Fertilizer leaven and preparation method and application thereof
A starter and fertilizer technology, applied in the field of fertilizer starter and its preparation, can solve problems such as environmental pollution, product quality cannot be effectively and stably controlled, and restrictions on the commercialization of fermented products
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1, preparation of starter and refined organic-inorganic compound fertilizer
[0039] 1. Preparation of starter
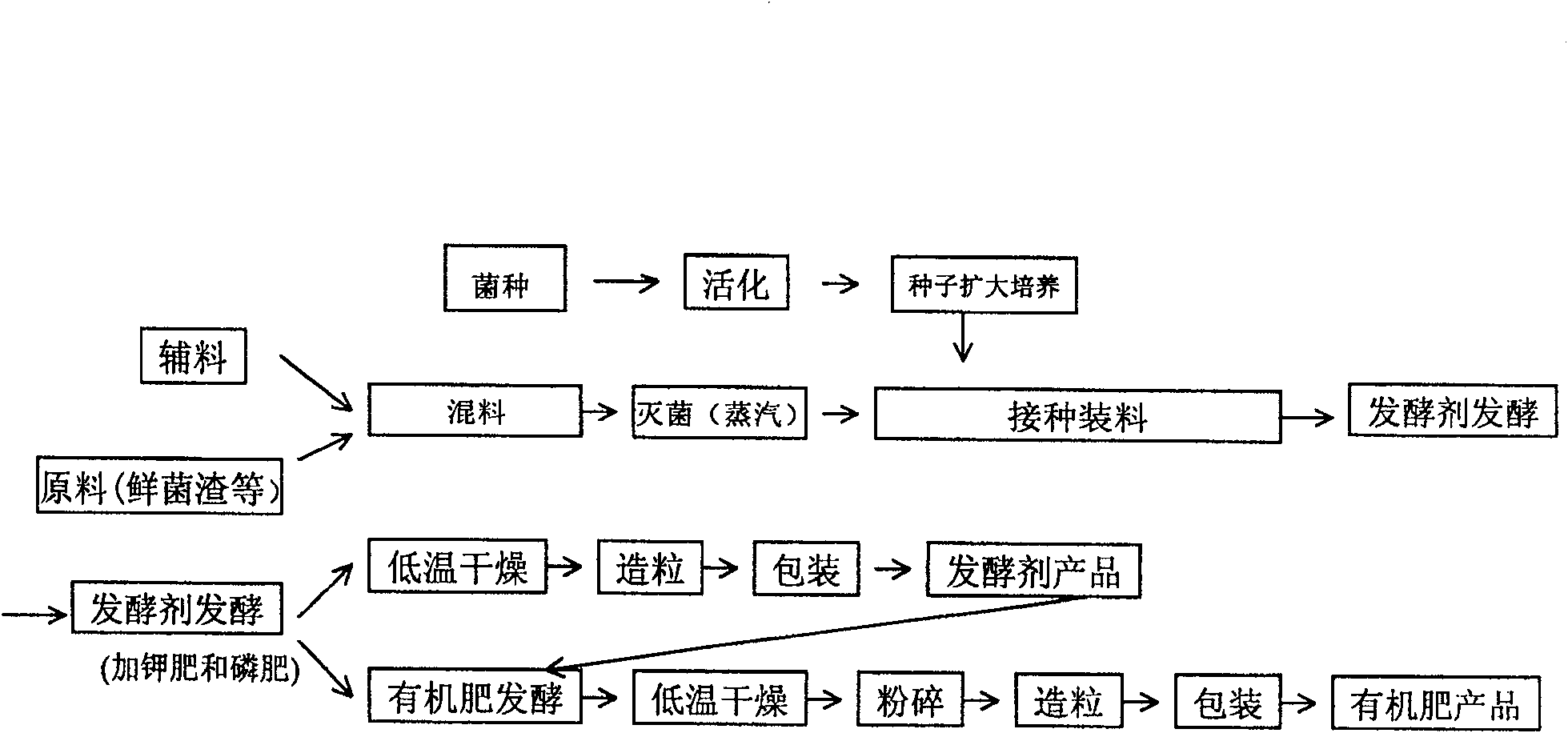
[0040] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of starter provided by the present invention may further comprise the steps:
[0041] 1. Activation of strains and seed culture
[0042] The formulations of the activation medium and the seed medium are: peptone 10g, yeast powder 10g, glucose 20g, beef extract 3g, sodium chloride 5g, dilute to 1000mL with water, pH 7.0±0.2.
[0043] The present embodiment adopts Bacillus megaterium (Bacillus megaterium) preservation number 1.217, giant bacillus (Bacillus megaterium) preservation number 1.217, Bacillus licheniformis (Bacillus licheniformis) preservation number 1.518, plant lactobacillus (Lactobacillus plantarum) preservation number 1.555 and button capsule For the strain combination of Saccharomycopsis fibuligera preservation number 2.1145, the above-mentioned microbial strains are activated a...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2, preparation of starter and refined organic-inorganic compound fertilizer
[0056] 1. Preparation of starter
[0057] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of starter provided by the present invention may further comprise the steps:
[0058] 1. Activation of strains and seed culture
[0059] The formulations of the activation medium and the seed medium are: peptone 10g, yeast powder 10g, glucose 20g, beef extract 3g, sodium chloride 5g, dilute to 1000mL with water, pH 7.0±0.2.
[0060] In this embodiment, the bacterial strain combination of Saccharomycopsis fibuligera (Saccharomycopsis fibuligera) preservation number 2.1145 is adopted, and the above-mentioned microbial strains are activated and seed cultured before the preparation of the starter. In the activation medium, cultivate it at 28°C (25-28°C is acceptable) for 1 day, then inoculate the activated bacterial strain in the seed medium in an amount of 10%, and cultivate it under the same co...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3, preparation of starter and refined organic-inorganic compound fertilizer
[0073] 1. Preparation of starter
[0074] Such as figure 1 Shown, the preparation method of starter provided by the present invention may further comprise the steps:
[0075] 1. Activation of strains and seed culture
[0076] The formulations of the activation medium and the seed medium are: peptone 10g, yeast powder 10g, glucose 20g, beef extract 3g, sodium chloride 5g, dilute to 1000mL with water, pH 7.0±0.2.
[0077] The present embodiment adopts the strain combinations of Azotobacter chroococcum preservation number 1.212, Bacillus megaterium preservation number 1.217 and Lactobacillus plantarum preservation number 1.555. The strains are activated and seed cultured, the method is as follows: inoculate the above-mentioned 3 kinds of strains in the activation medium according to the amount of 5%, and cultivate them at 37°C (33-37°C) for 1 day, and then inoculate the activated 3 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com