Patient identification for point of care diagnostics
A technology for on-site nursing and patient care, applied in the direction of diagnosis, human identification, vaccination and ovulation diagnosis, etc., to achieve the effect of improving reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
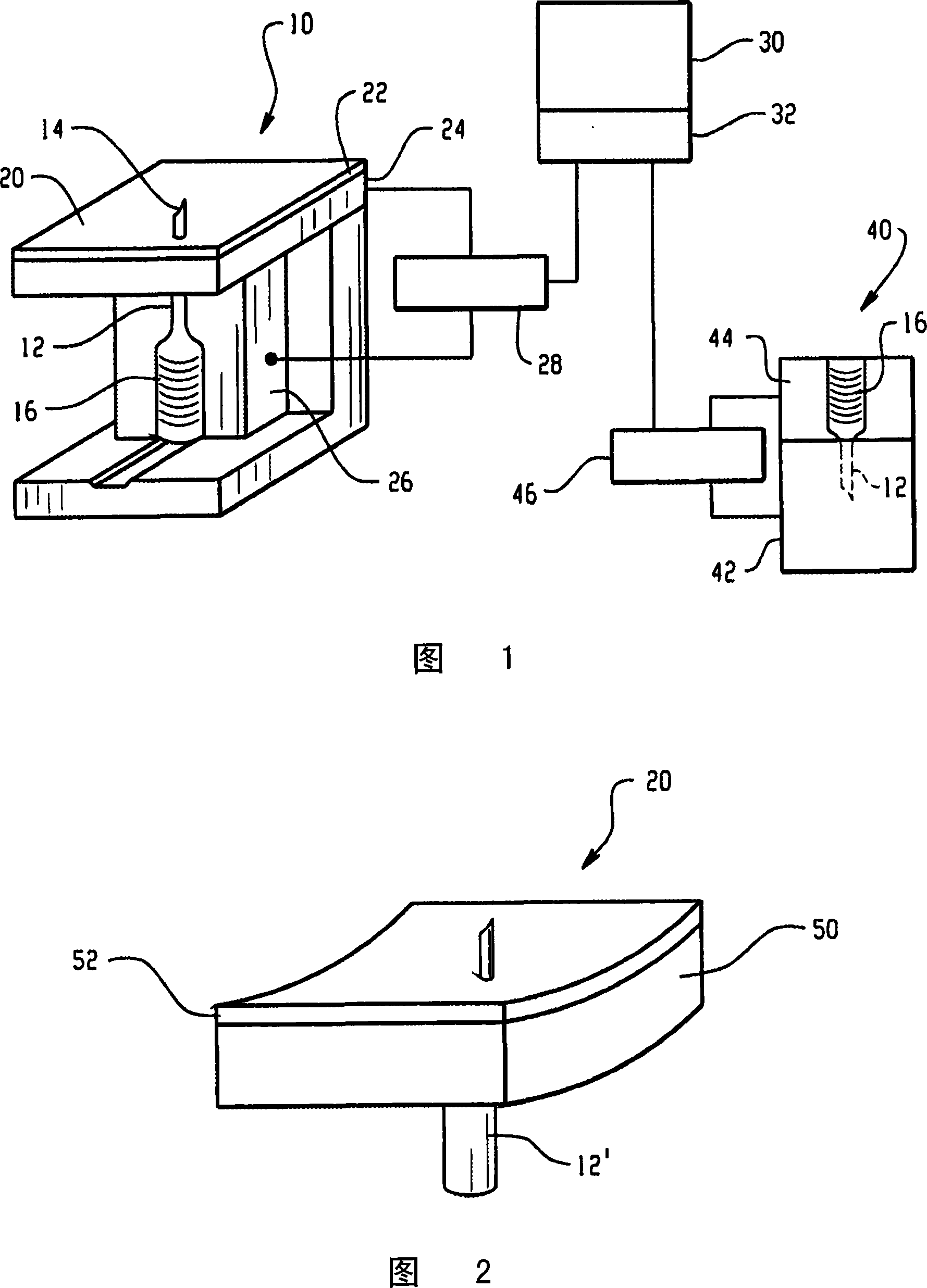
[0016] Referring to FIG. 1 , a body fluid or tissue sampling device 10 includes a container, such as a capillary 12 , for receiving blood or other tissue or fluid samples. The capillary contains a needle 14 for pricking the patient's finger to obtain a small sample of blood drawn into the capillary. The capillary further contains a label 16 carrying a unique serial number in machine readable form.
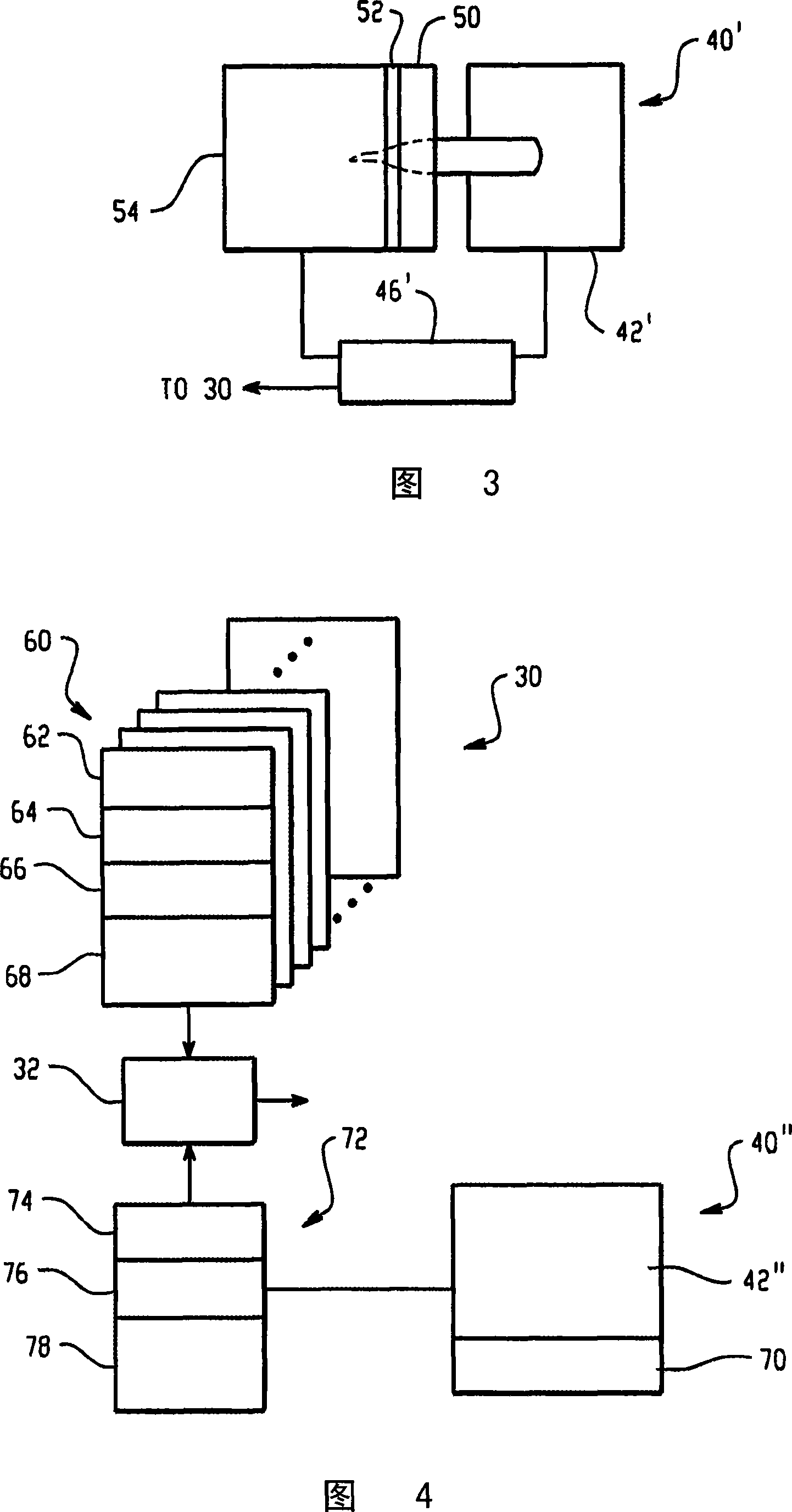
[0017] The needle end 14 of the capillary protrudes through a biometric sensor surface 20 . More particularly for the illustrated embodiment, the sensor surface 20 is a glass or transparent plate 22 under which a fingerprint scanner 24 is mounted. The scanner reads the patient's fingerprint as the patient presses their finger against the glass plate 22 and capillary needle 14 to draw a blood sample. At the same time, the reader 26 reads the unique identification on the tag 16 . Processor 28 receives fingerprint information from the scanner and a unique serial number from reader ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com