Voltage averaged allocator for charging and discharging lithium battery
A voltage averaging, lithium battery technology, applied in battery circuit devices, current collectors, electric vehicles, etc., can solve problems such as power loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
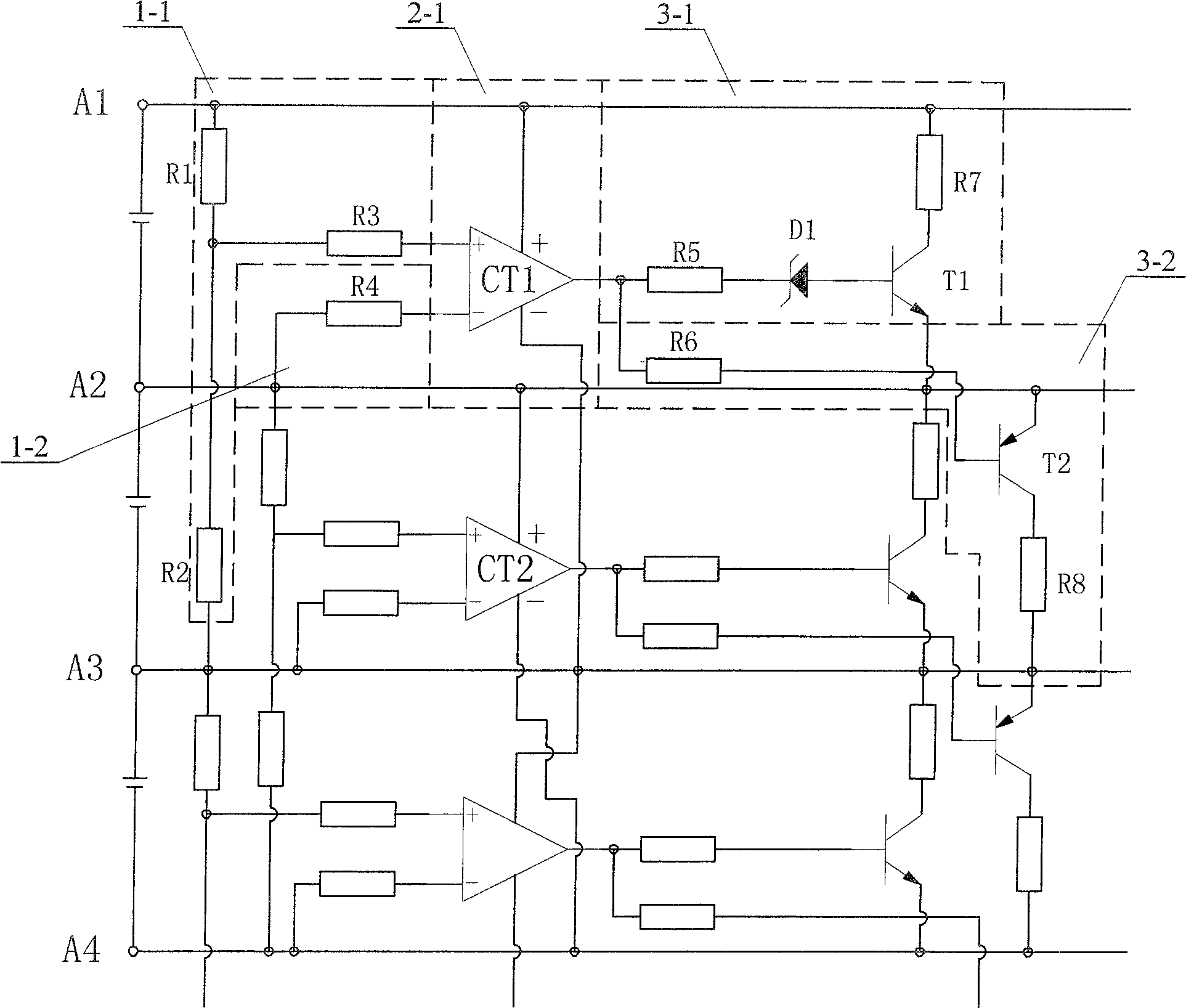
[0005] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 This embodiment will be specifically described. In this embodiment, N-1 voltage sampling circuits 1, N-2 voltage comparison circuits 2, N-1 shunt circuits 3, A threshold limiting circuit 4 and N nodes arranged in sequence, the N nodes are sequentially composed of the first node A1, the second node A2 ... and the Nth node AN, and every two adjacent nodes are connected in parallel A voltage sampling circuit 1 and a corresponding shunt circuit 3 are connected; the two input terminals of the voltage comparison circuit 2 are respectively connected to the output terminals of two adjacent voltage sampling circuits 1, and the two outputs of each voltage comparison circuit 2 Each of the two shunt circuits 3 corresponding to the two voltage sampling circuits 1 input to the signal of the voltage comparator circuit 2 is respectively connected to each controlled end of the two adjacent shunt circuits 3, and the t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0006] Specific implementation mode two: the following combination figure 2 This embodiment will be specifically described. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the No. 1 voltage sampling circuit 1-1 between the first node A1 and the second node A2 is composed of a first resistor R1, a second resistor R2 and a third resistor R3. The second voltage sampling circuit 1-2 between the second node A2 and the third node A3 is composed of the fourth resistor R4, the voltage comparison circuit 2-1 is composed of the first integrated operational amplifier CT1, the first node A1 and the second node A2 The No. 1 shunt circuit 3-1 between is composed of the fifth resistor R5, the seventh resistor R7, the first Zener diode D1 and the first triode T1, and the No. 2 shunt circuit between the second node A2 and the third node A3 The shunt circuit 3-2 is composed of the sixth resistor R6, the eighth resistor R8 and the second transistor T2. One end of the first resi...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0007] Specific implementation mode three: the following combination image 3 This embodiment will be specifically described. The difference between this embodiment and the second embodiment is: the threshold limiting circuit 4-1 connected in parallel between the first node A1 and the fourth node A4 is composed of the ninth resistor R9, the tenth resistor R10, the eleventh resistor R11, the Twelfth resistor R12, thirteenth resistor R13, fourteenth resistor R14, fifteenth resistor R15, sixth zener diode D6, seventh zener diode D7, third transistor T3, fourth transistor T4 Composed of the third integrated operational amplifier CT3, the resistance value of the tenth resistor R10 is equal to the resistance value of the eleventh resistor R11, one end of the tenth resistor R10 is connected to the first node A1, one end of the twelfth resistor R12 and the third third The emitter of the pole tube T3, the other end of the tenth resistor R10 is connected to one end of the eleventh resi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com