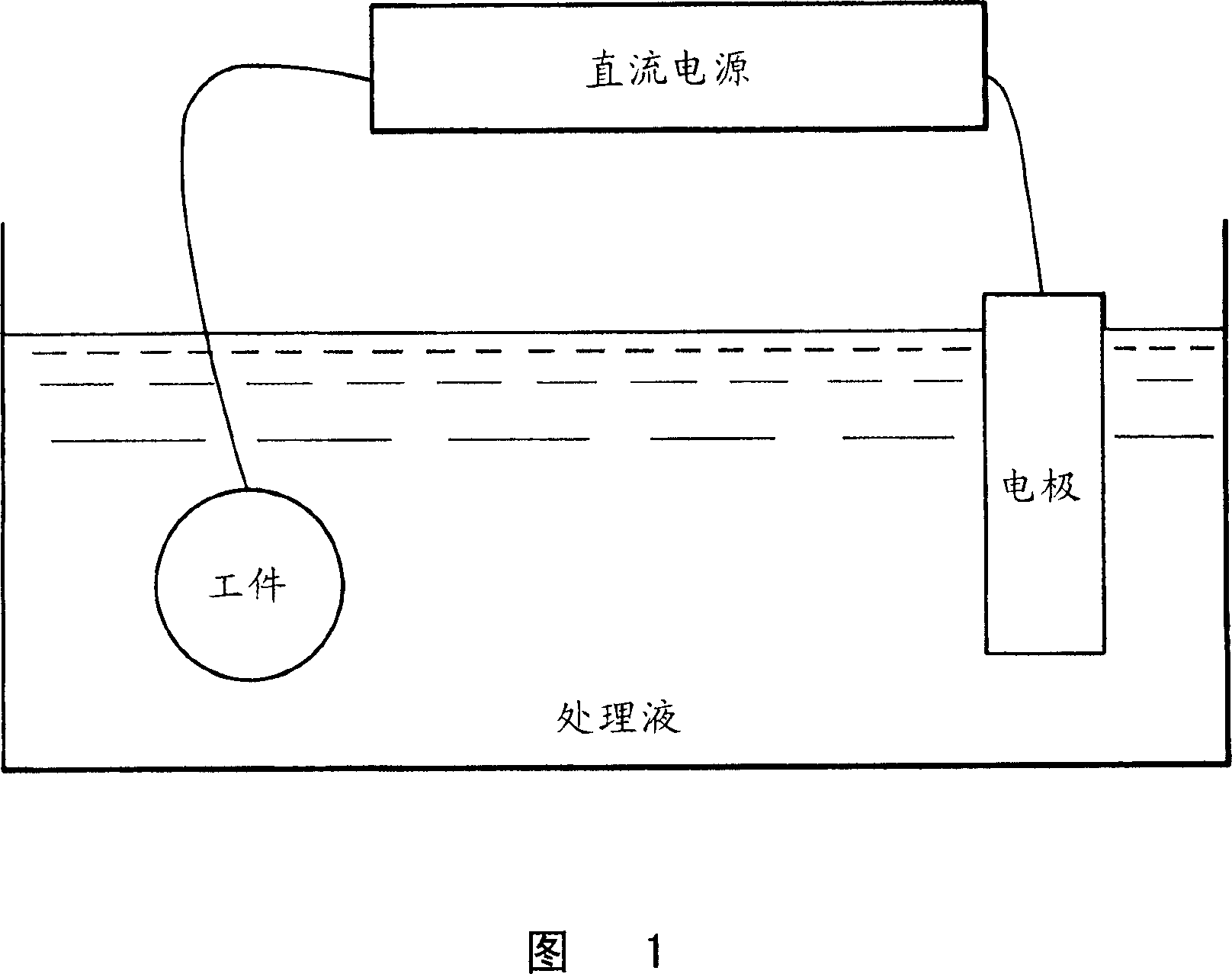
Electrolytic phosphating treatment method and warm or hot forging method
A treatment method, a technique for electrolytic phosphating, applied in the direction of phosphating, etc., capable of solving problems such as the possibility of not teaching or suggesting warm forging or hot forging applications, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-5
[0181] (I. Improvement of electrolytic phosphating treatment efficiency)
[0182] Table 4 shows the treatment liquid conditions in Examples 1-5 and Comparative Example 1.
[0183] Table 4
[0184]
[0185] In the comparative example, the concentrations of phosphoric acid and phosphate ions were higher than 1 / 2 of metal ions (Ni). In this case, the treatment liquid is out of the scope of the treatment liquid of the present invention.
[0186] The electrolytic phosphating treatment was carried out in these treatment solutions, and Table 5 shows the outline.
[0187] table 5
[0188] Trial Products / Test Conditions
[0189] Incidentally, the film thickness was measured by using an electromagnetic film thickness tester (LE-300J, K.K. Ketto Kagaku Kenkyujo).
Embodiment 6-8
[0216] (II. Application in warm forging)
[0217] Automobile engine parts (lower body: material SCM415) are used. Figure 9 shows the situation before warm forging, and Figure 10 shows the situation before and after warm forging.
[0218] Table 9 shows the warm forging process steps in Examples 6-8 and Comparative Example 2. However, water washing and hot water washing are omitted. In warm forging pressing, a solid lubricant (graphite) was sprayed onto a die in Examples 6-8 and Comparative Example 2 under the same conditions.
[0219] Table 9
[0220] steps
Example 6
Example 7
Example 8
Comparative example 2
previous steps
Cold-rolled film with phosphating treatment + lubricant (stearin) formed by lubricating treatment
salt) coil
1
Sandblasting
o
o
o
-(0)
2
skim
o
o
o
-(0)
3
electrolytic phosphating formation site
Reason: Metal + Phosphate
o
o
...
Embodiment 9
[0247] (organic fatty acid salt is used for the embodiment of lubricant)
[0248] Use automotive engine parts (NB cylinder: material SUJ2: Cr-containing alloy steel). Figures 15 and 16 show the shapes of the NB cylinders before and after warm forging, respectively.
[0249] Table 13 shows the warm forging steps of Example 9 and Comparative Example 5.
[0250] Incidentally, the lubricant was sprayed onto the dies under the same conditions in the warm forging of Example 9 and Comparative Example 5.
[0251] Table 13
[0252] steps
Example 9
Comparative example 5
1
Sandblasting
o
-(0)
2
skim
o
-(0)
3
surface adjustment
o
-(0)
4
Electrolytic Phosphating: Metal
+ phosphate
o
-(0)
5
Lubrication treatment
o: sodium stearate, 3-6%: dissolved at 85°C
liquid, 3 minutes
-(0)
6
Heating: 850°C
o
o
7
warm forging
o
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com