Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Cheyne-stokes breathing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
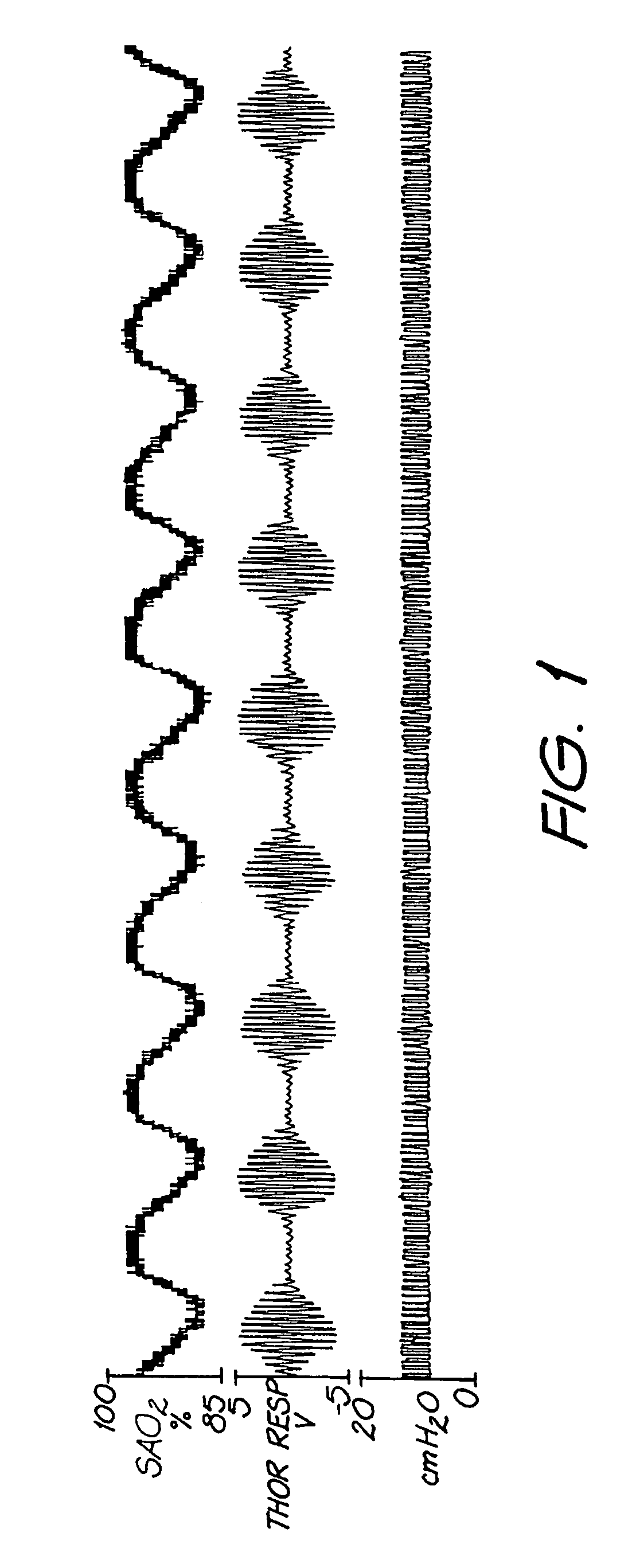
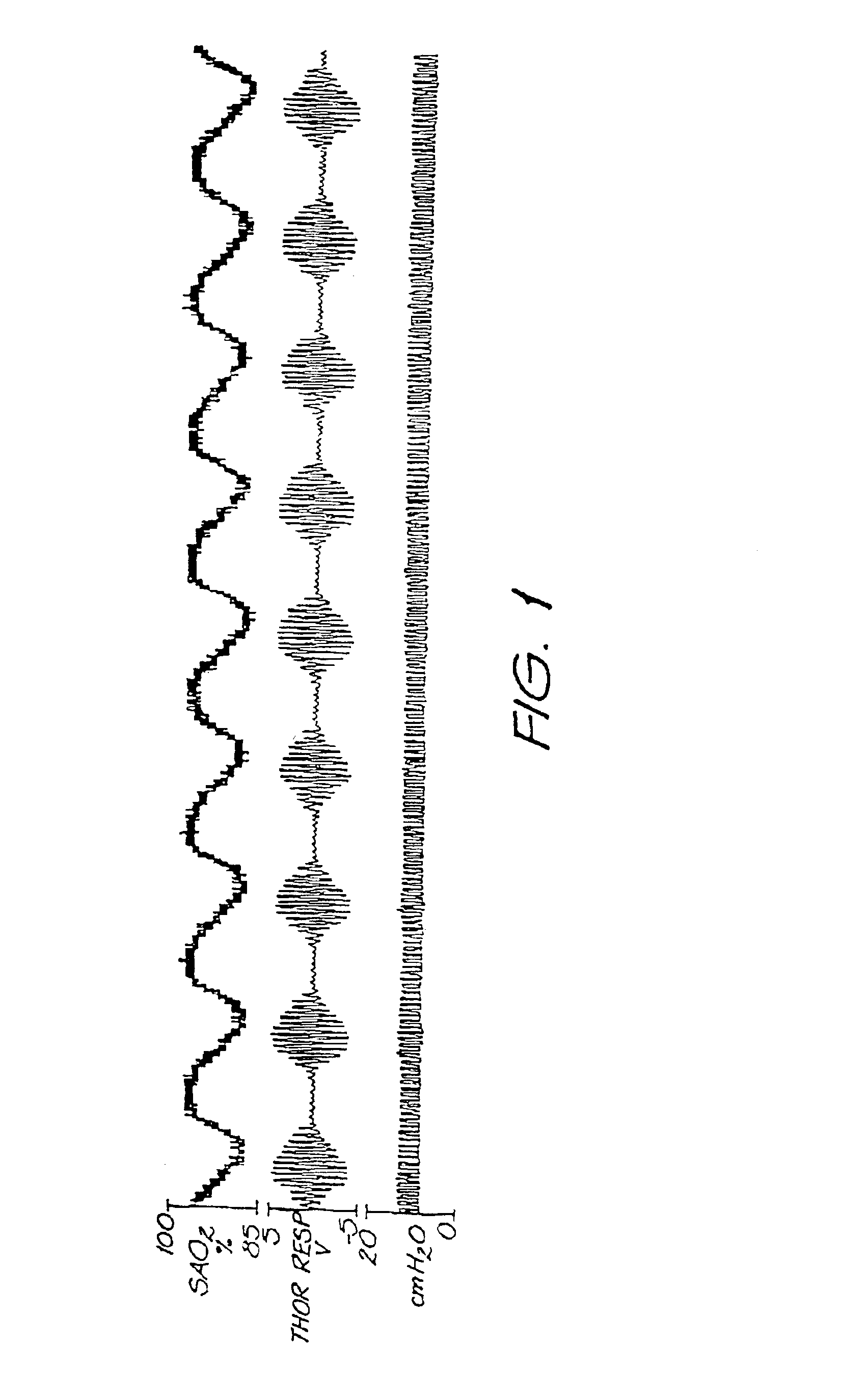
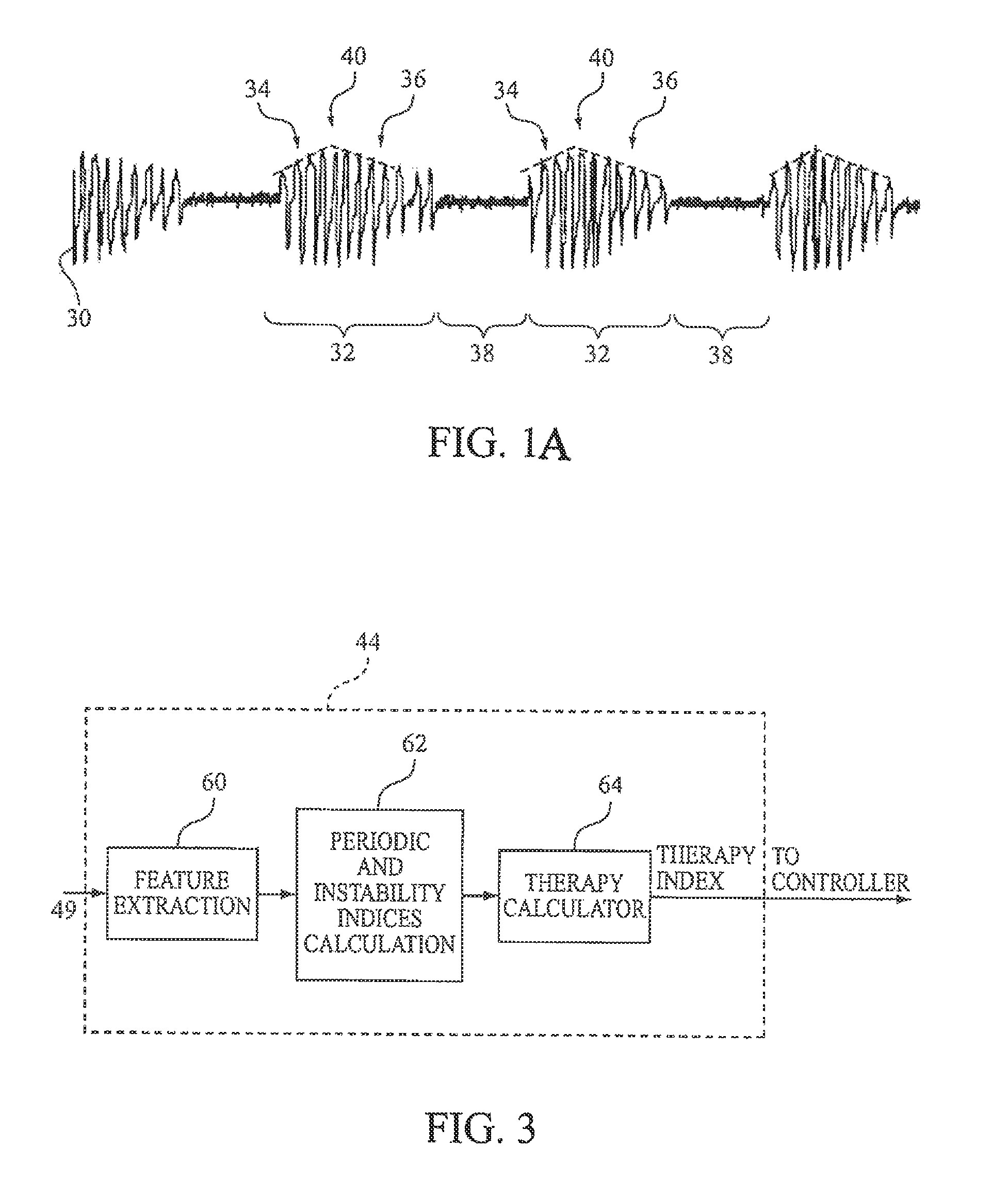
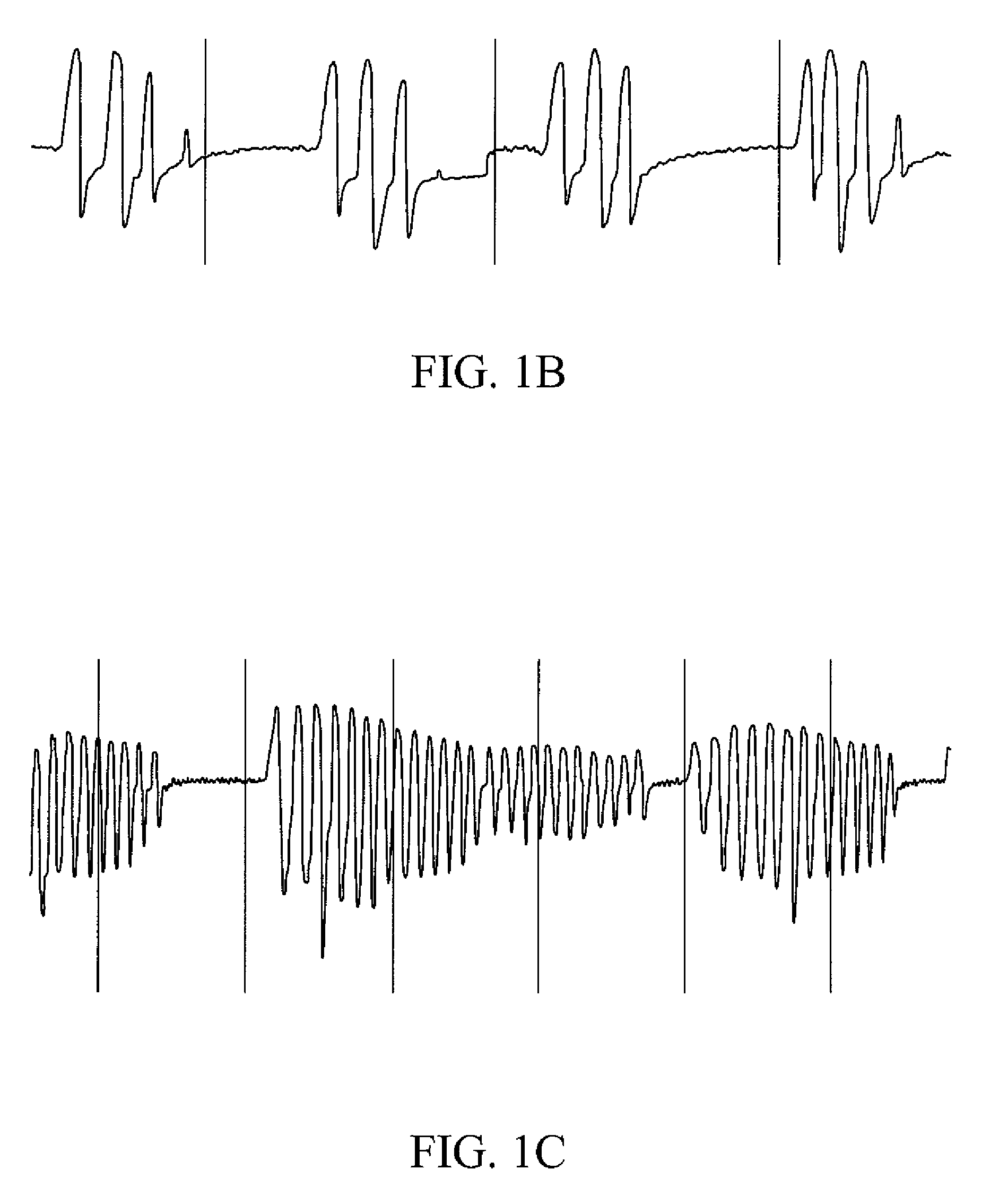
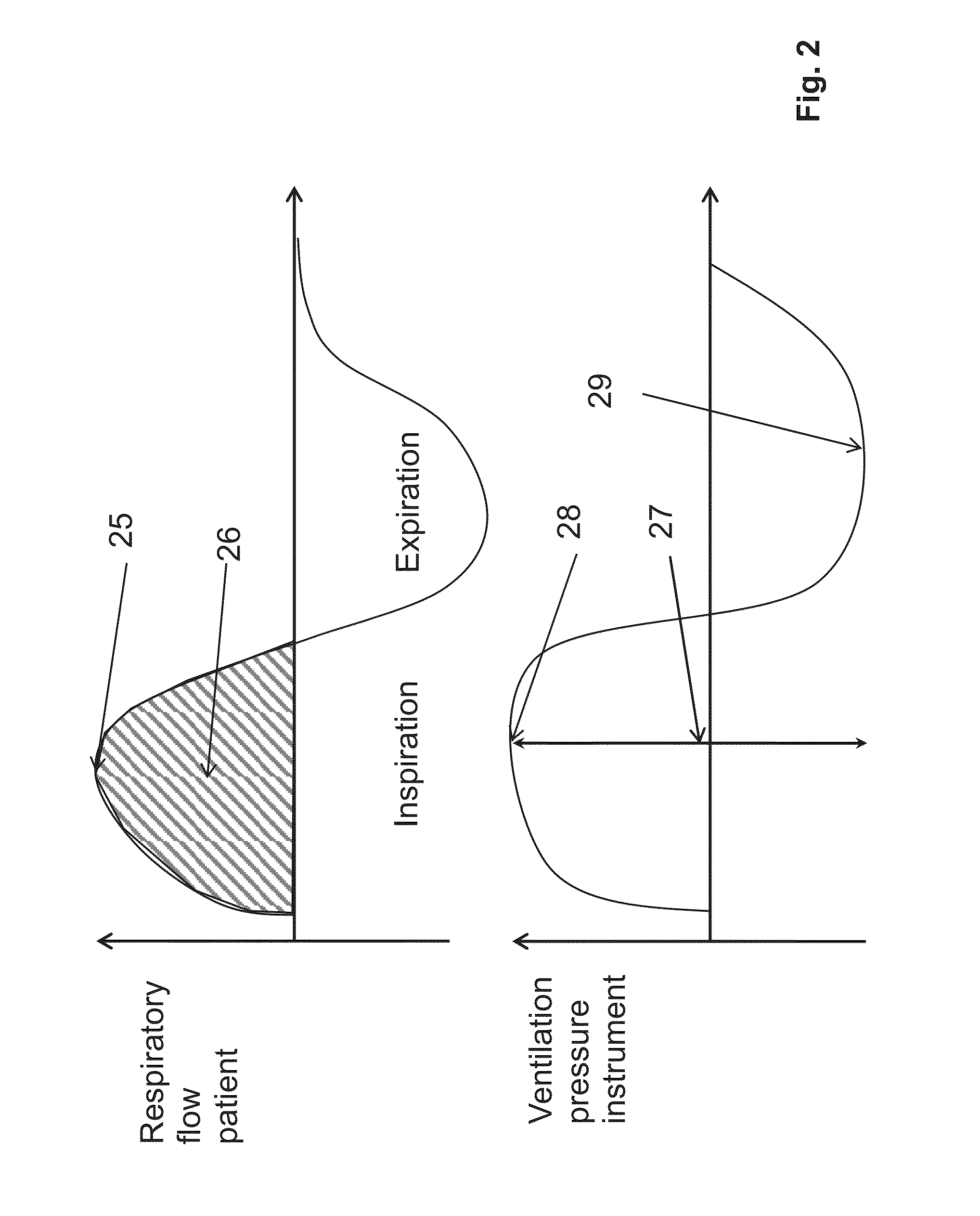
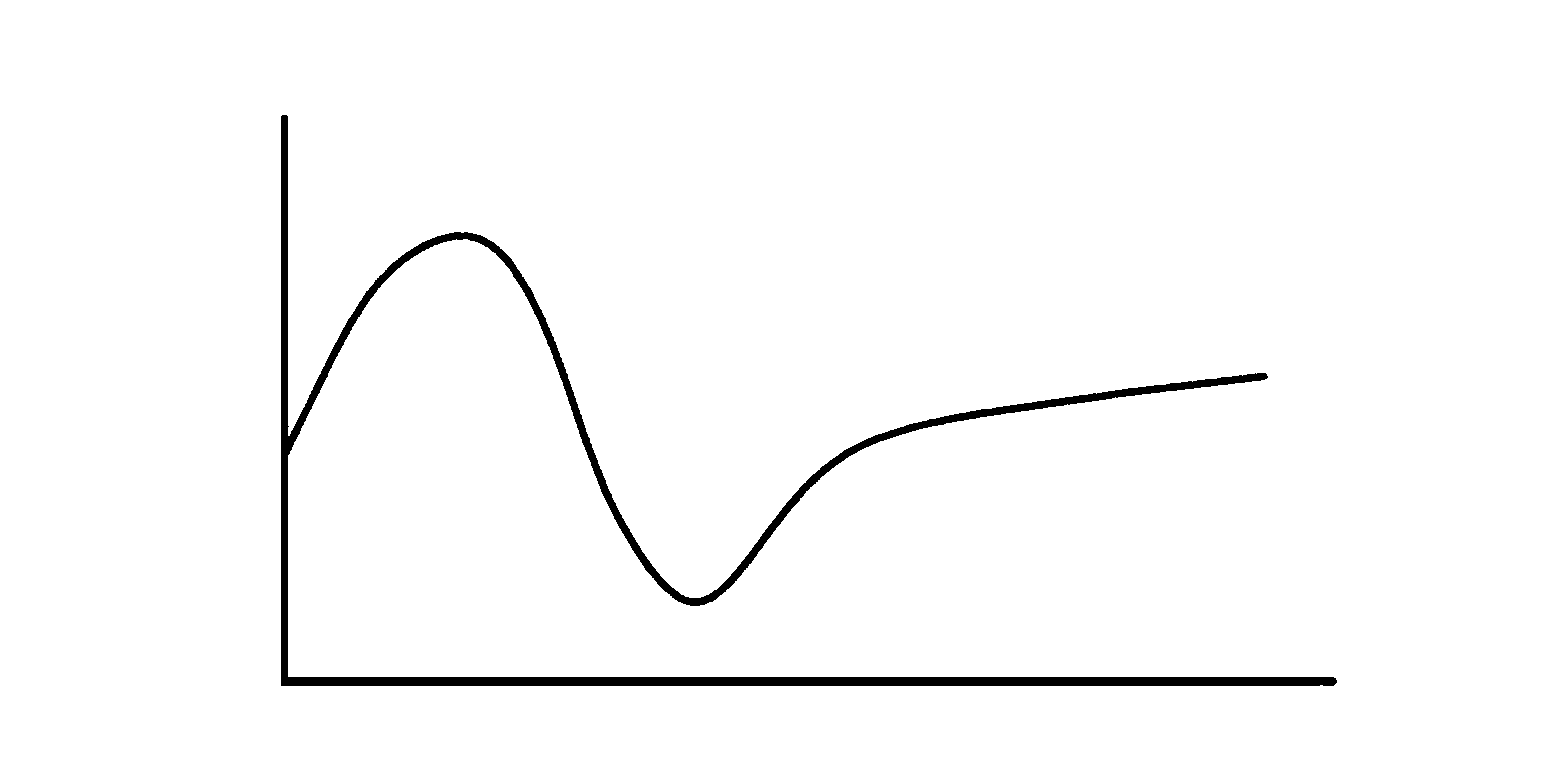
Graph showing the Cheyne–Stokes respiration and other pathological breathing patterns. Cheyne–Stokes respiration /ˈtʃeɪnˈstoʊks/ is an abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by progressively deeper, and sometimes faster, breathing followed by a gradual decrease that results in a temporary stop in breathing called an apnea.
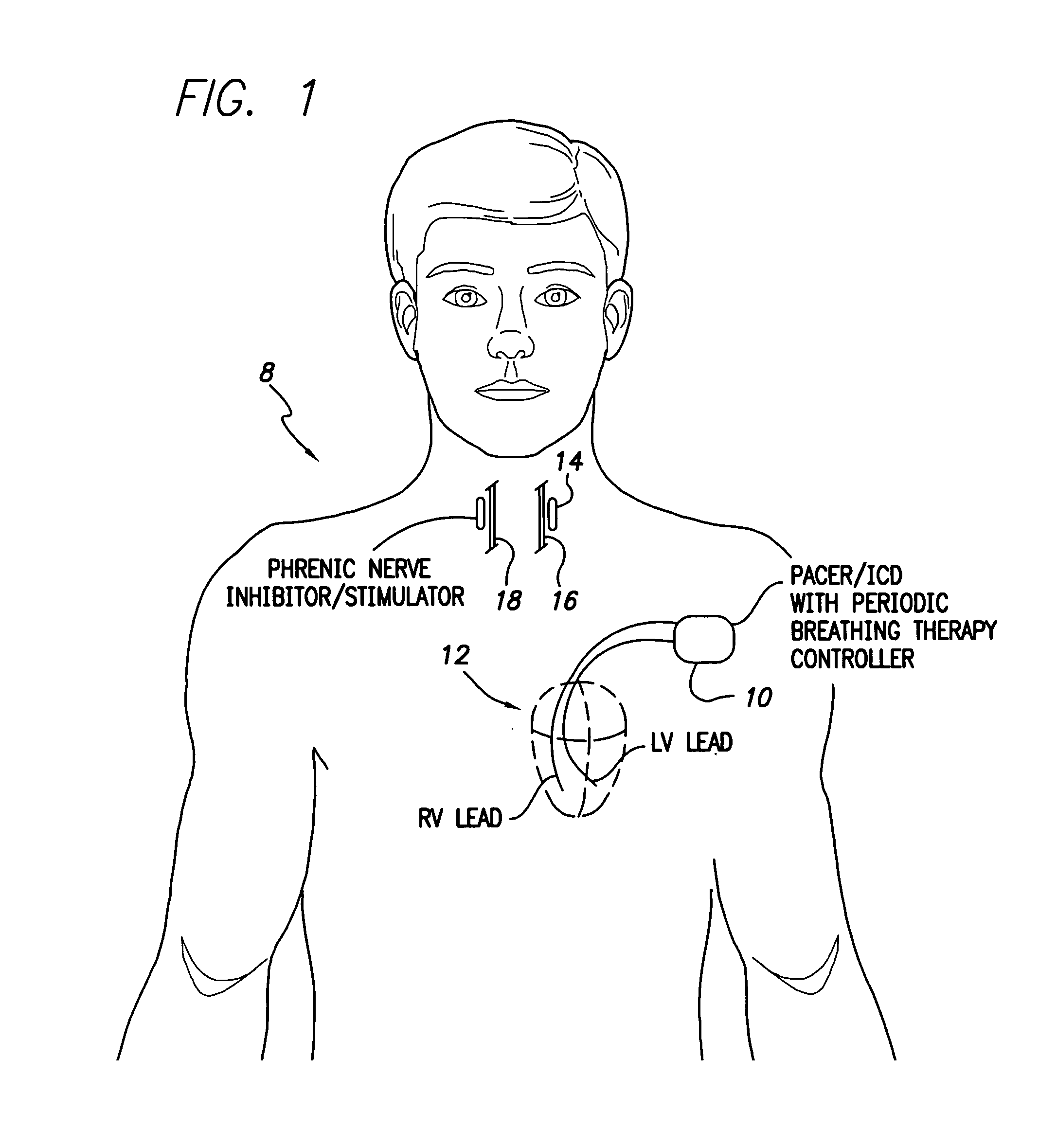
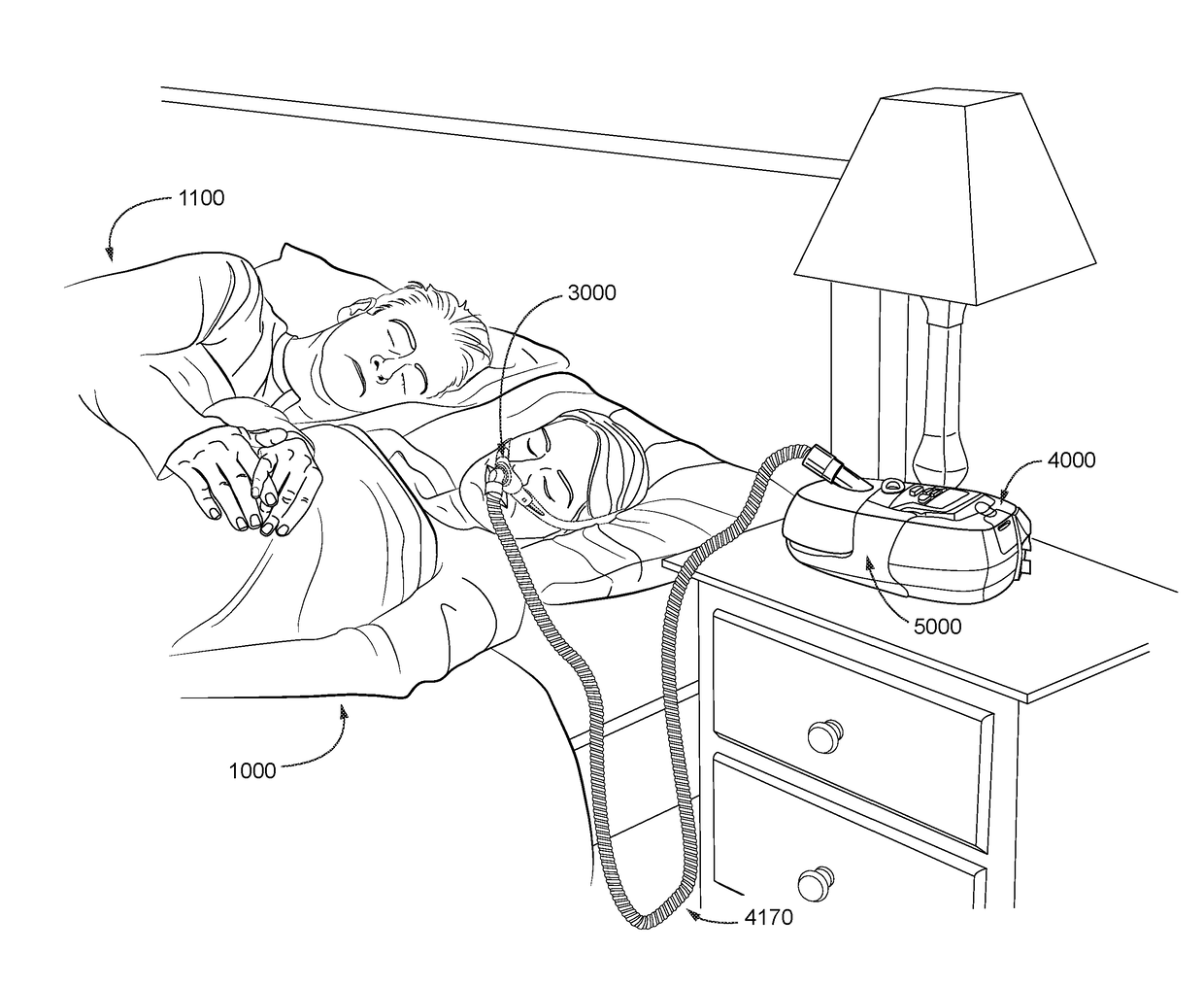
Method and apparatus to detect and treat sleep respiratory events
InactiveUS6641542B2CatheterRespiratory organ evaluationCheyne–Stokes respirationCheyne-stokes breathing
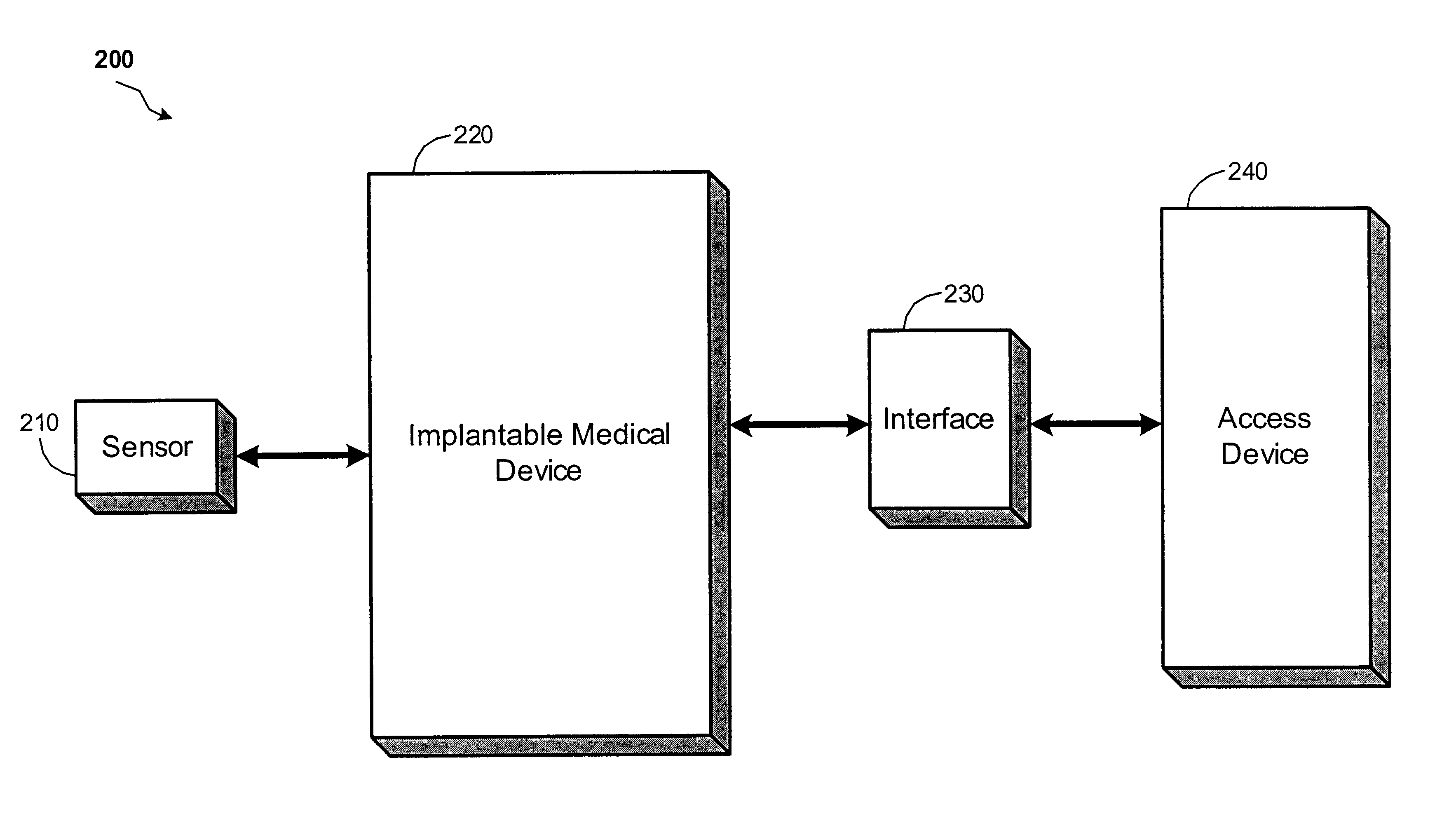
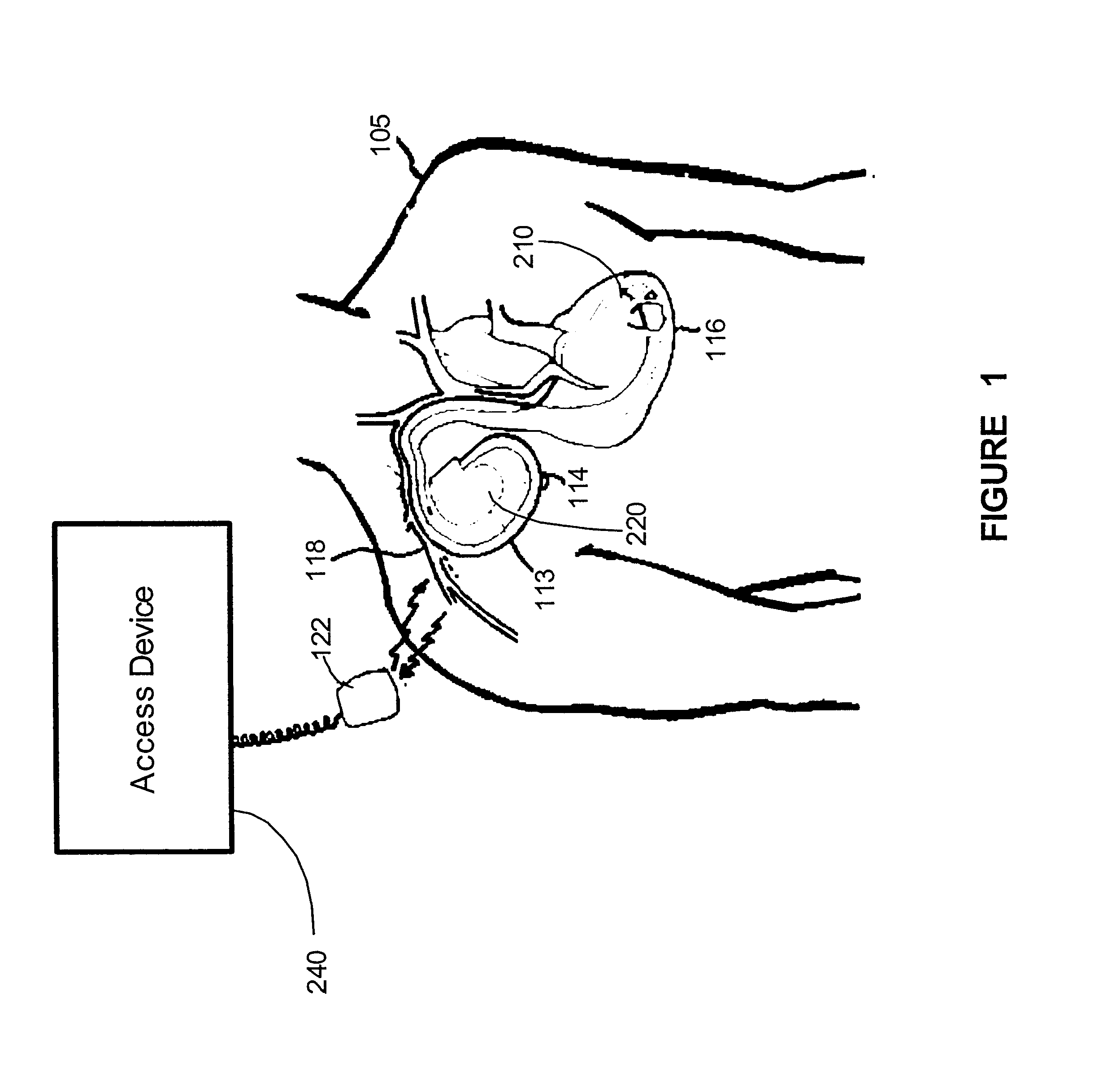
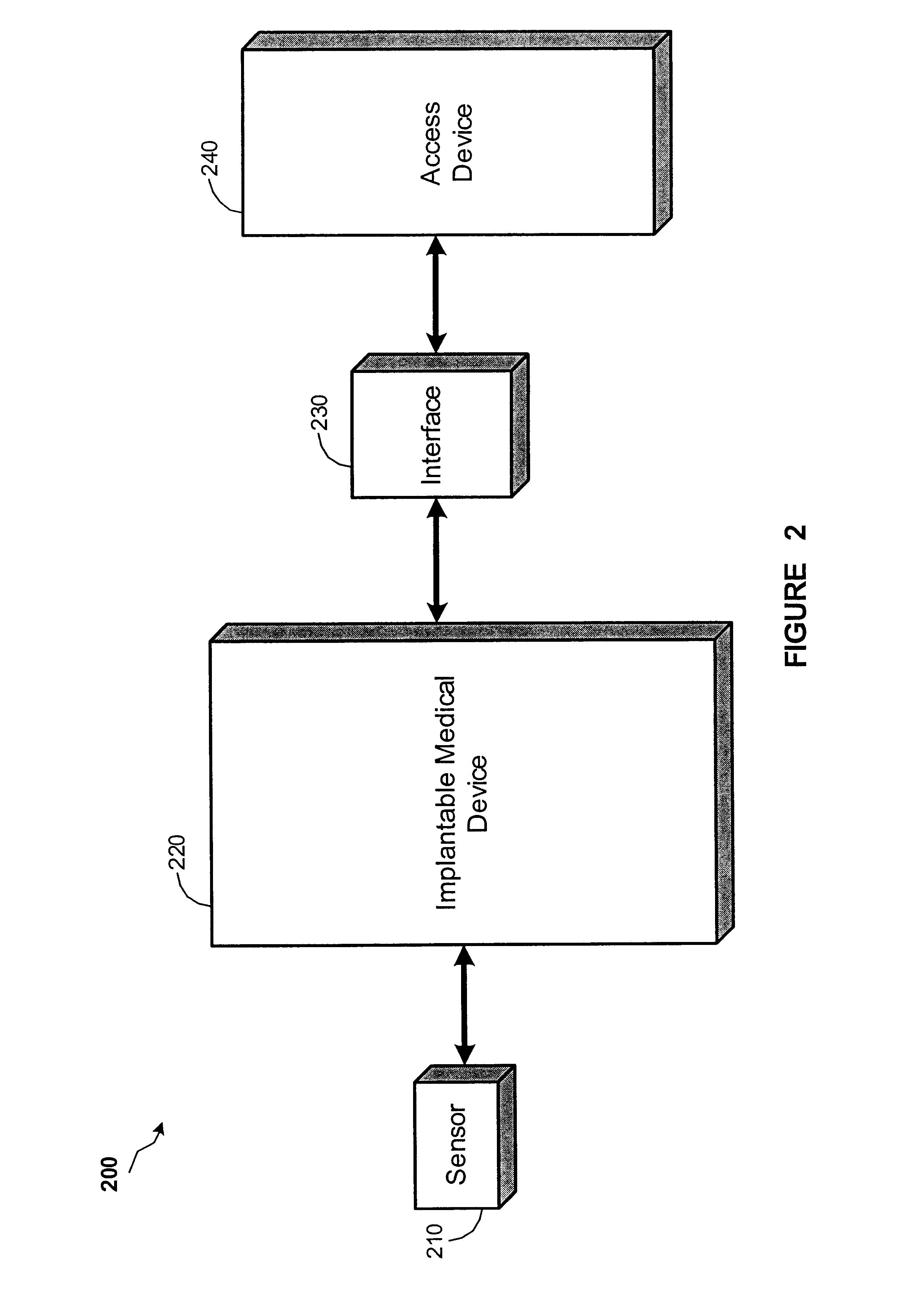
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting and treating sleep respiratory events that includes a plurality of sensors gathering physiological data related to sleep respiratory events. A processor extracts an average cycle length and a frequency of at least one of Cheyne-Stokes respiration and periodic breathing based upon the physiological data, and determines whether therapy is required based on the average cycle length and the frequency.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
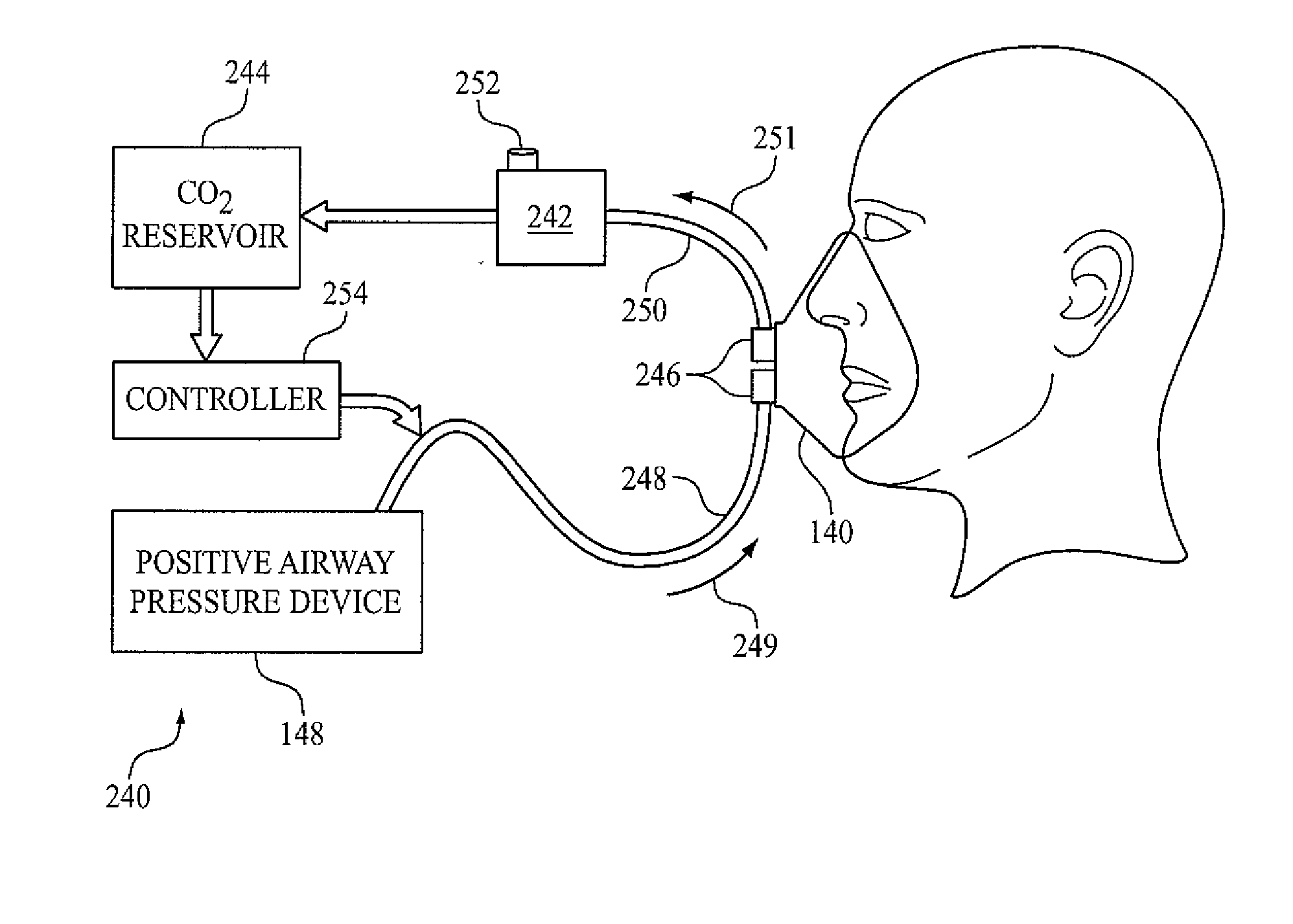
Method and apparatus for providing variable positive airway pressure
InactiveUS6752151B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive airway pressureCombined use
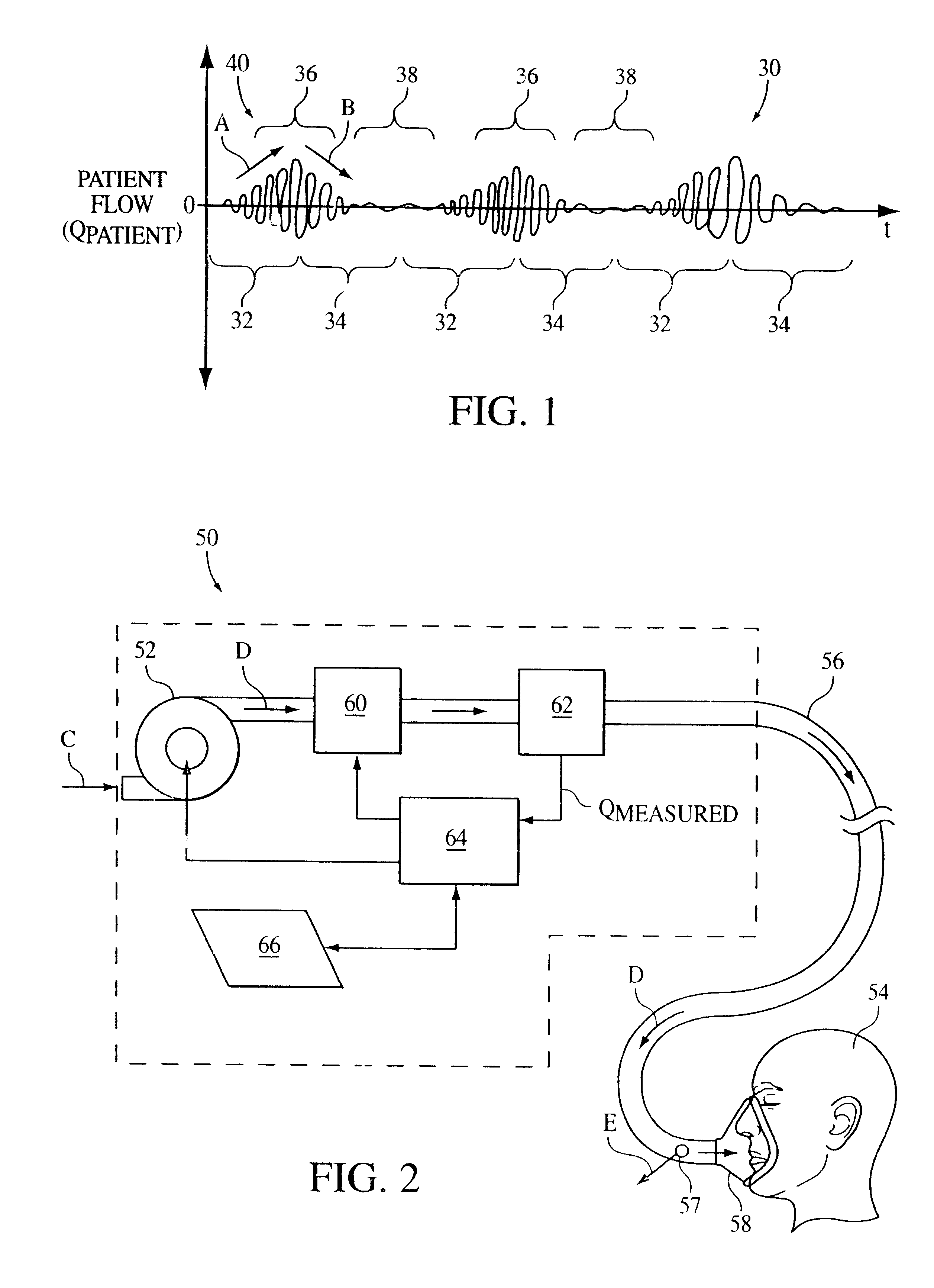
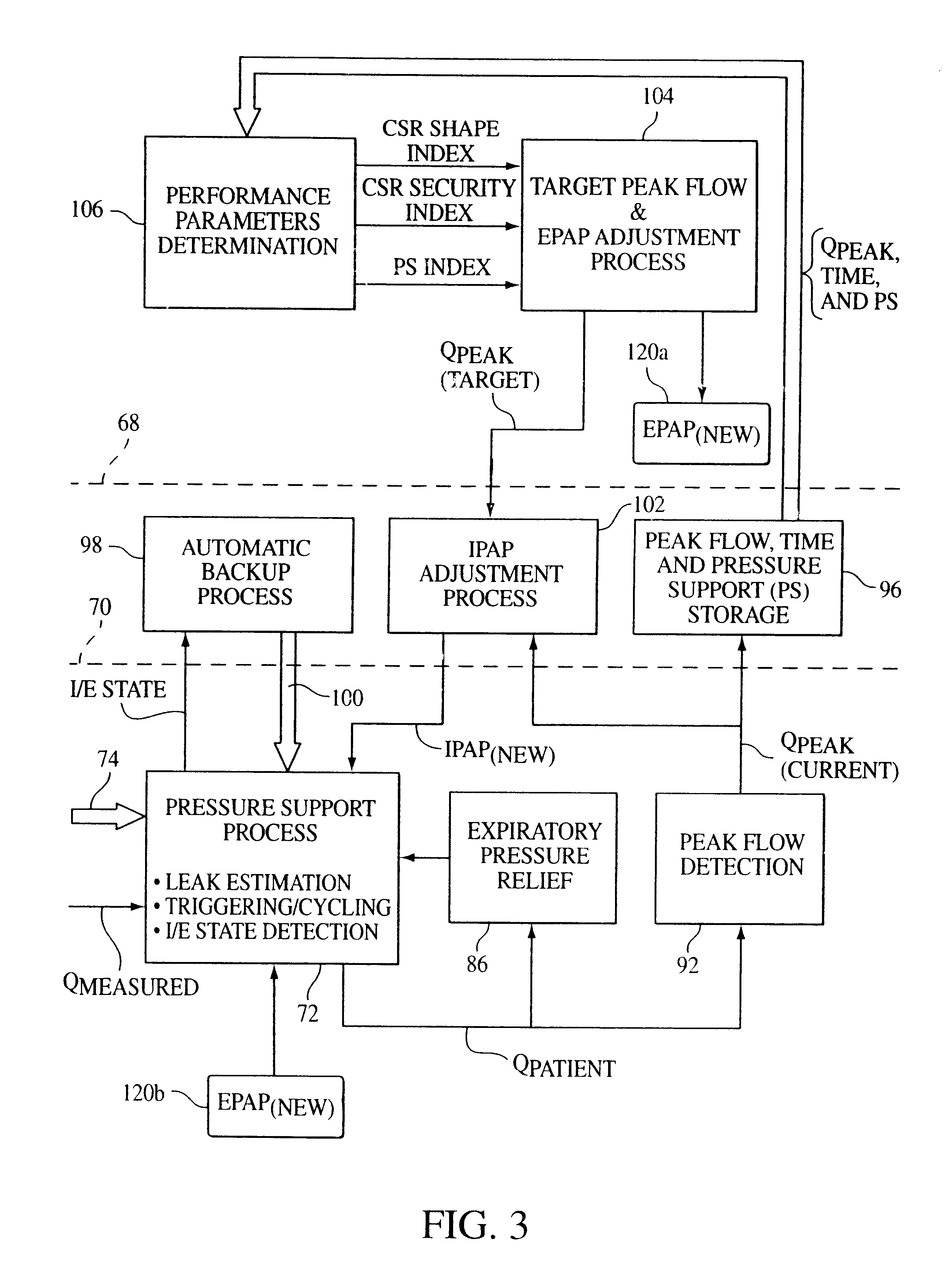
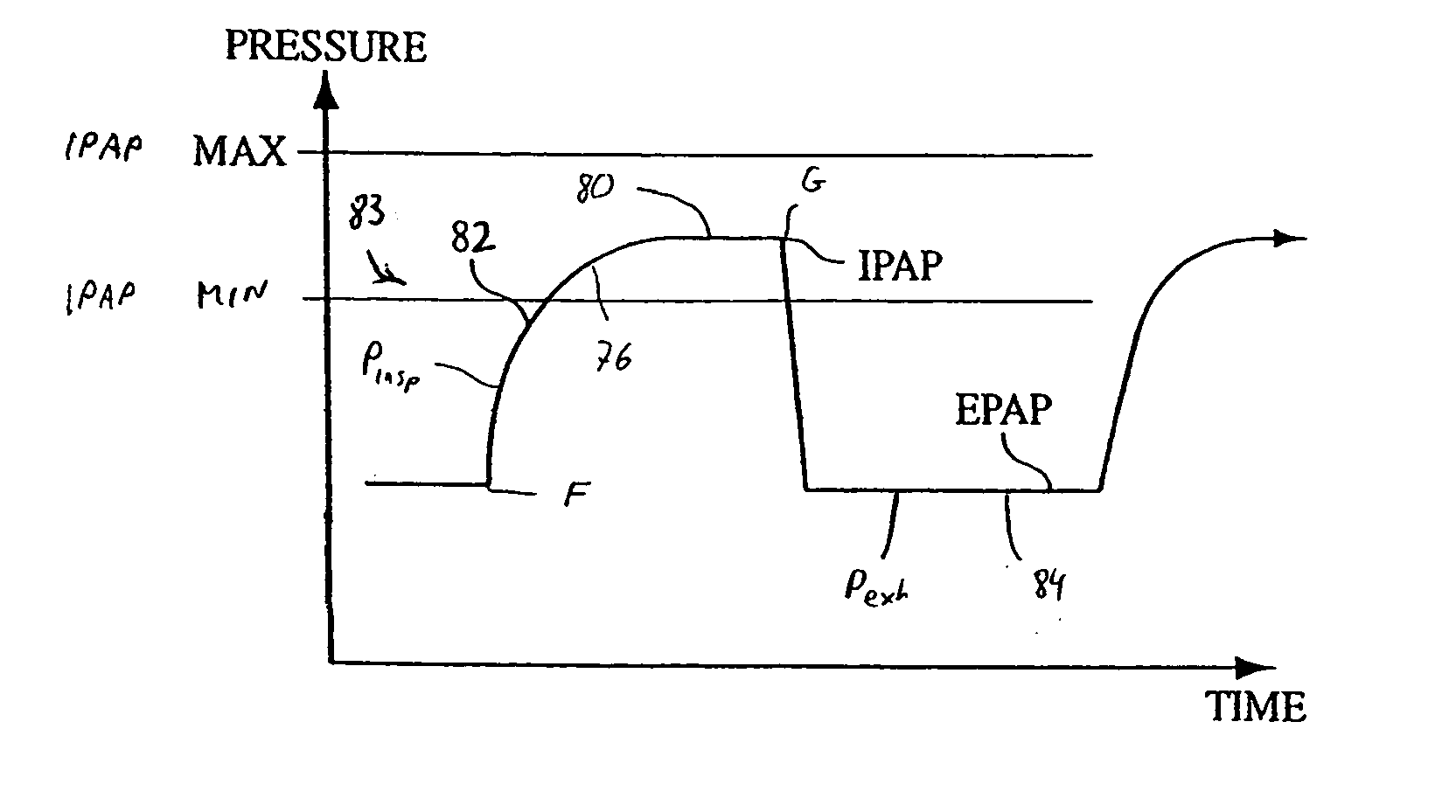
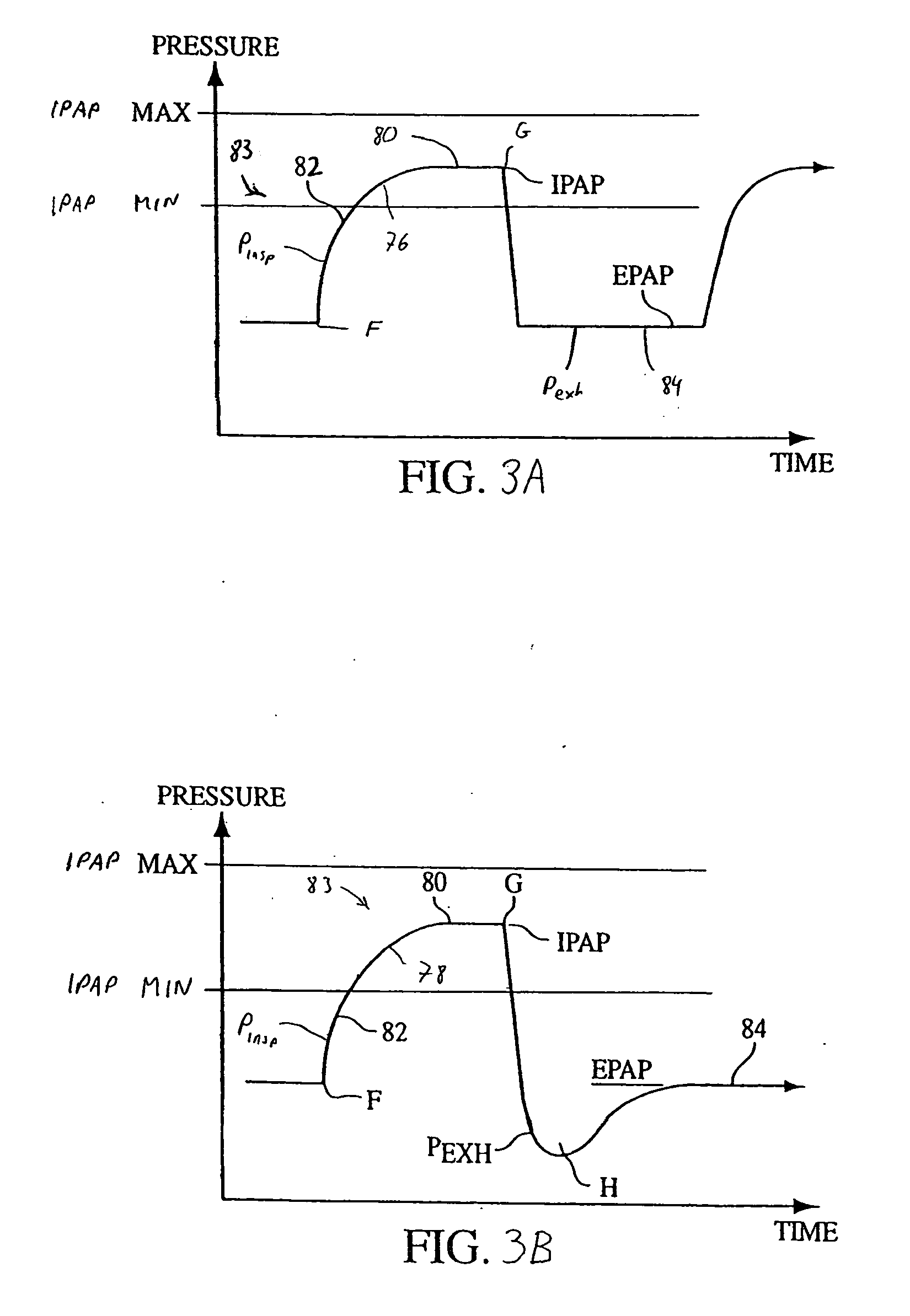
A method and apparatus for treating a breathing disorder and, more particularly, a method and apparatus for providing a pressurized air flow to an airway of a patient to treat congestive heart failure in combination with Cheyne-Stokes respiration and / or sleep apnea or other breathing disorders. A positive airway pressure ventilator is utilized in combination with an algorithm that adjusts IPAP and EPAP in order to counter a Cheyne-Stokes breathing pattern. Cheyne-Stokes respiration is detected by monitoring a peak flow of the patient.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and apparatus to detect and treat sleep respiratory events
InactiveUS20020193697A1CatheterRespiratory organ evaluationCheyne–Stokes respirationCheyne-stokes breathing
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting and treating sleep respiratory events that includes a plurality of sensors gathering physiological data related to sleep respiratory events. A processor extracts an average cycle length and a frequency of at least one of Cheyne-Stokes respiration and periodic breathing based upon the physiological data, and determines whether therapy is required based on the average cycle length and the frequency.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
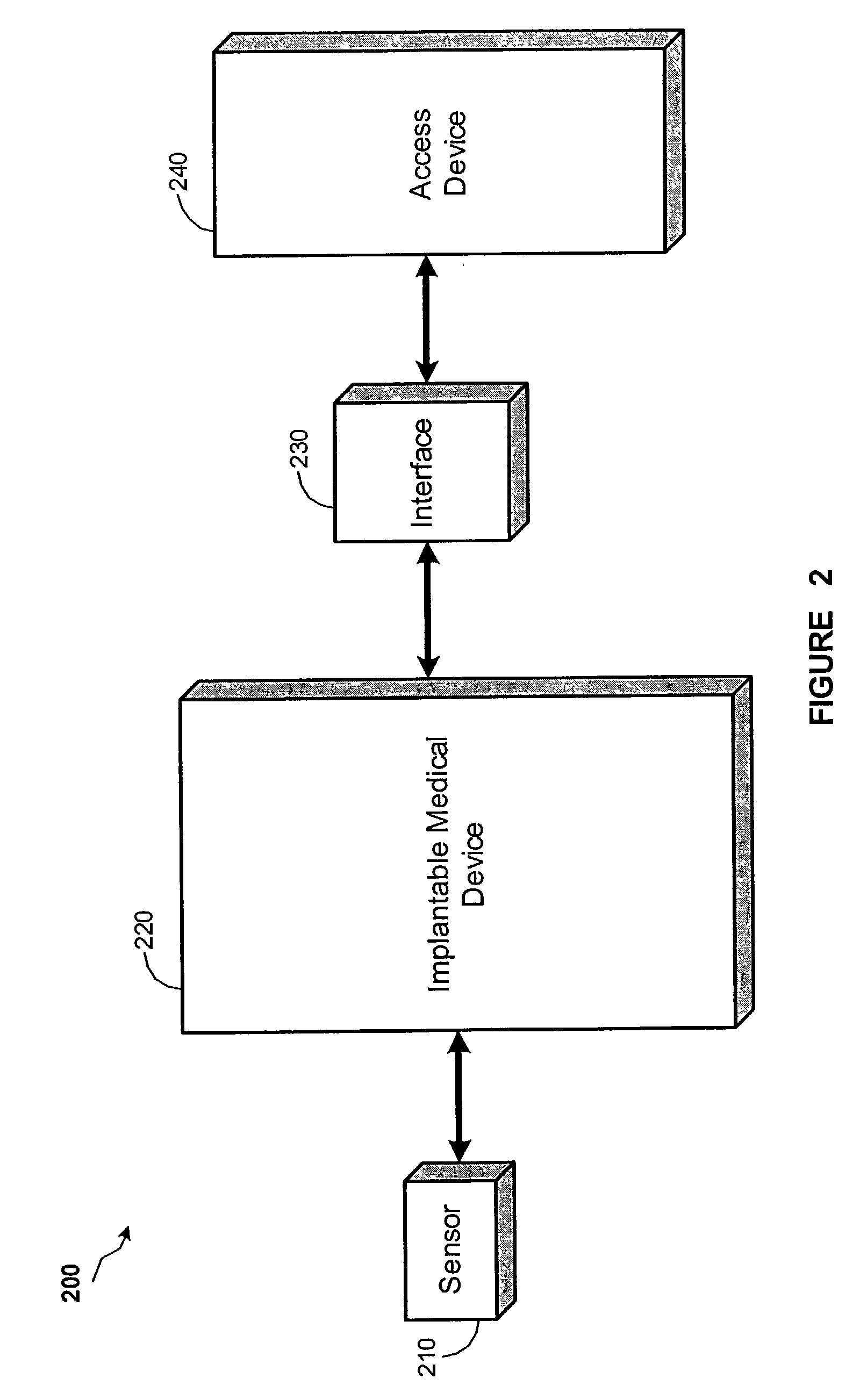
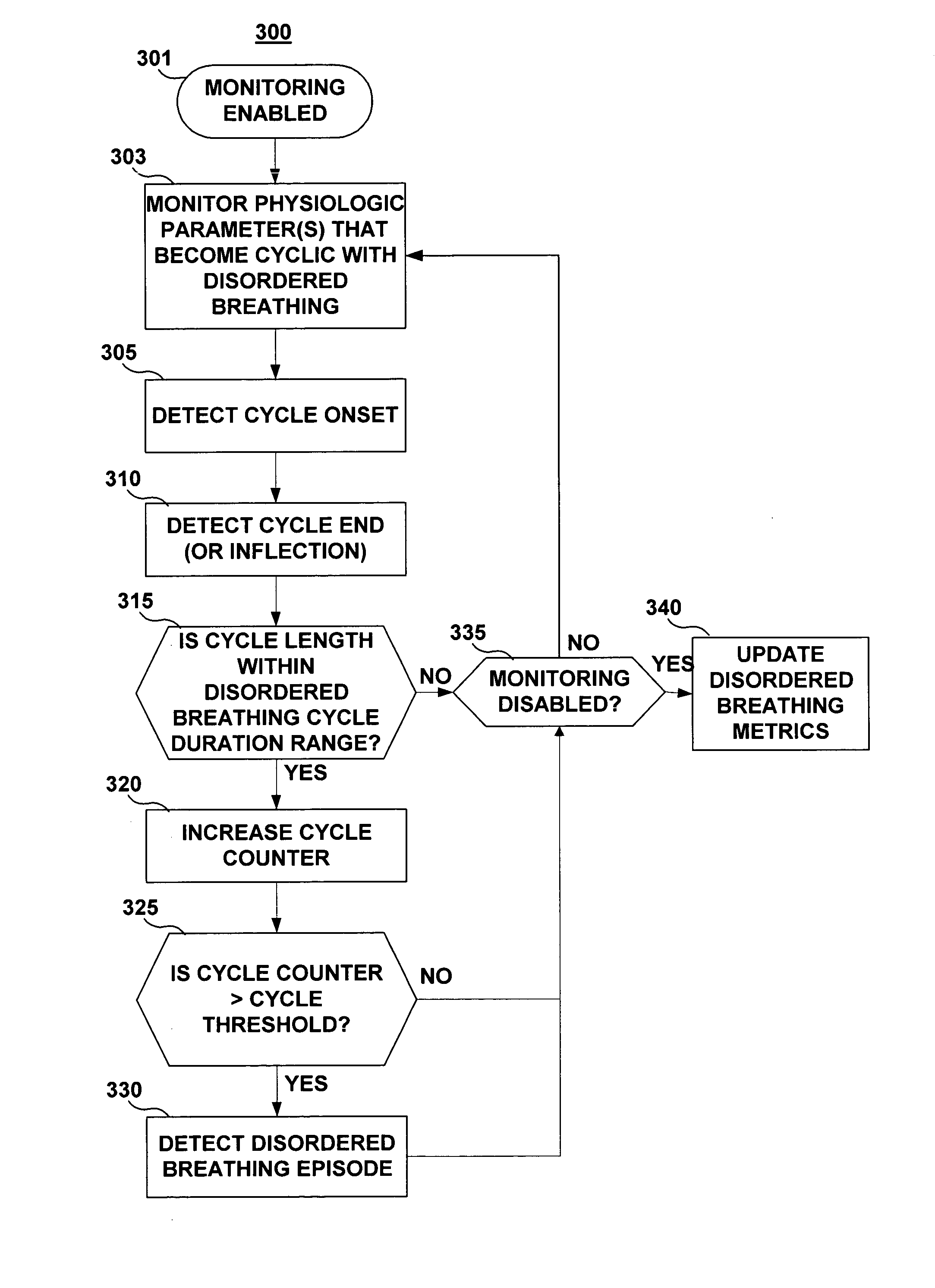
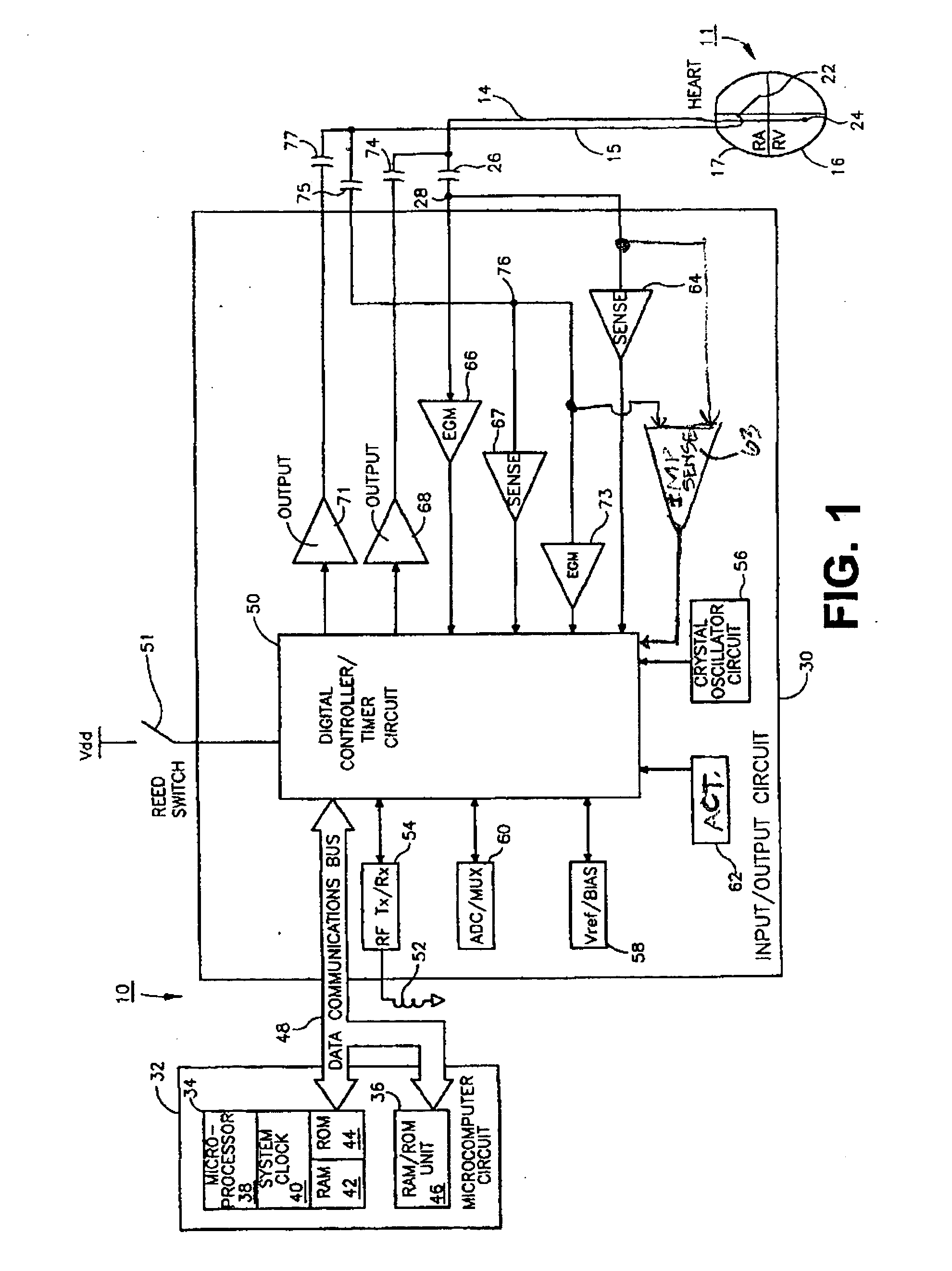
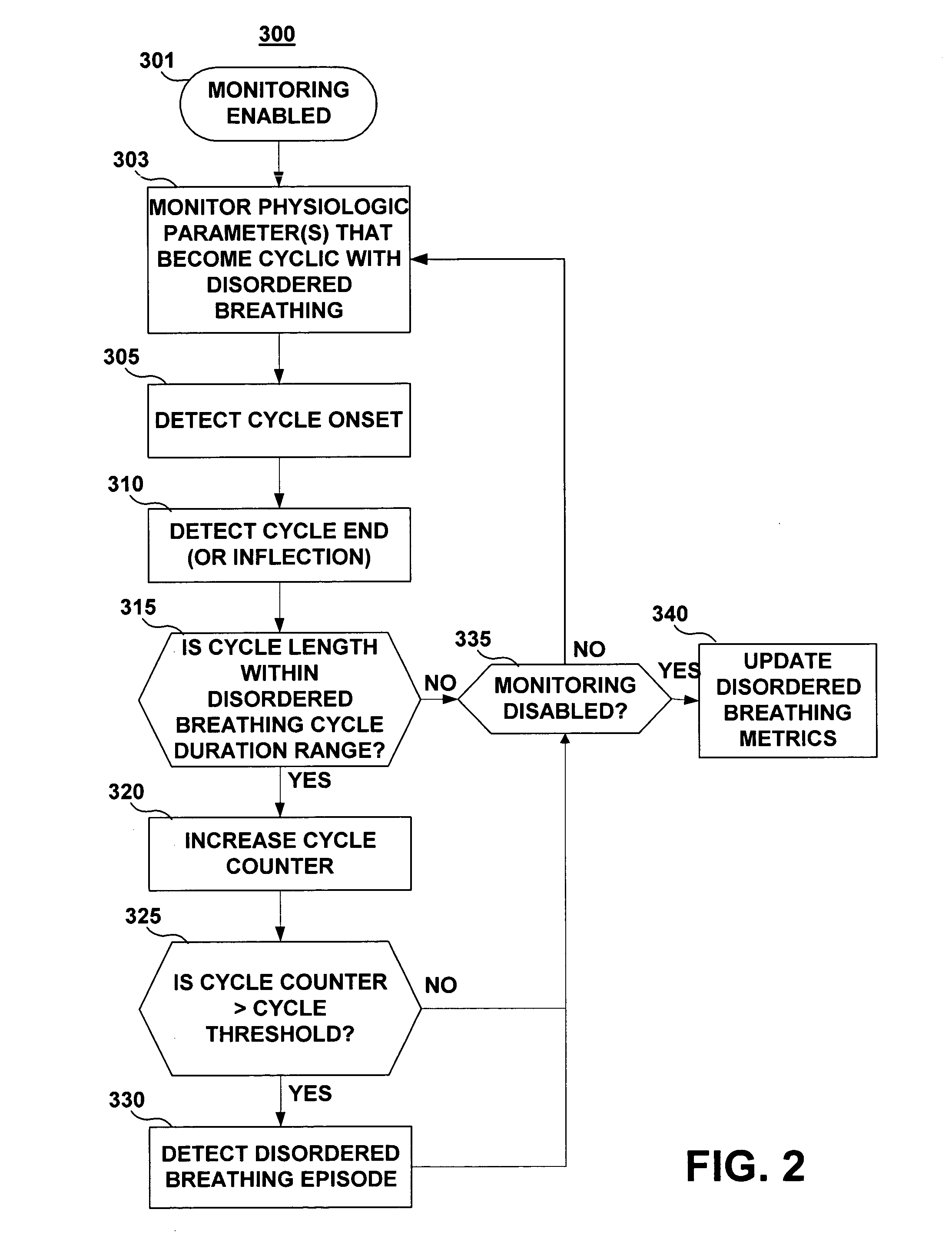
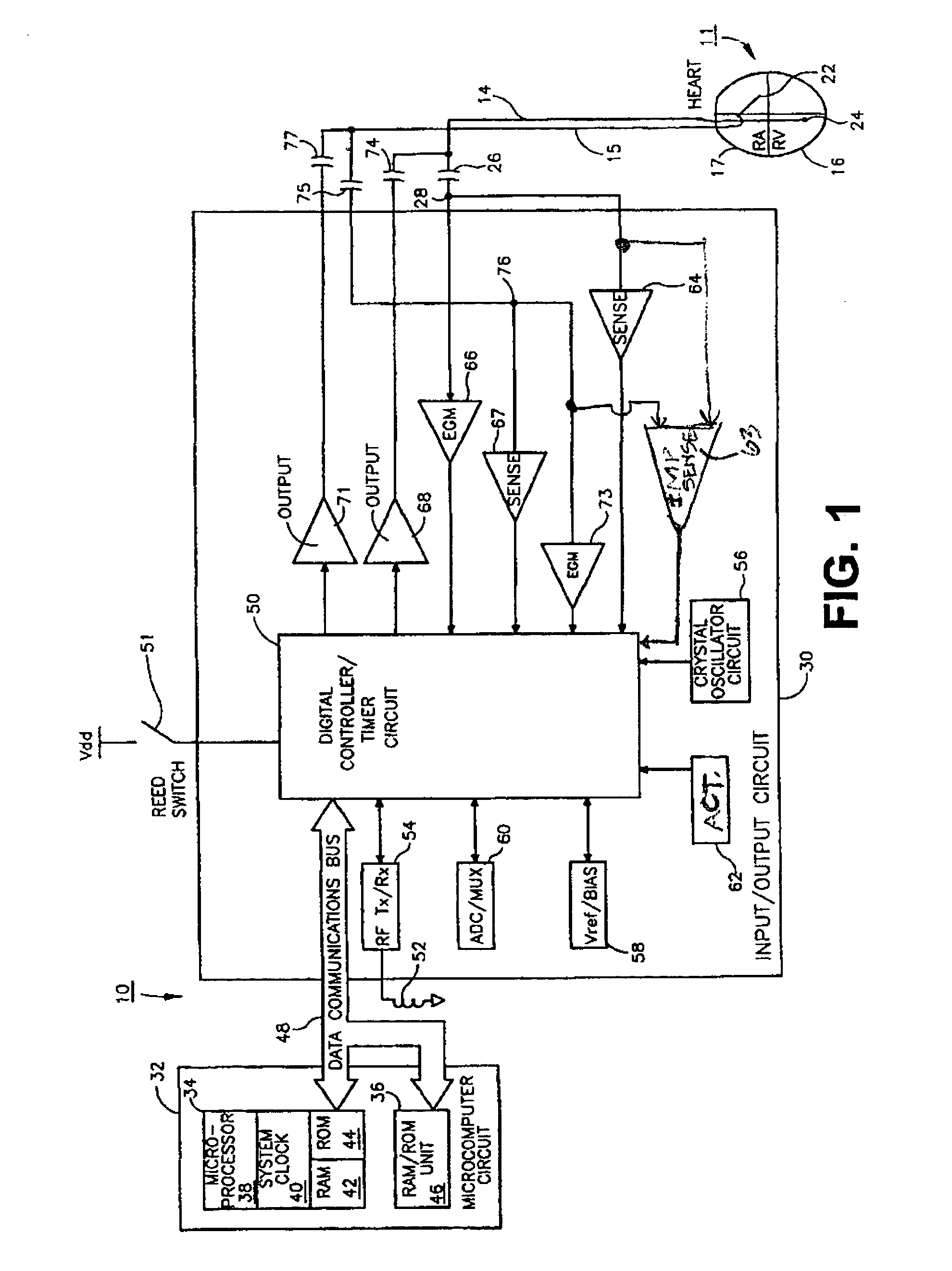
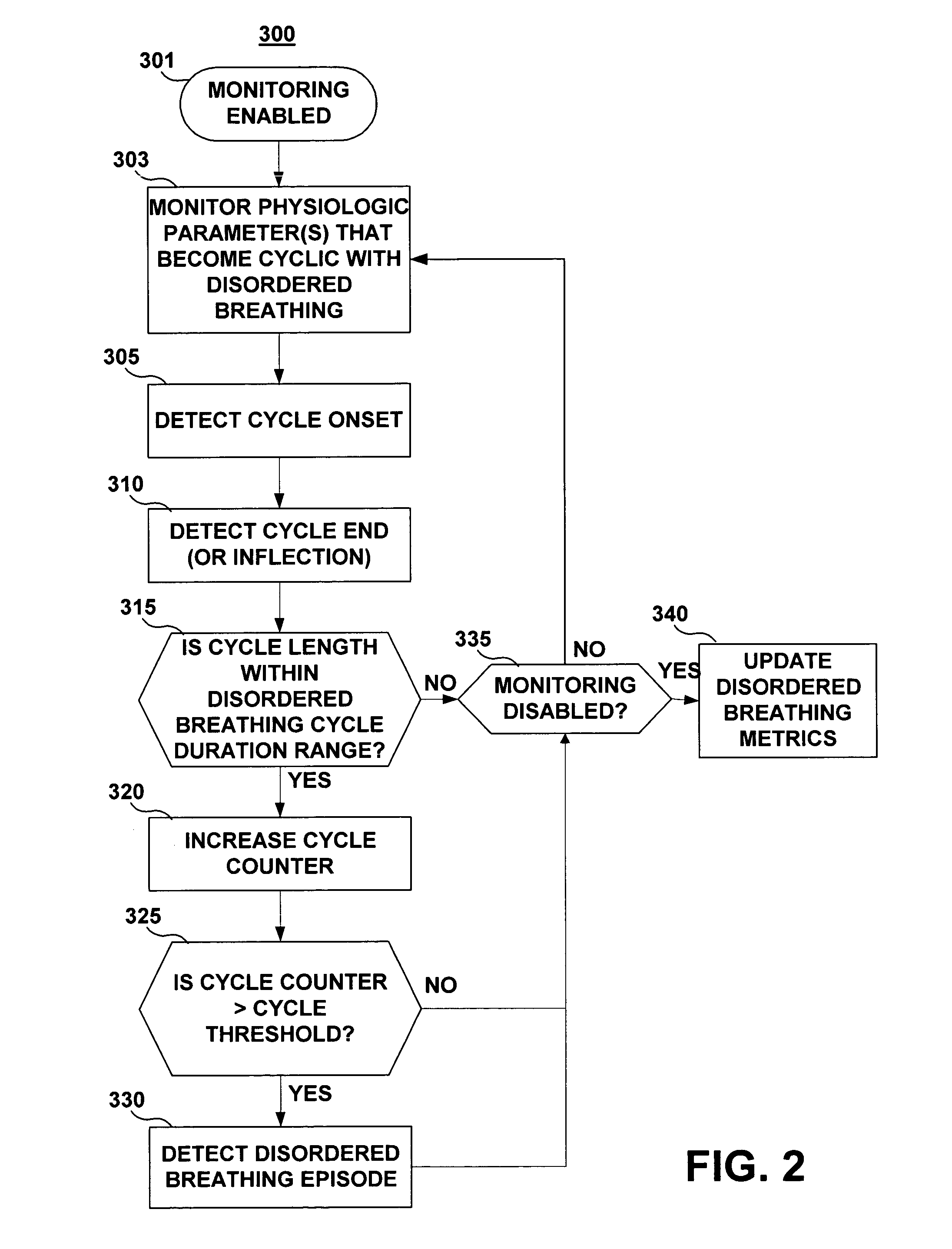
Apparatus and method for monitoring for disordered breathing
ActiveUS20050119711A1Increased computational burdenElectrotherapyCatheterSleep disordered breathingCheyne-stokes breathing
The present invention relates to a device and method for monitoring for sleep disordered breathing or other types of disordered breathing such as Cheyne-Stokes breathing. More specifically, a device and method for detecting disordered breathing is provided that monitors a physiological parameter, which becomes cyclical due to apnea-hyperpnea (or arousal) alternation and provides the basis for the determination of a number of breathing disorder metrics.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for treating cheyne-stokes respiration
ActiveUS20060070624A1Increase flow pressureReduce pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCheyne–Stokes respirationSleep disordered breathing
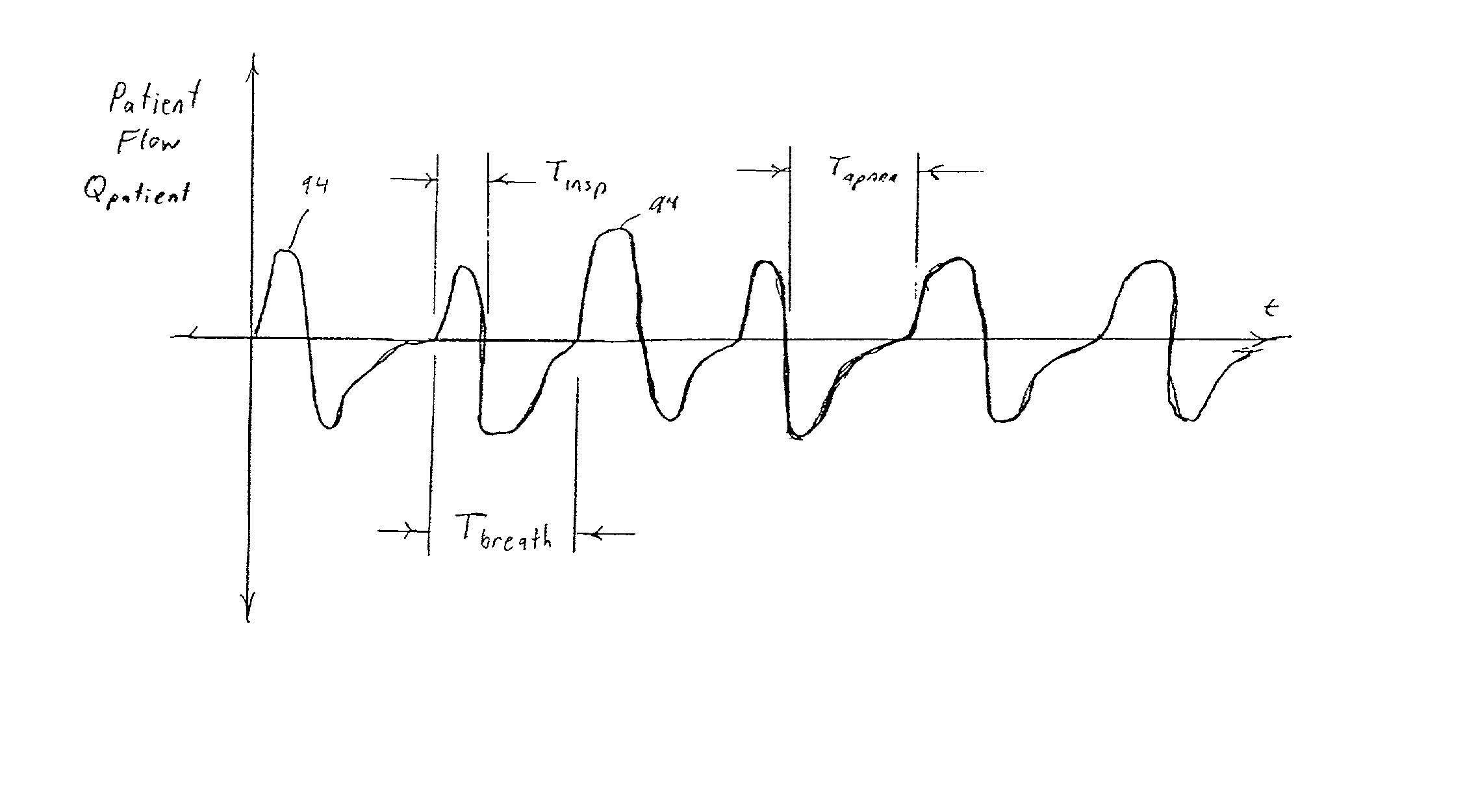
A system and method for delivering a flow of breathing gas to an airway of a patient. The system monitors a characteristic that varies based on variations of the flow of the breathing gas and determines a Target Flow for the gas to be delivered to the patient based on the monitored characteristic. The Target Flow is set to a level sufficient to treat Cheyne-Stokes respiration or a sleep disordered breathing event. The system also alters the Target Flow based on a determination that the patient is experiencing a sleep disordered breathing event. In a further embodiment, the system determines an apnea detection time (Tapnea) as Tinsp plus a constant, and delivers a machine triggered breath if an amount since the start of inspiration reaches Tapnea. Yet another embodiment, monitors the characteristic during an inspiratory phase of a respiratory cycle, and controls the flow of gas during the inspiratory phase of the respiratory cycle based on a result of this comparison.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Method for detecting Cheyne-Stokes respiration in patients with congestive heart failure
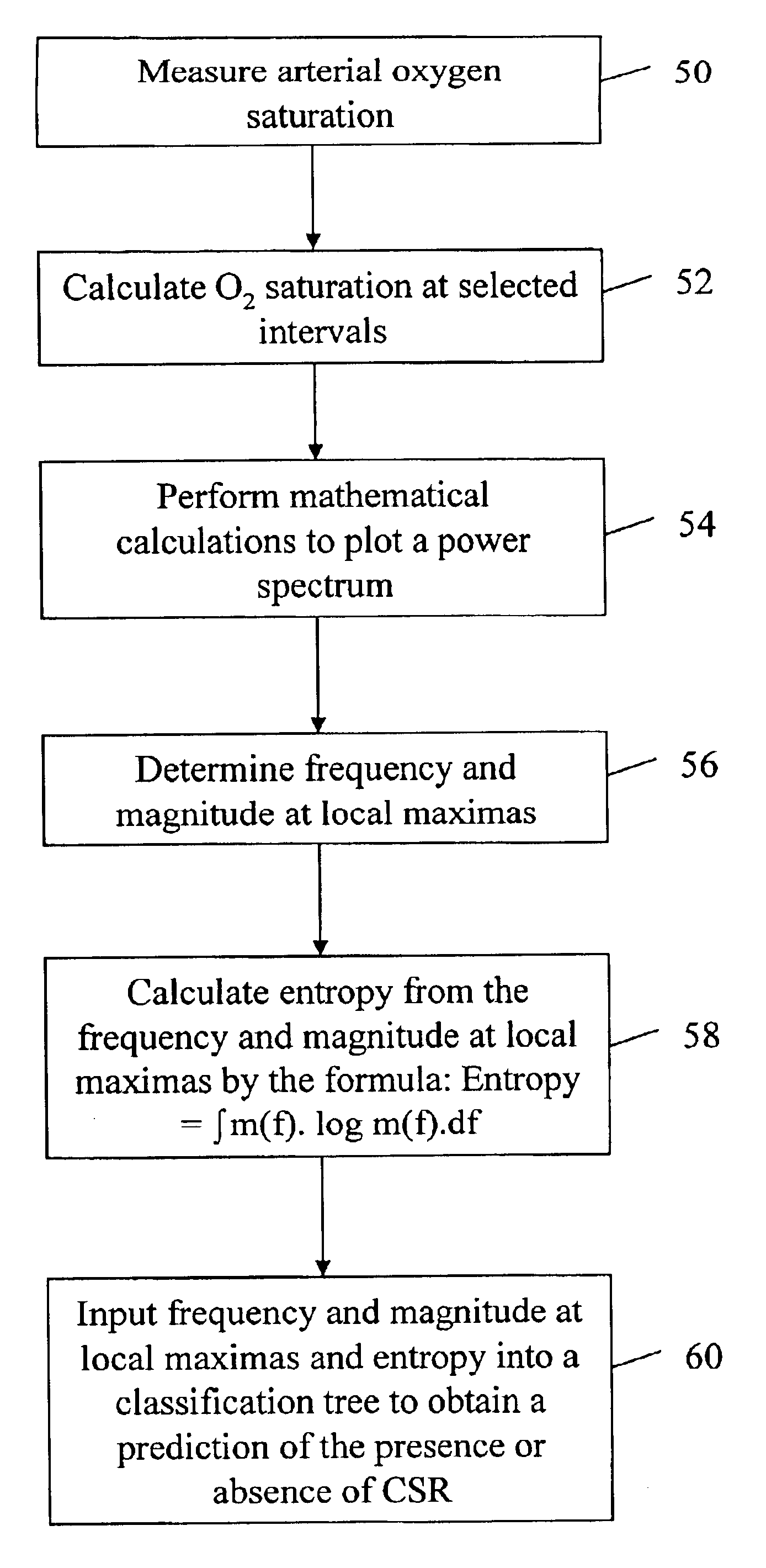
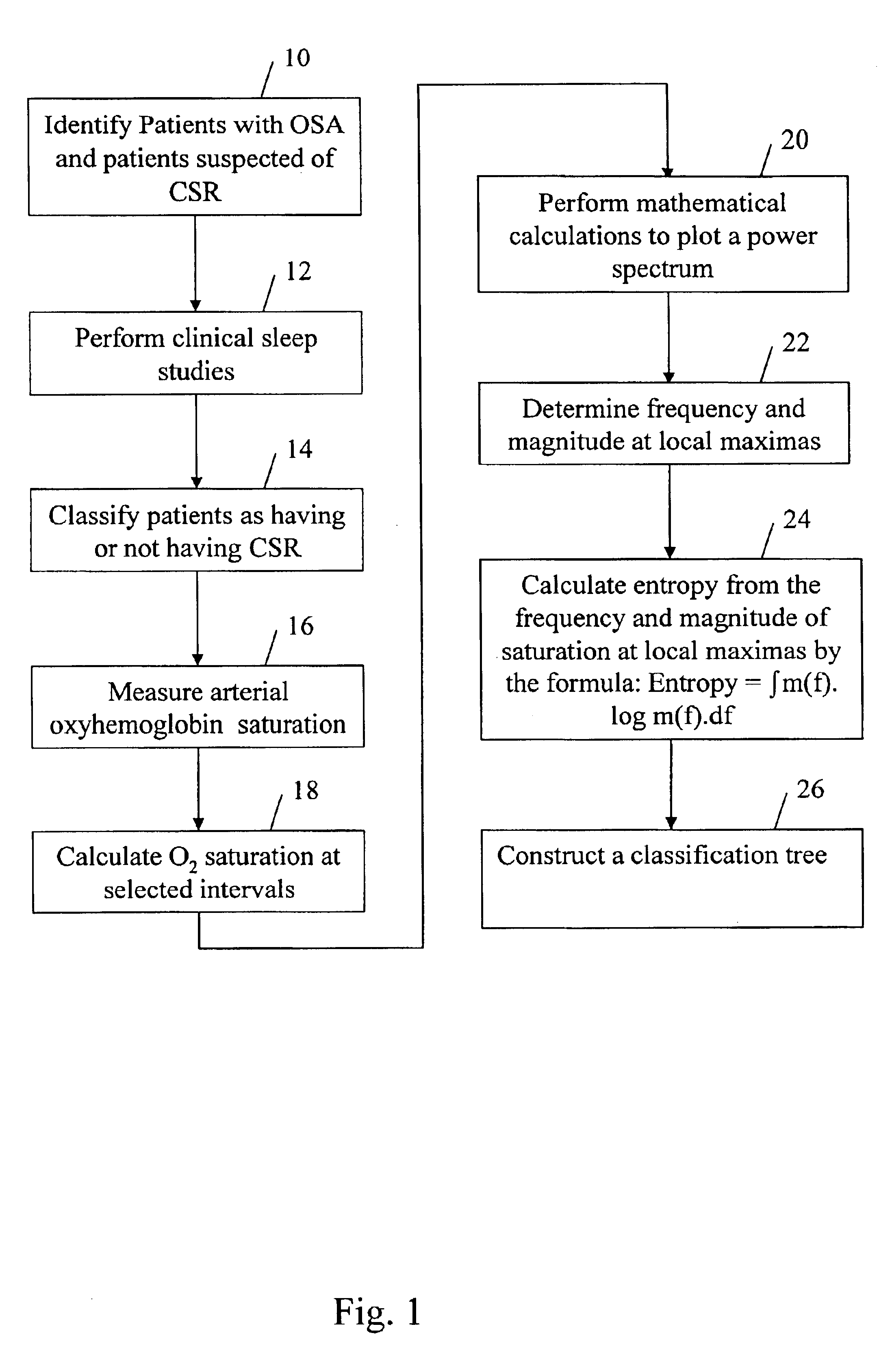
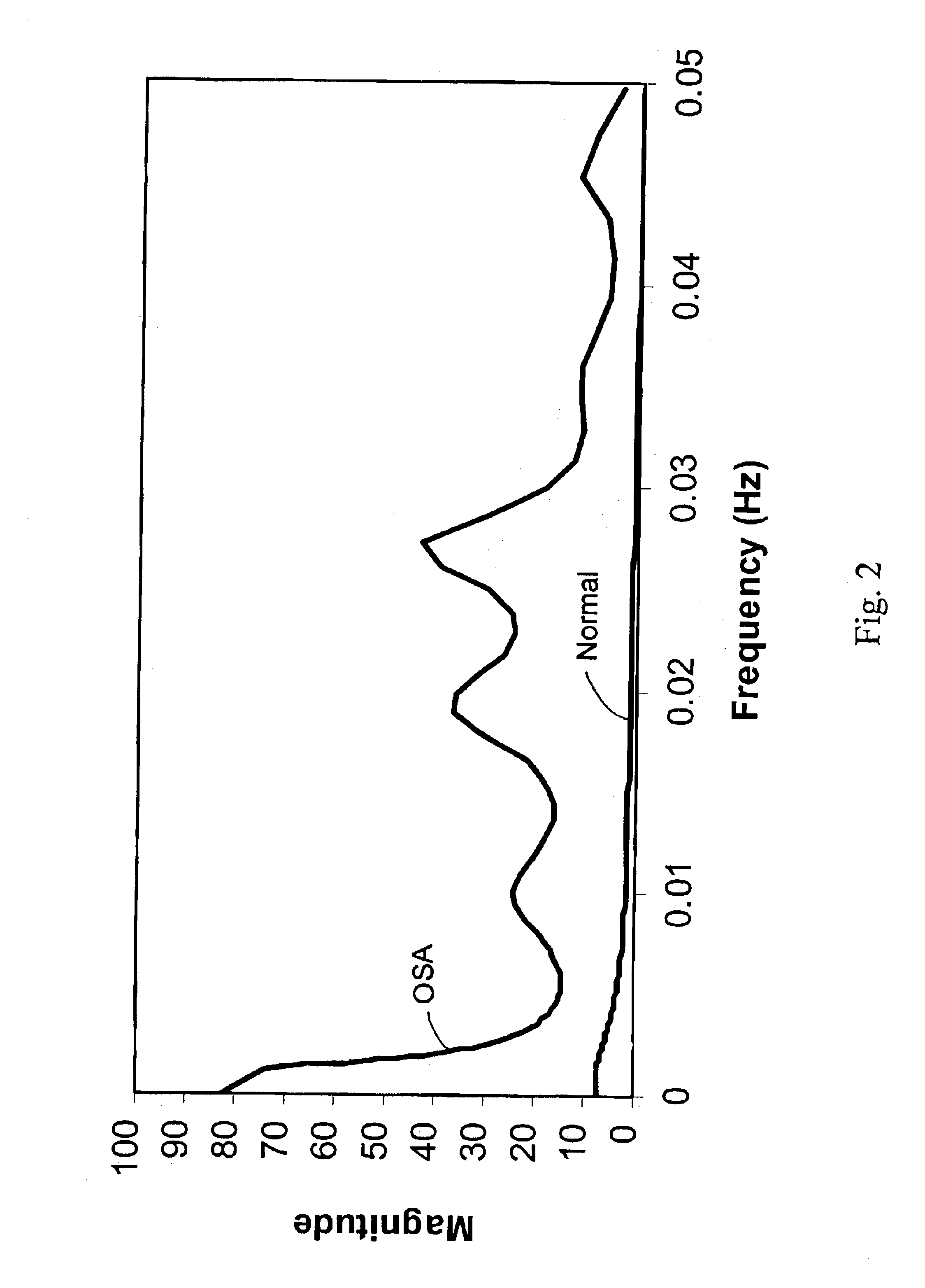
The present invention provides a diagnostic tool for detection of Cheyne-Stokes Respiration (CSR). This invention also provides a method for development of the diagnostic tool. The method comprises the steps of performing overnight oximetry recordings in patients suspected of sleep disordered breathing. Spectral analysis is performed on the oximetry recordings to obtain a set of parameters which can be used in the construction of a classification tree and a trained neural network. The diagnostic tools of the present invention can be used for classification of a patient as having CSR or obstructive sleep apnea.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS +1
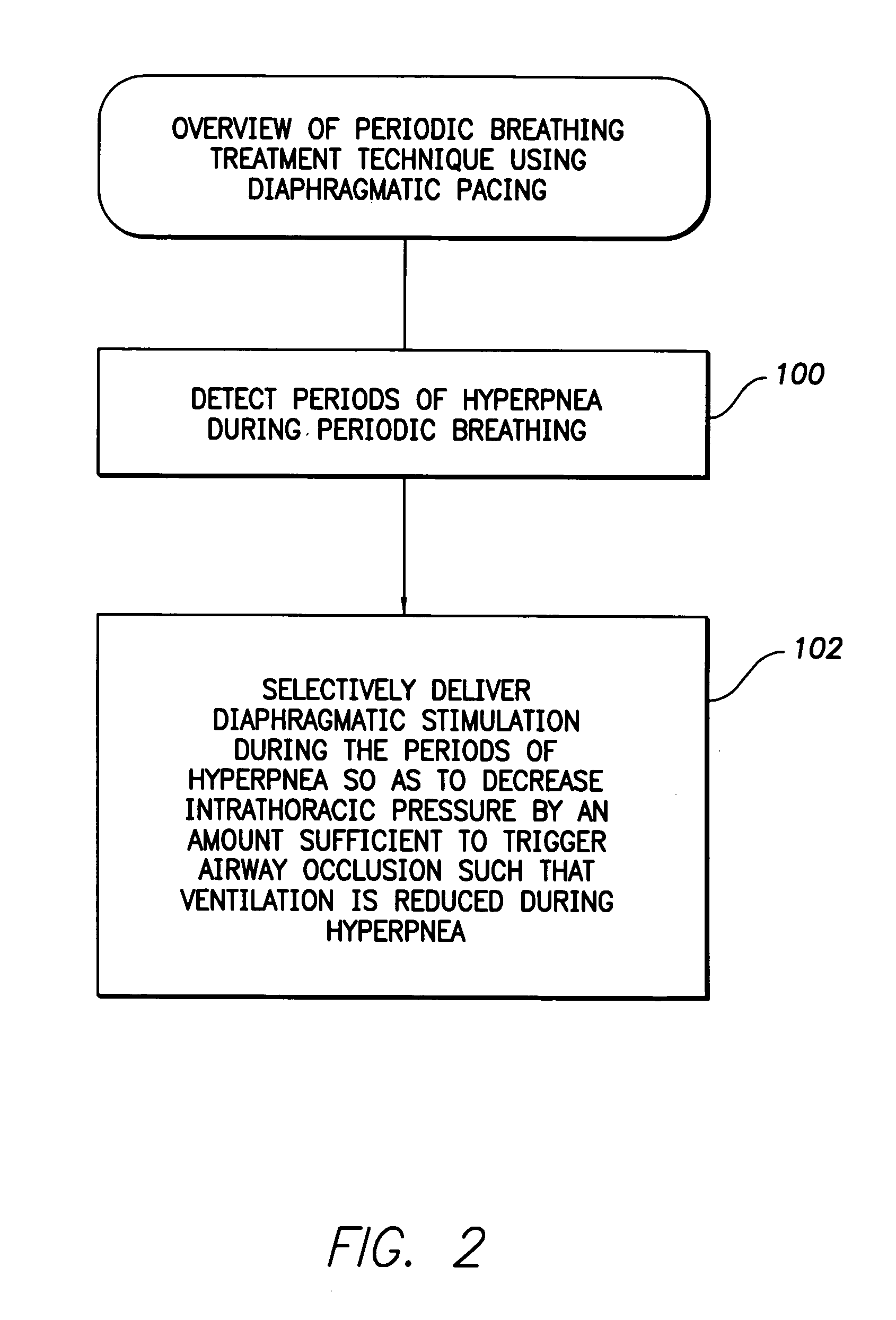
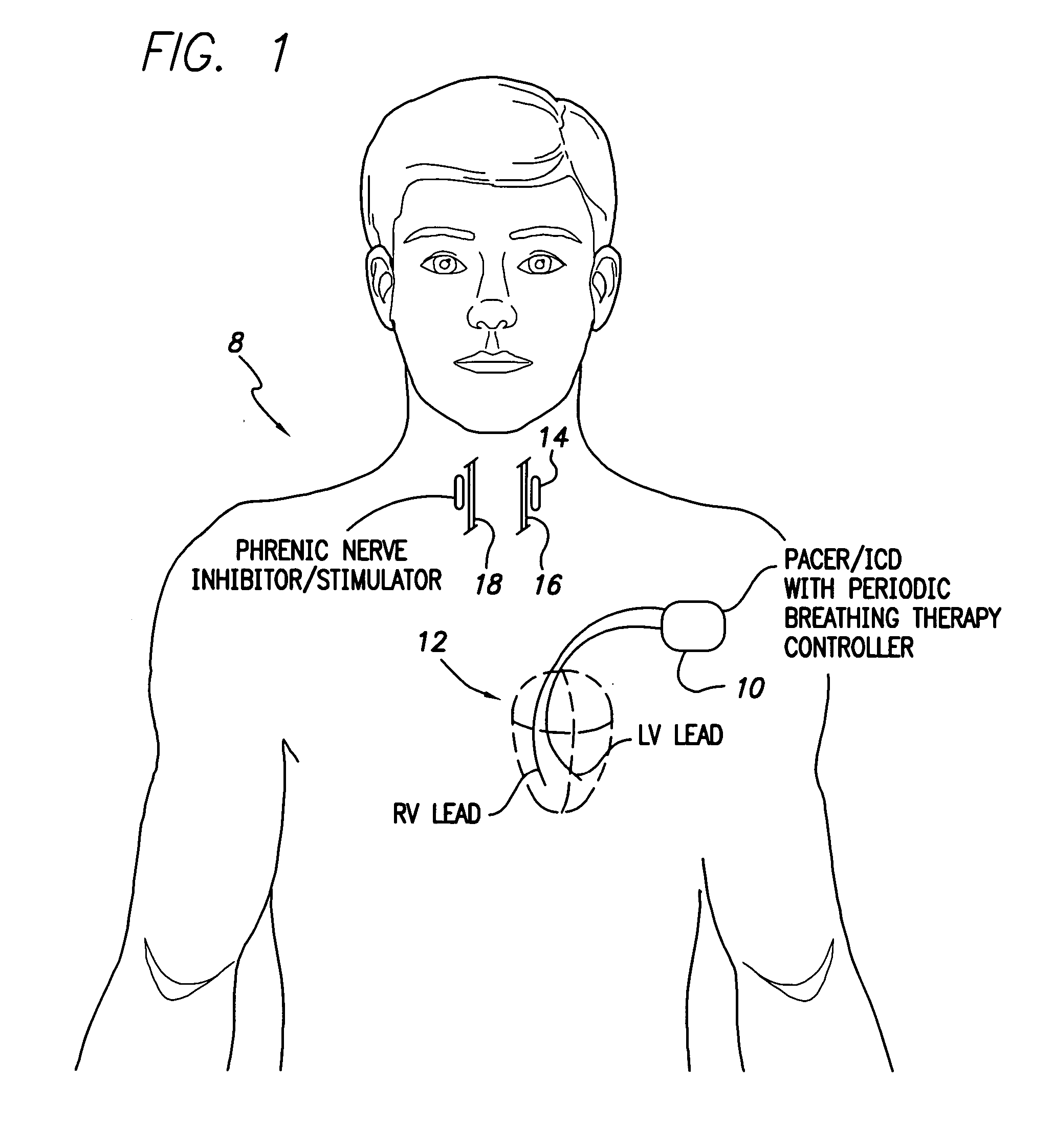
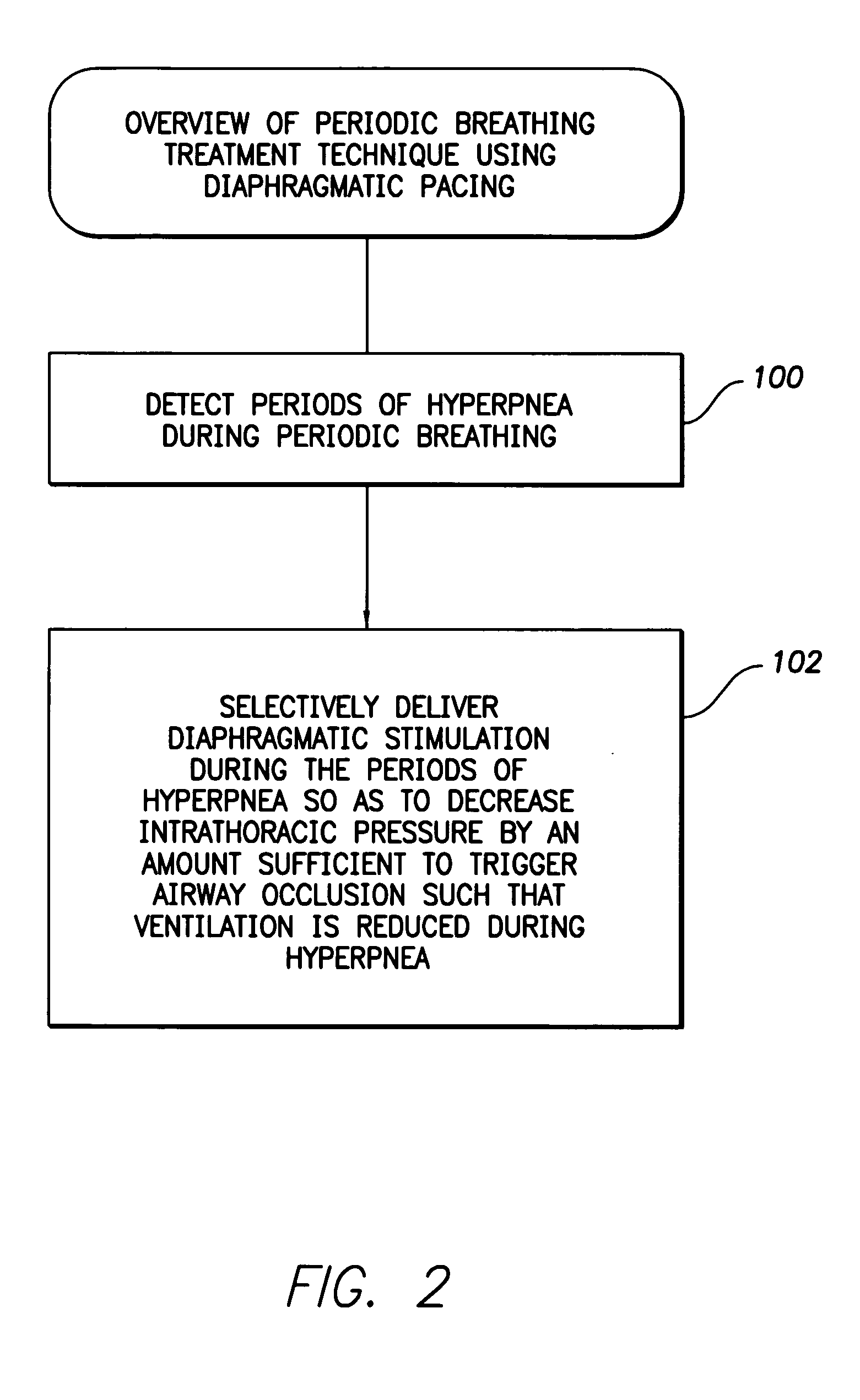
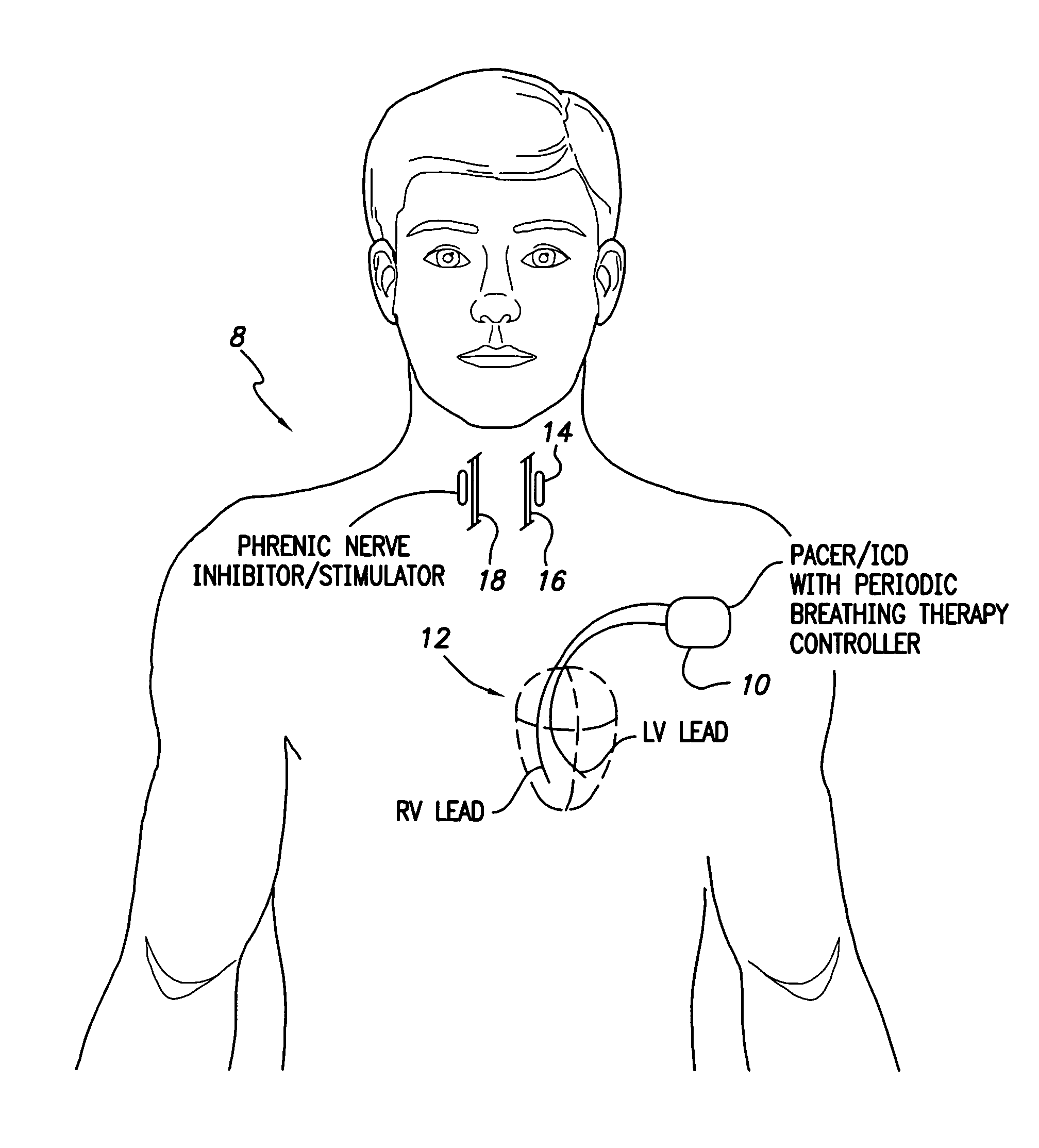
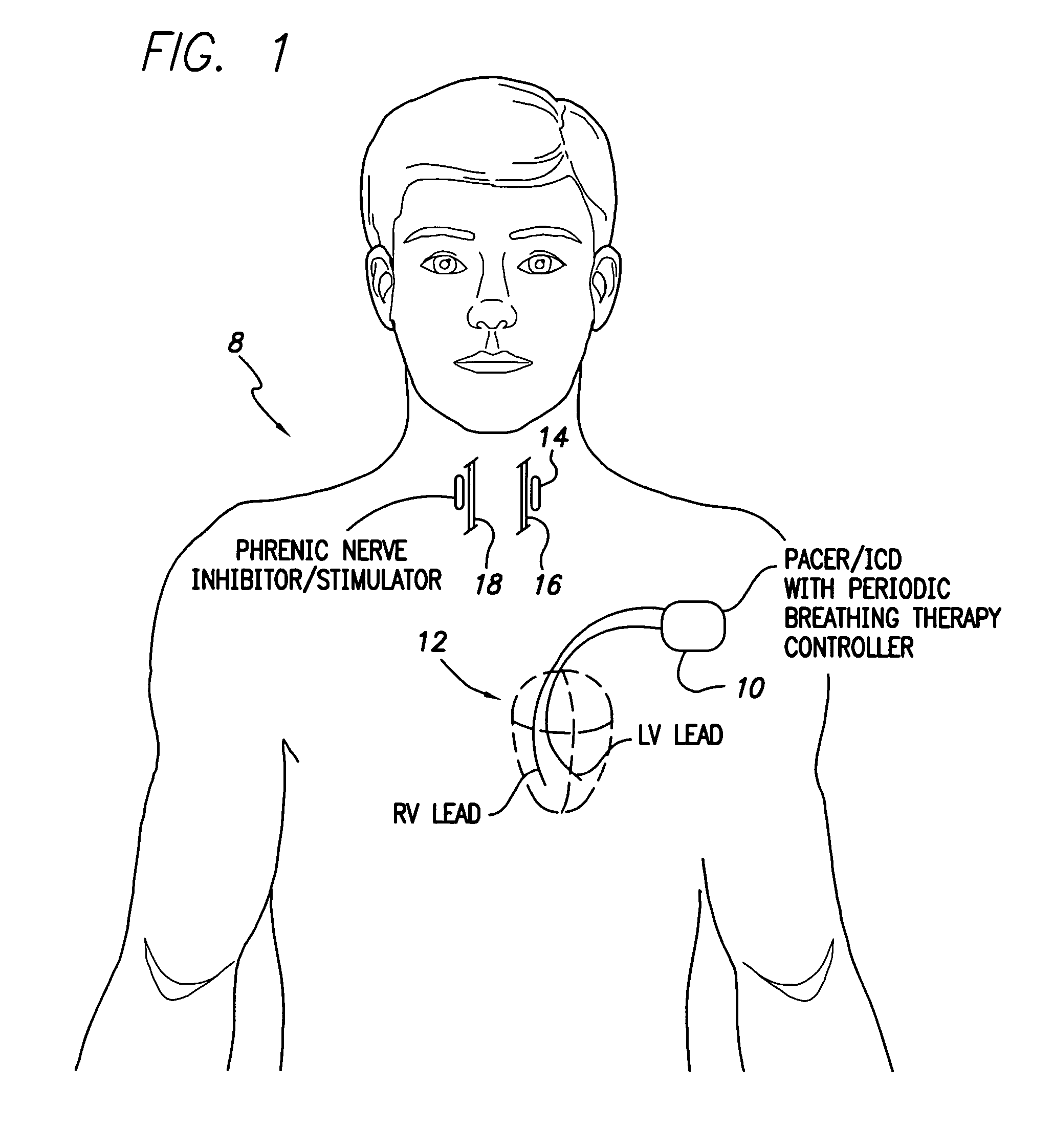
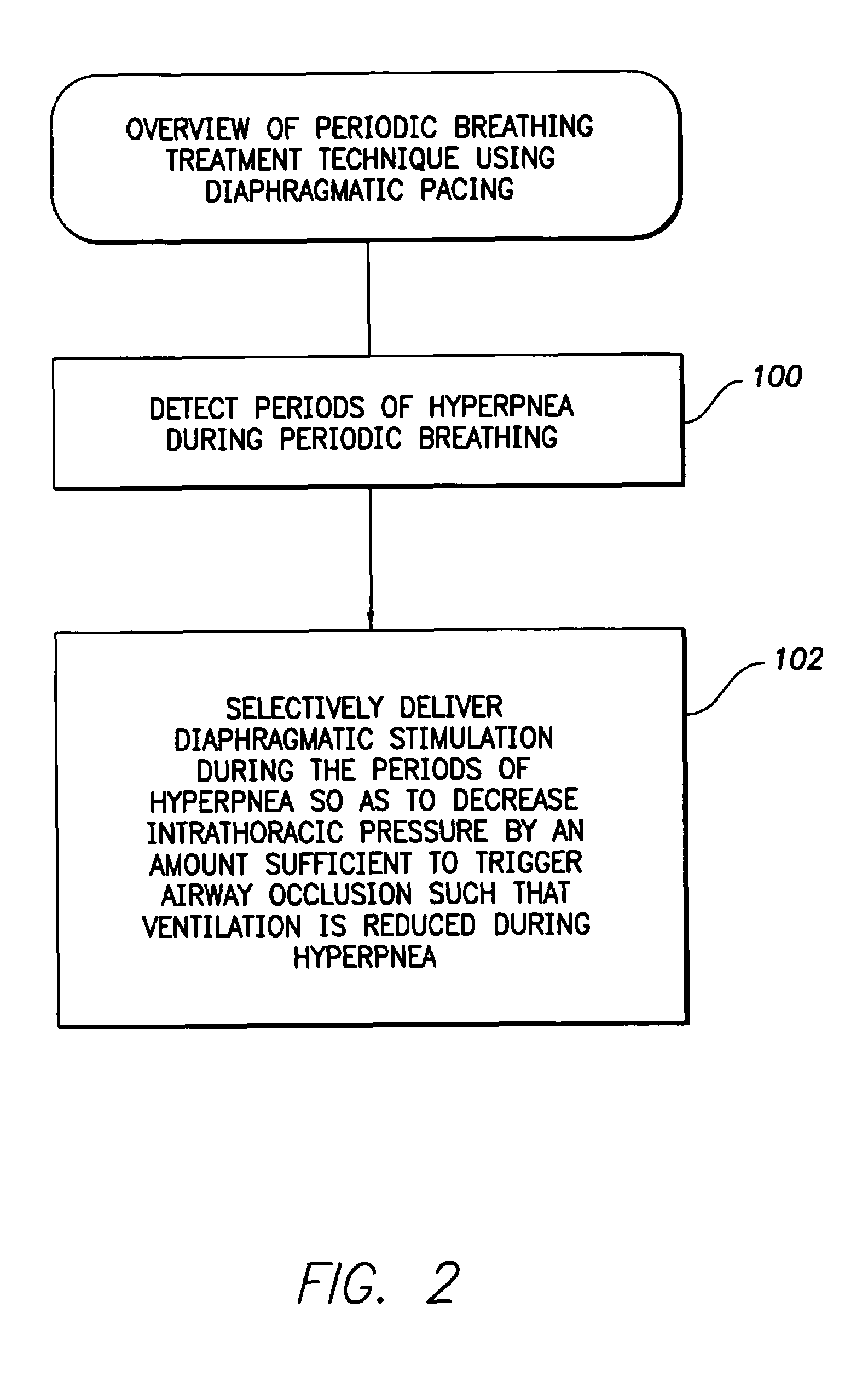
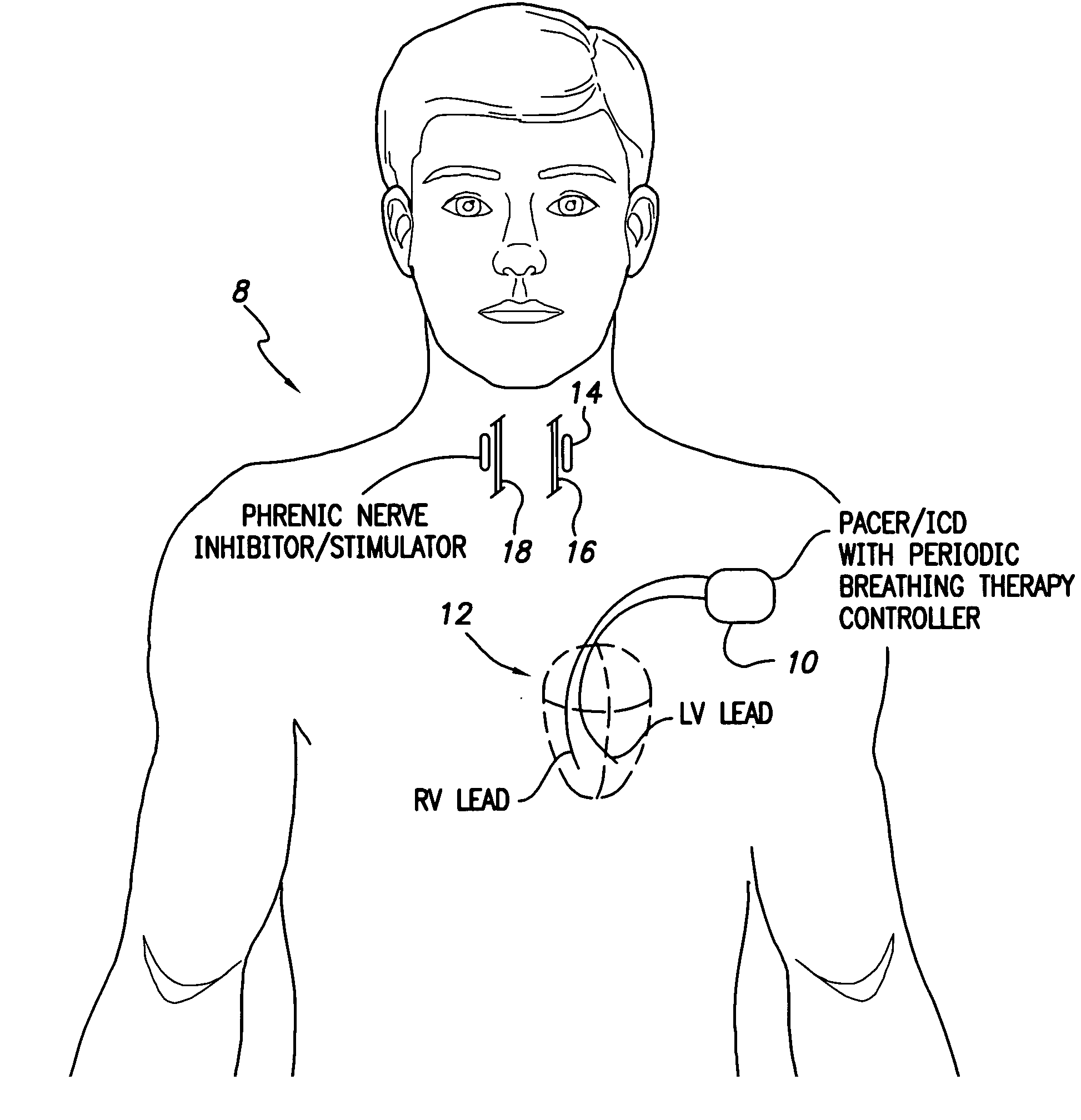
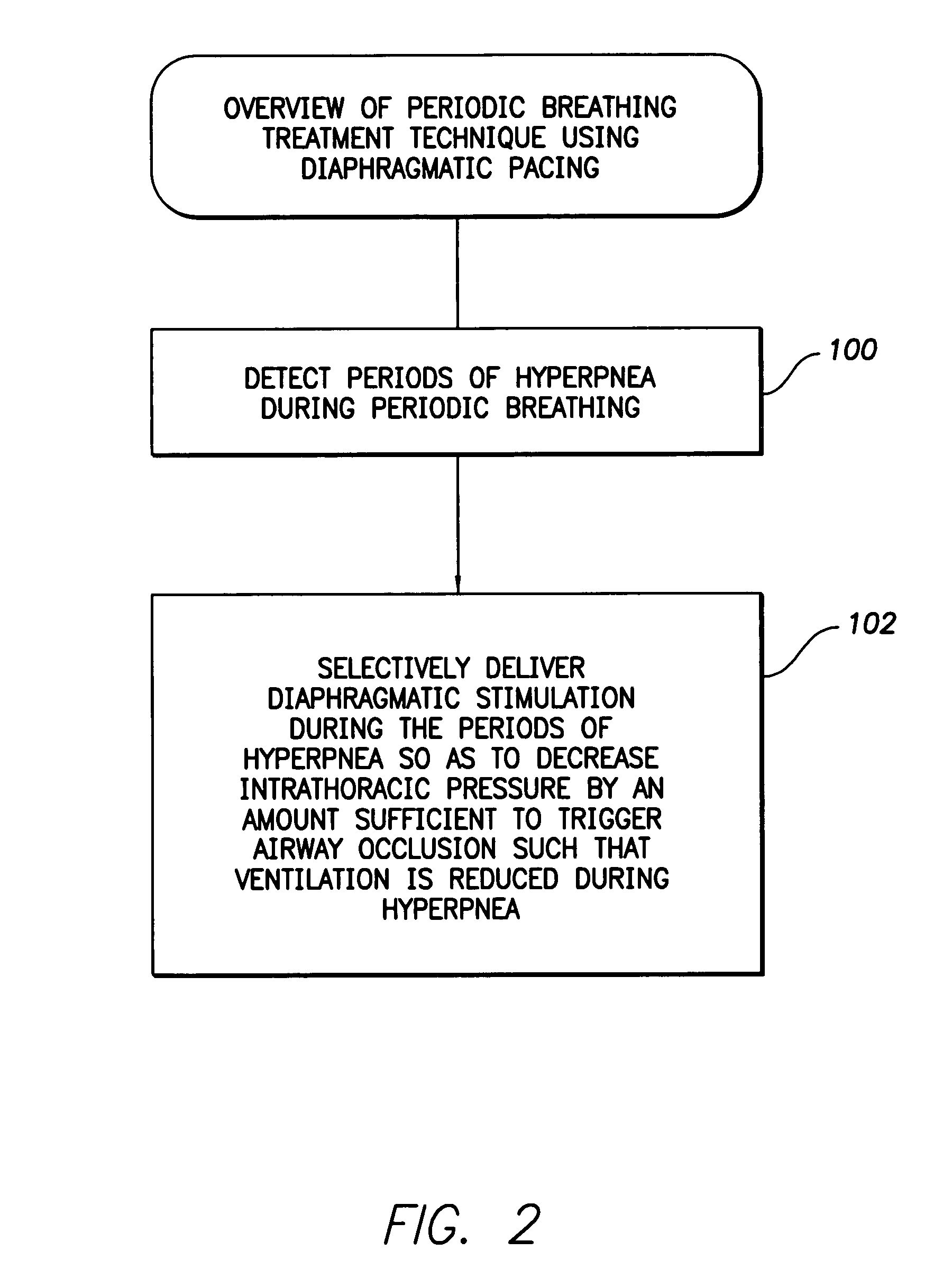
System and method for applying therapy during hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing using an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7082331B1Reducing cyclic blood chemistry imbalanceReduce ventilationElectrotherapyCheyne–Stokes respirationTreatment typology
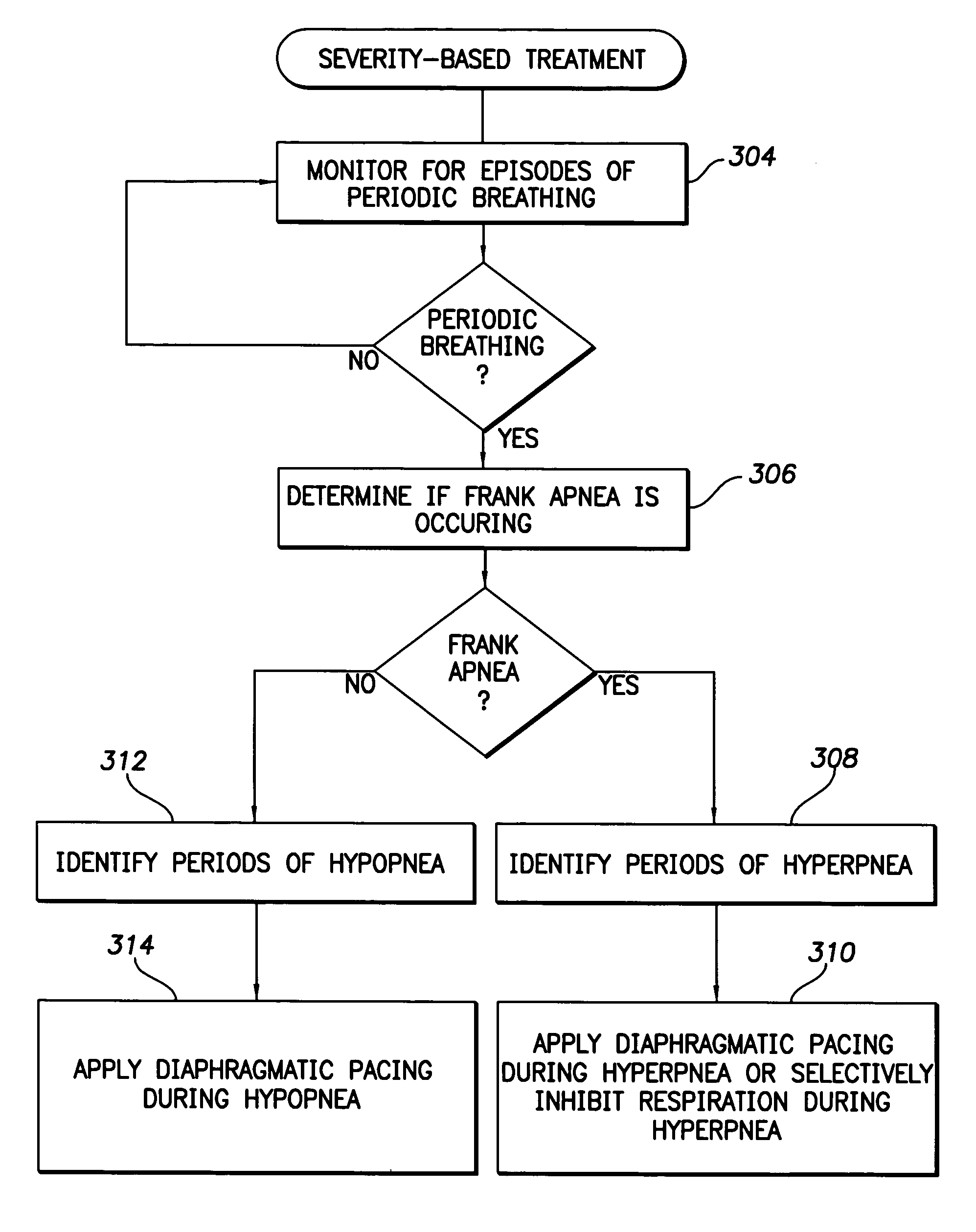
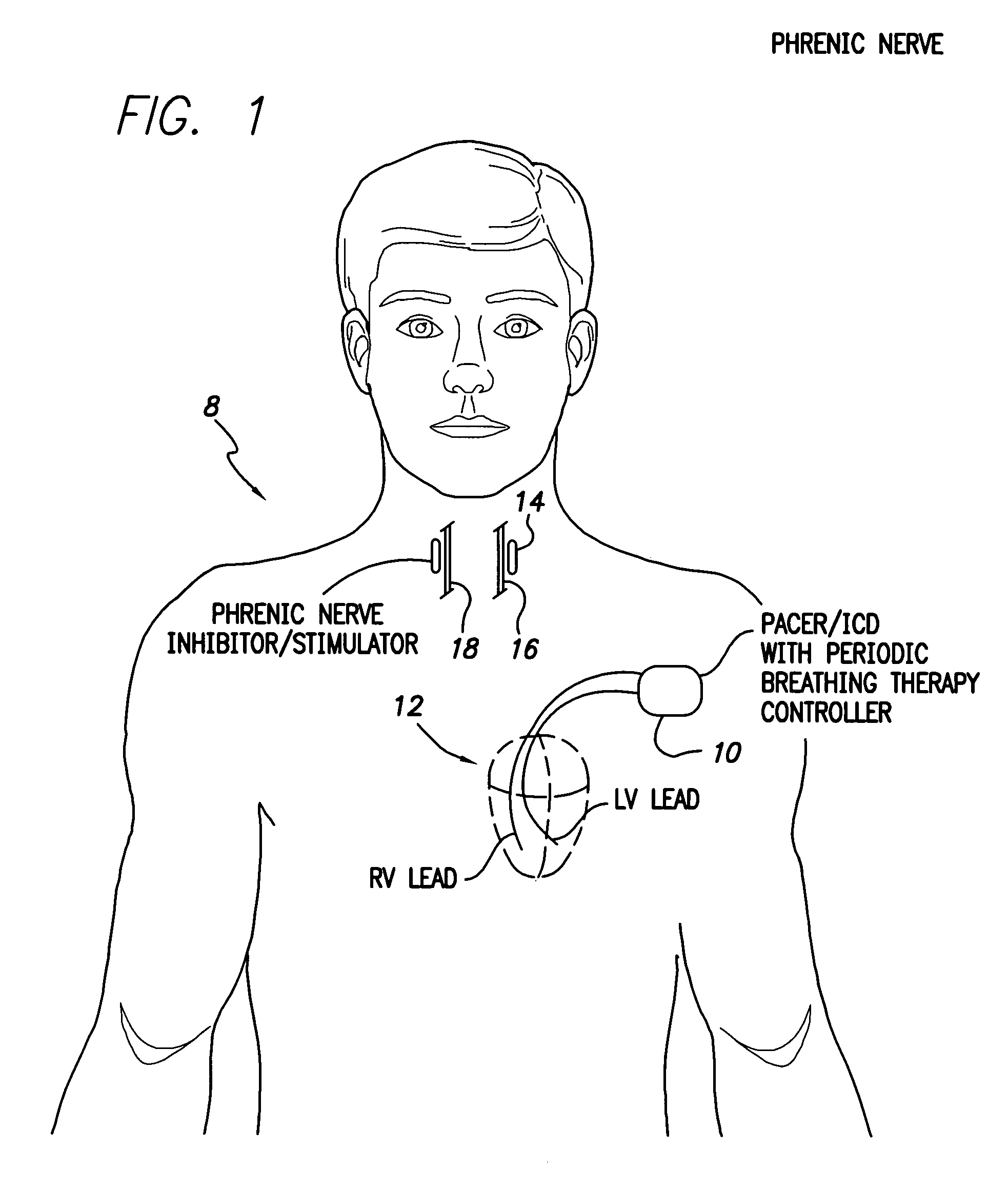
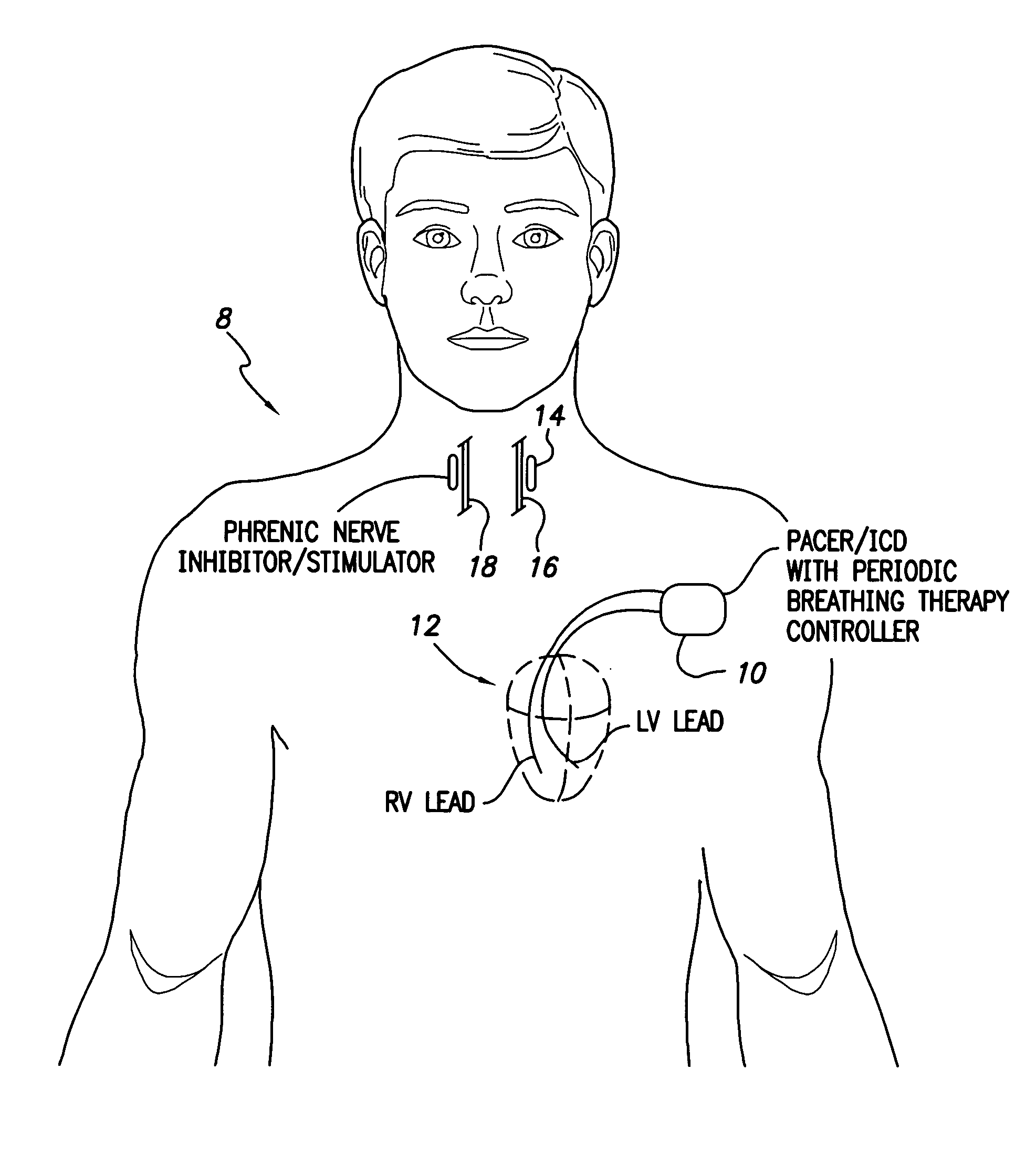
Techniques are provided for treating periodic breathing, such as Cheyne-Stokes Respiration, using an implantable medical system. In one technique, diaphragmatic stimulation is delivered during a hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing via electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves. Diaphragmatic stimulation is synchronized with intrinsic inspiration so as to increase the amplitude of diaphragmatic contraction during inspiration. This tends to decrease intrathoracic pressure leading to occlusion of the respiratory airway. Occlusion reduces actual ventilation during hyperpnea, thus reducing the cyclic blood chemistry imbalance that sustains periodic breathing so as to either mitigate periodic breathing or eliminate it completely. In another technique, respiration is instead inhibited during the hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing by blocking phrenic nerve signals to the extent necessary to reduce ventilation to terminate periodic breathing or at least mitigate its severity. Techniques are also described for controlling the type of therapy applied in response to periodic breathing.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and Method for Treating Ventilatory Instability
ActiveUS20080302364A1Increase COIncrease pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCheyne-stokes breathingCheyne–Stokes respiration
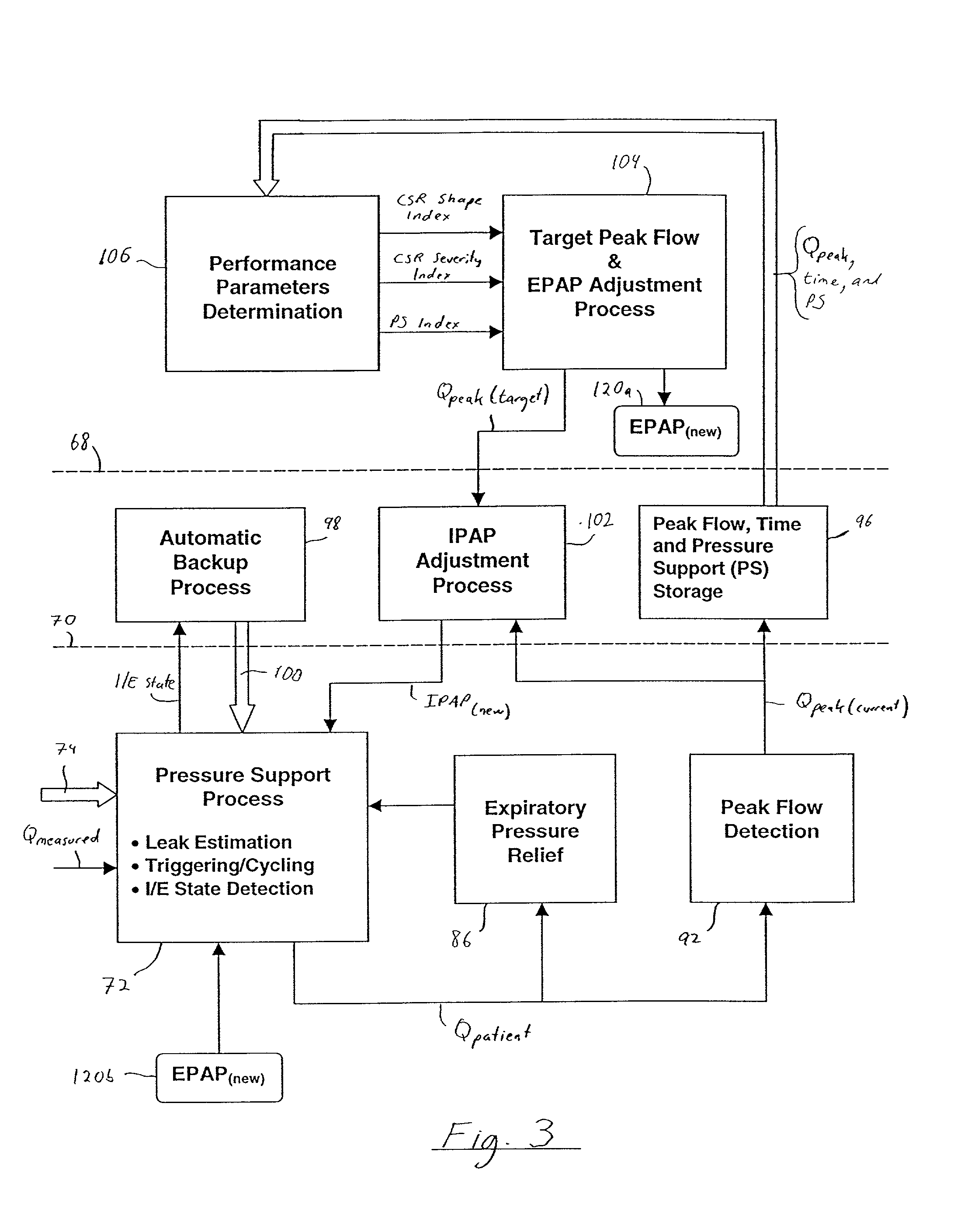
A therapy system adapted to treat a patient's ventilatory instability using a ventilatory therapy, a gas modulation therapy, or both. The algorithm implemented by the therapy system monitors the ventilatory instability, such as Cheyne Stokes Respiration (CSR), mixed apneas, CPAP emergent apneas, and complex sleep disordered breathing (CSDB) and treats the ventilatory instability. The algorithm also determine a reference point with respect to the ventilatory instability. The therapy delivery system initiate the treatment based on the reference point.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Method and apparatus for providing variable positive airway pressure
InactiveUS20020088465A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive airway pressureCheyne–Stokes respiration
A method and apparatus for treating a breathing disorder and, more particularly, a method and apparatus for providing a pressurized air flow to an airway of a patient to treat congestive heart failure in combination with Cheyne-Stokes respiration and / or sleep apnea or other breathing disorders. A positive airway pressure ventilator is utilized in combination with an algorithm that adjusts IPAP and EPAP in order to counter a Cheyne-Stokes breathing pattern. Cheyne-Stokes respiration is detected by monitoring a peak flow of the patient.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Apparatus and method for monitoring for disordered breathing
ActiveUS7438686B2Increased computational burdenElectrotherapyCatheterSleep disordered breathingCheyne–Stokes respiration
The present invention relates to a device and method for monitoring for sleep disordered breathing or other types of disordered breathing such as Cheyne-Stokes breathing. More specifically, a device and method for detecting disordered breathing is provided that monitors a physiological parameter, which becomes cyclical due to apnea-hyperpnea (or arousal) alternation and provides the basis for the determination of a number of breathing disorder metrics.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
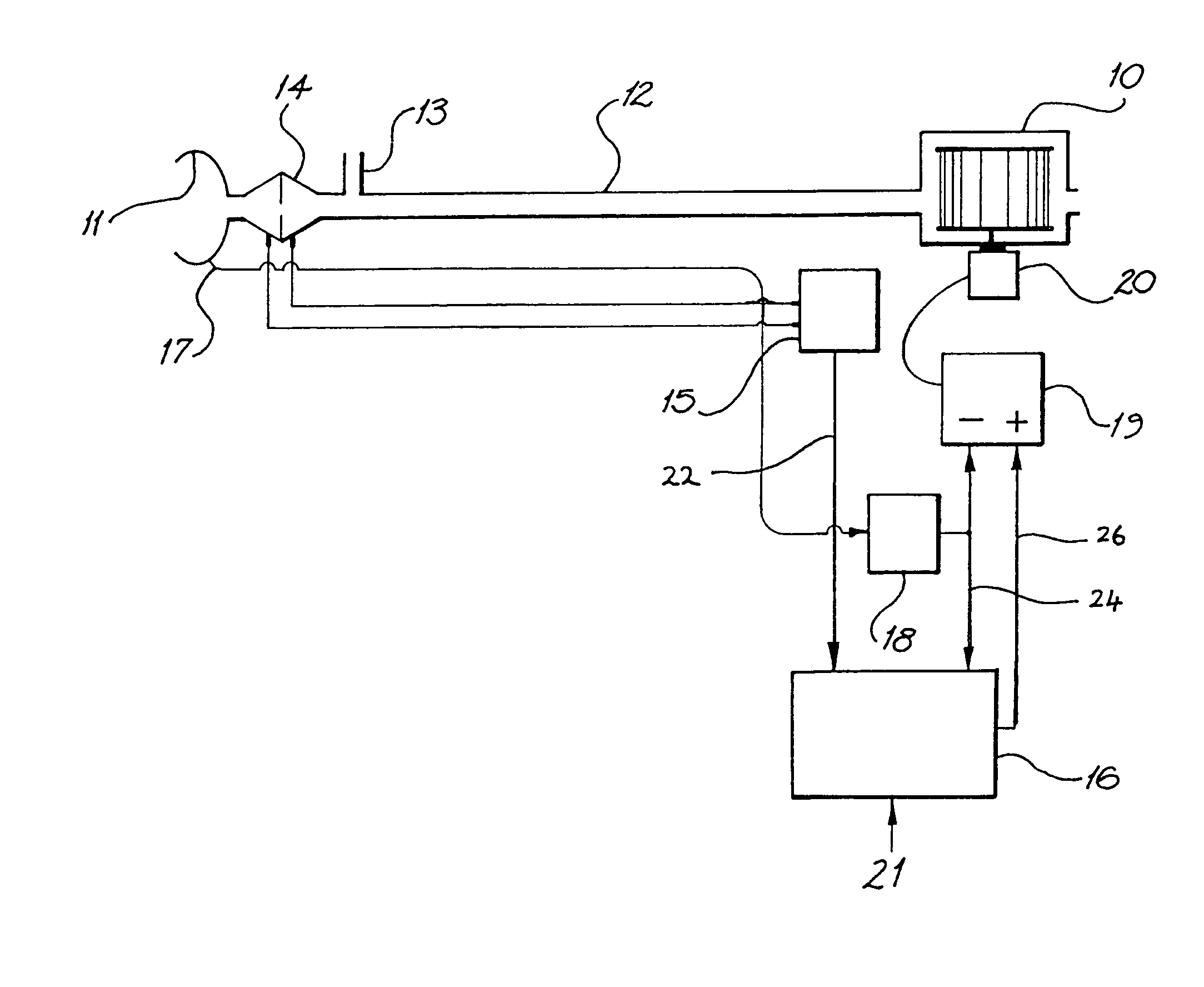
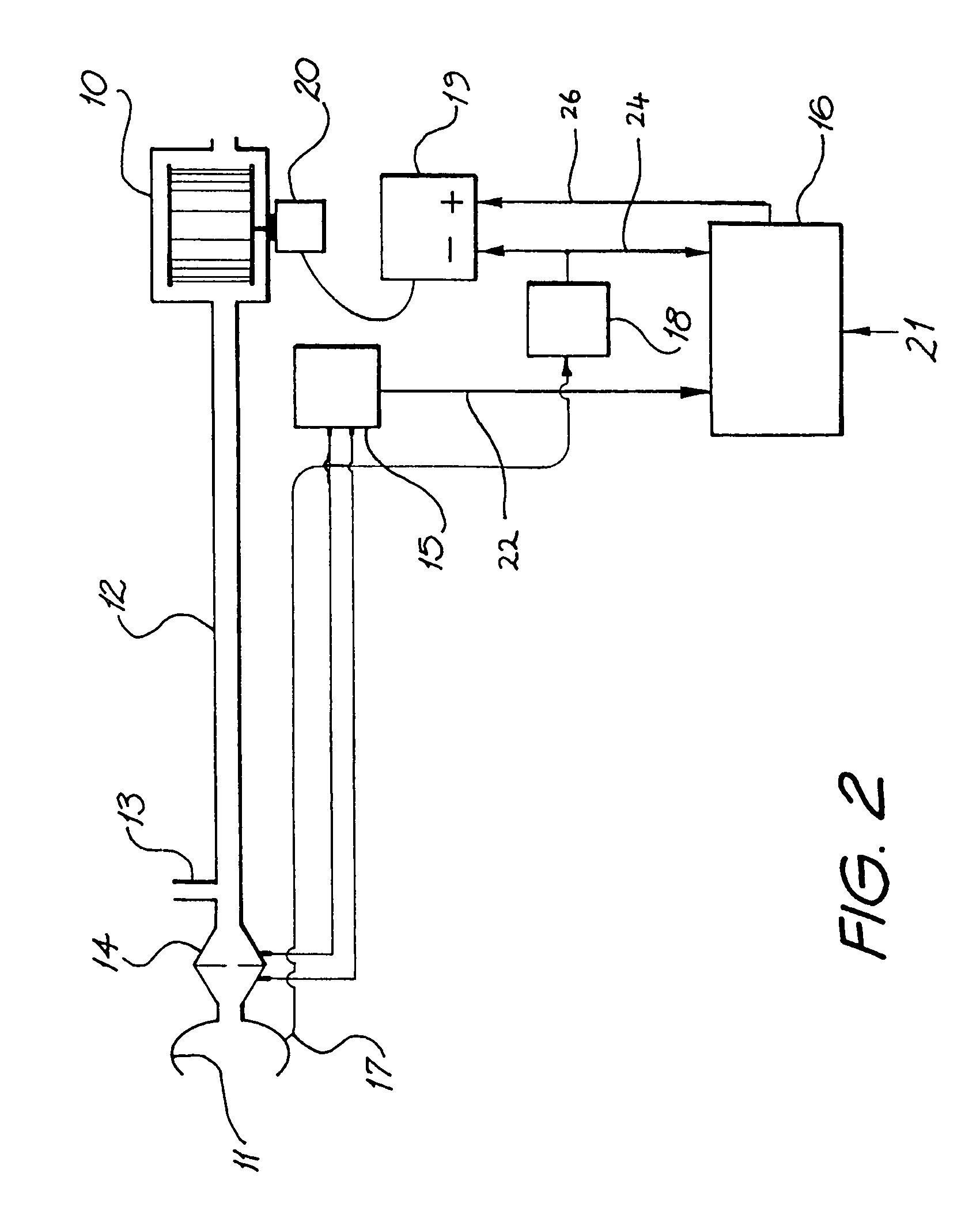
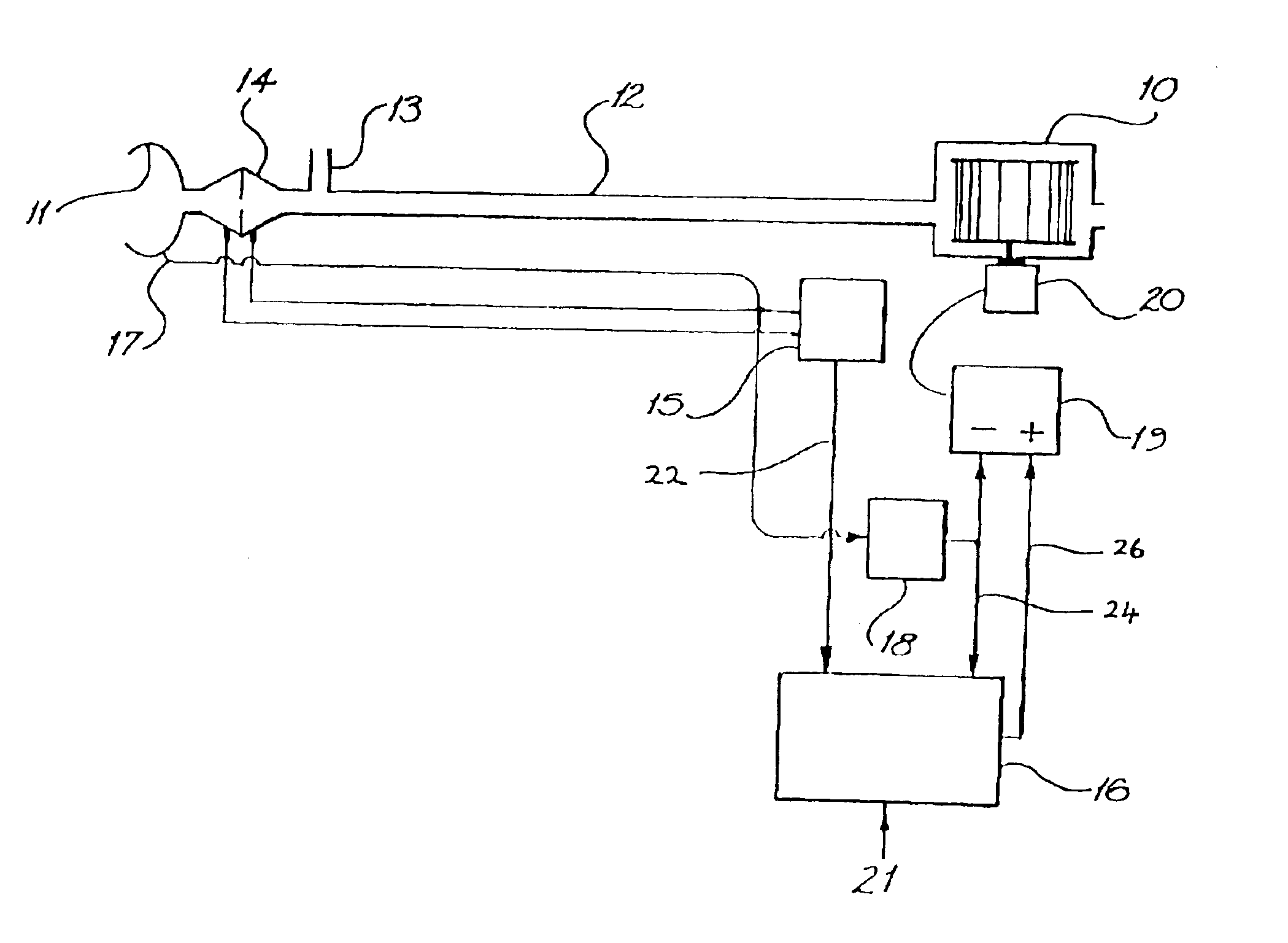
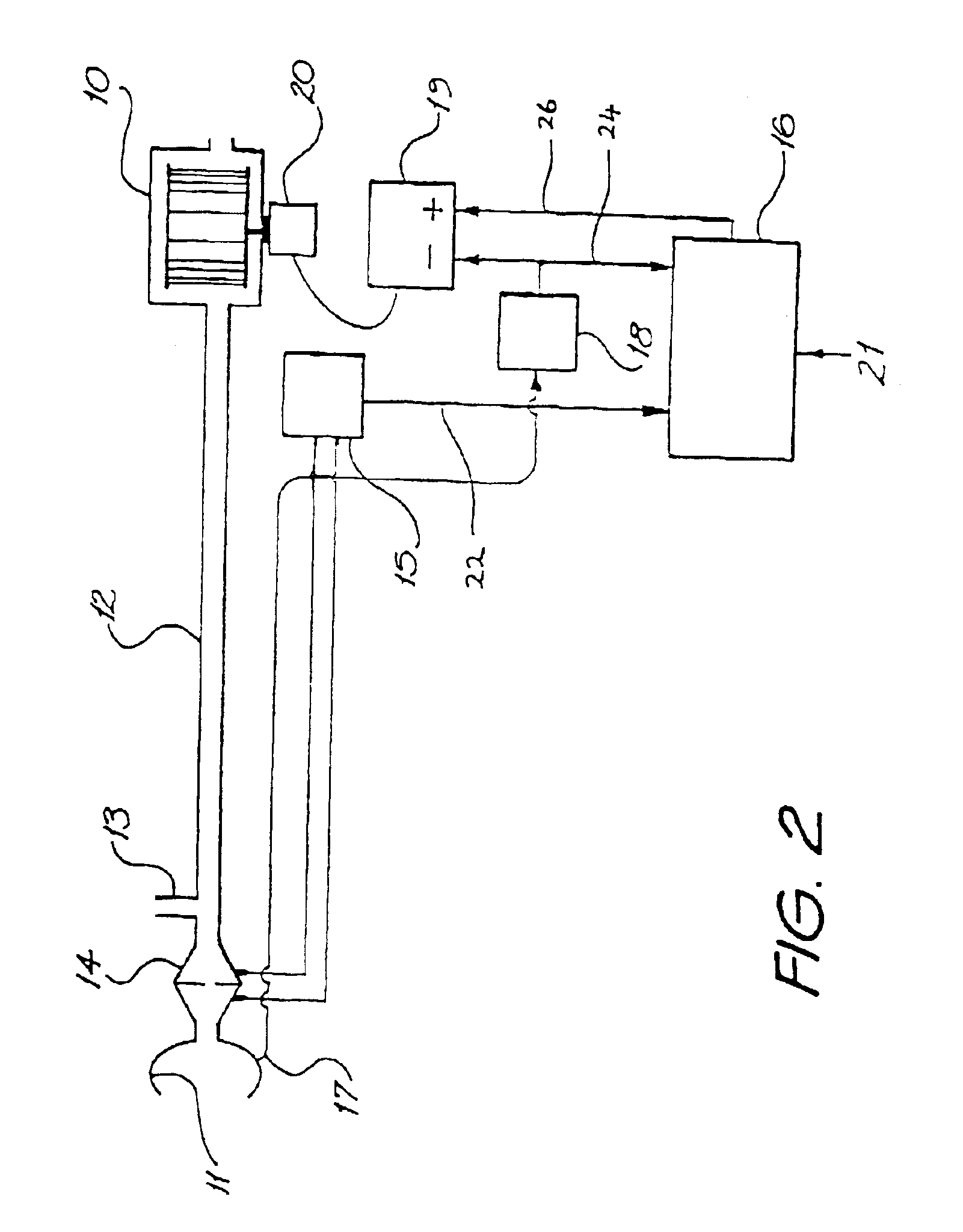
Ventilatory assistance for treatment of cardiac failure and Cheyne-Stokes breathing
InactiveUS7077132B2Signs improvedSymptoms improvedRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLow-pass filterPositive pressure
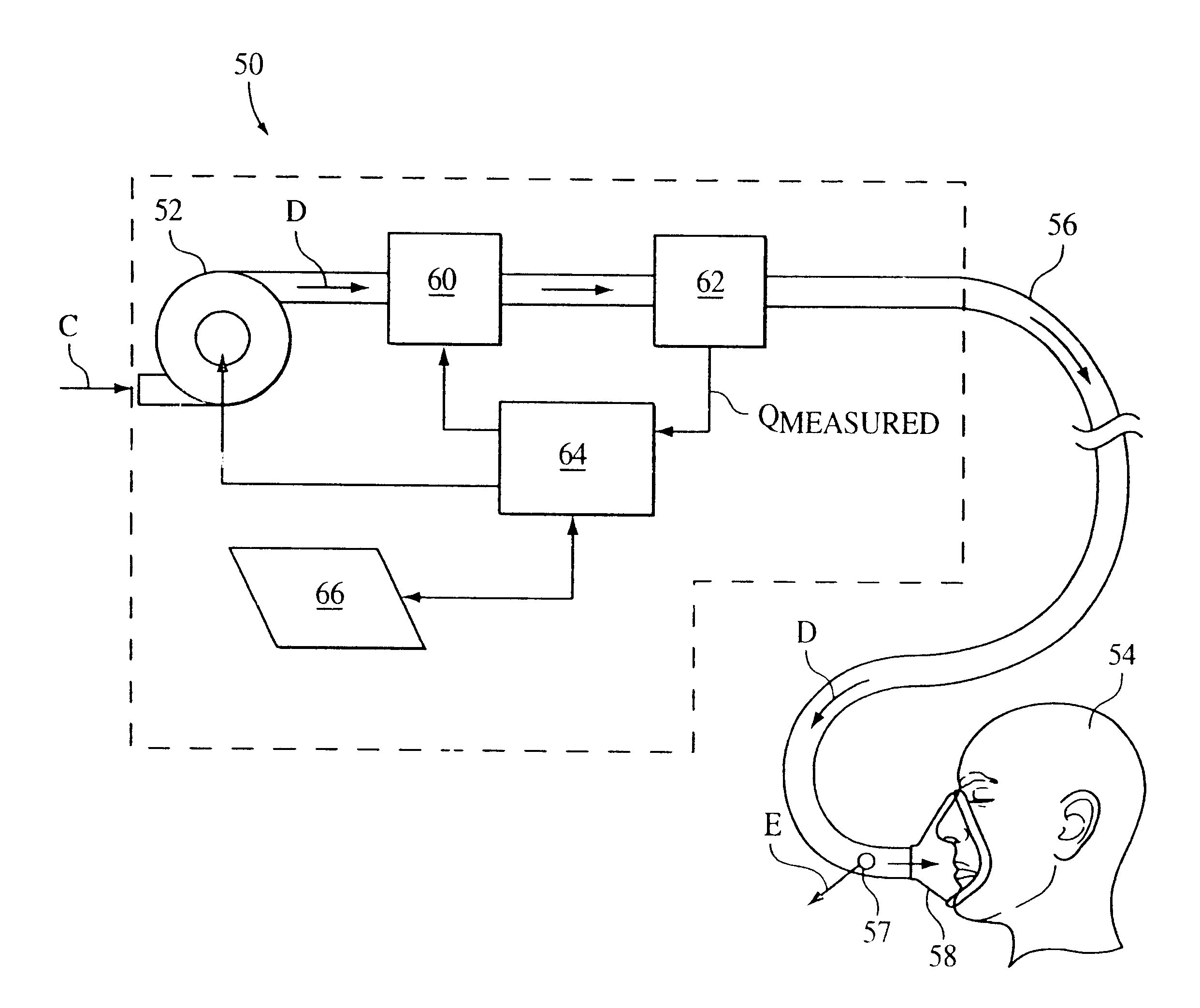
Method and apparatus for the treatment of cardiac failure, Cheyne Stokes breathing or central sleep apnea are disclosed. A subject is provided with ventilatory support, for example positive pressure ventilatory support using a blower and mask. Respiratory airflow is determined. From the respiratory airflow are derived a measure of instantaneous ventilation (for example half the absolute value of the respiratory airflow) and a measure of longterm average ventilation (for example the instantaneous ventilation low pass filtered with a 100 second time constant). A target ventilation is taken as 95% of the longterm average ventilation. The instantaneous ventilation is fed as the input signal to a clipped integral controller, with the target ventilation as the reference signal. The output of the controller determines the degree of ventilatory support. Clipping is typically to between half and double the degree of support that would do all the respiratory work. A third measure of ventilation, for example instantaneous ventilation low pass filtered with a time constant of 5 seconds, is calculated. Ventilatory support is in phase with the subject's respiratory airflow to the fuzzy extent that this ventilation is above target, and at a preset rate conversely.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Ventilatory assistance for treatment of cardiac failure and cheyne-stokes breathing
InactiveUS6951217B2Improve comfortStabilization prevention of Cheyne-StokesRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLow-pass filterPositive pressure
Method and apparatus for the treatment of cardiac failure, Cheyne Stokes breathing or central sleep apnea are disclosed. A subject is provided with ventilatory support, for example positive pressure ventilatory support using a blower and mask. Respiratory airflow is determined. From the respiratory airflow are derived a measure of instantaneous ventilation (for example half the absolute value of the respiratory airflow) and a measure of longterm average ventilation (for example the instantaneous ventilation low pass filtered with a 100 second time constant). A target ventilation is taken as 95% of the longterm average ventilation. The instantaneous ventilation is fed as the input signal to a clipped integral controller, with the target ventilation as the reference signal. The output of the controller determines the degree of ventilatory support. Clipping is typically to between half and double the degree of support that would do all the respirator work. A third measure of ventilation, for example instantaneous ventilation low pass filtered with a time constant of 5 seconds, is calculated. Ventilatory support is in phase with the subject's respiratory airflow to the fuzzy extent that this ventilation is above target, and at a preset rate conversely.
Owner:RESMED LTD
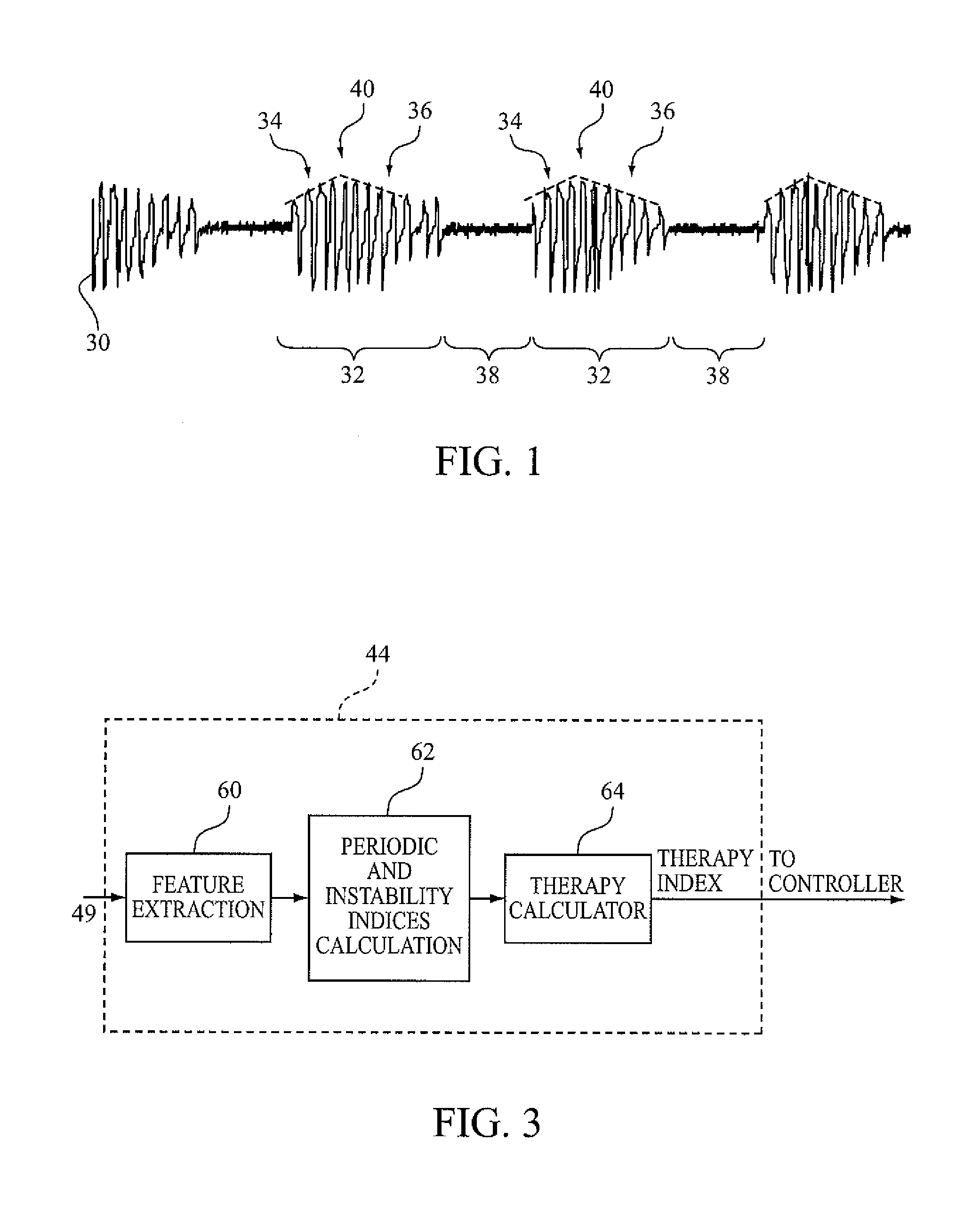
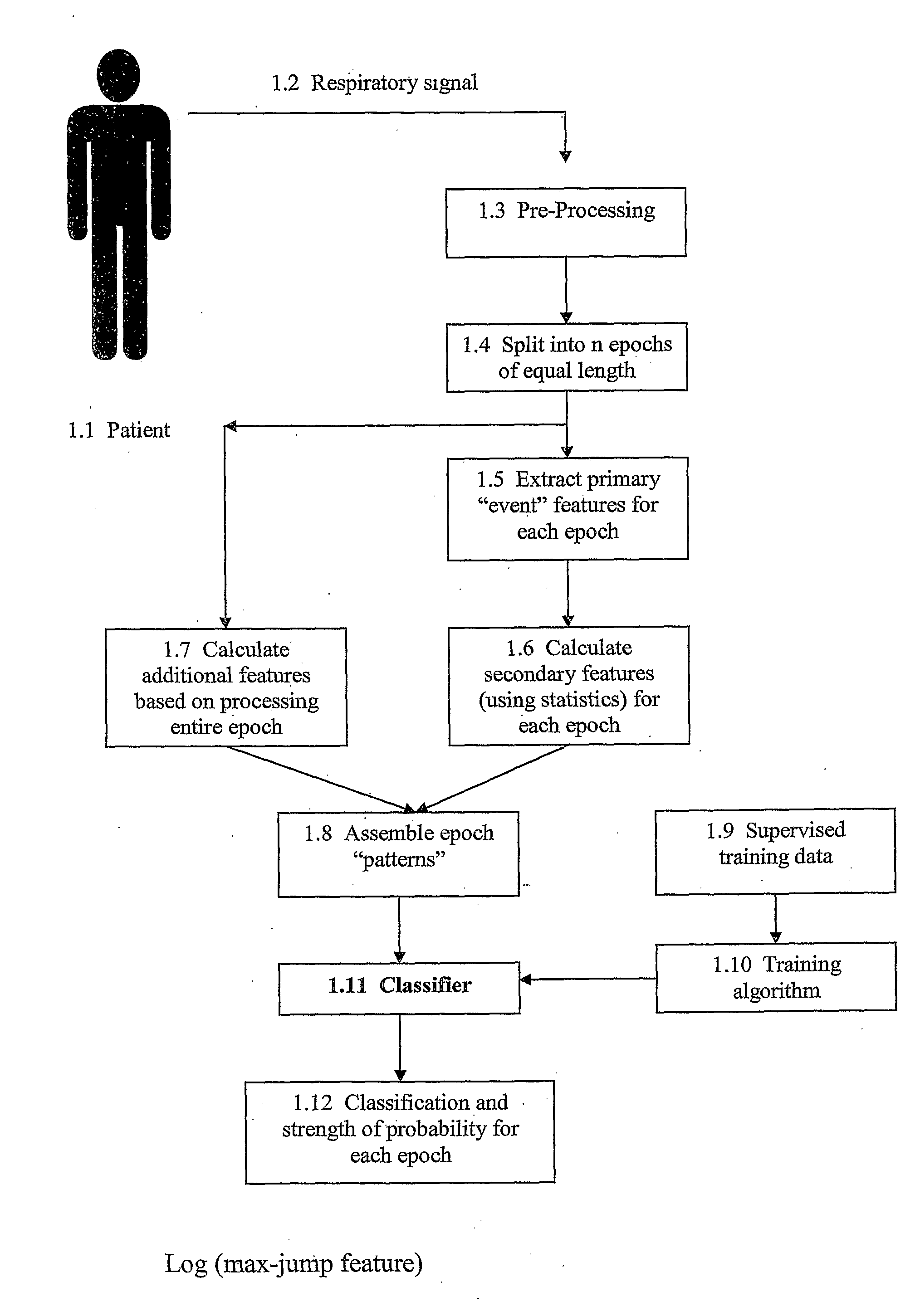
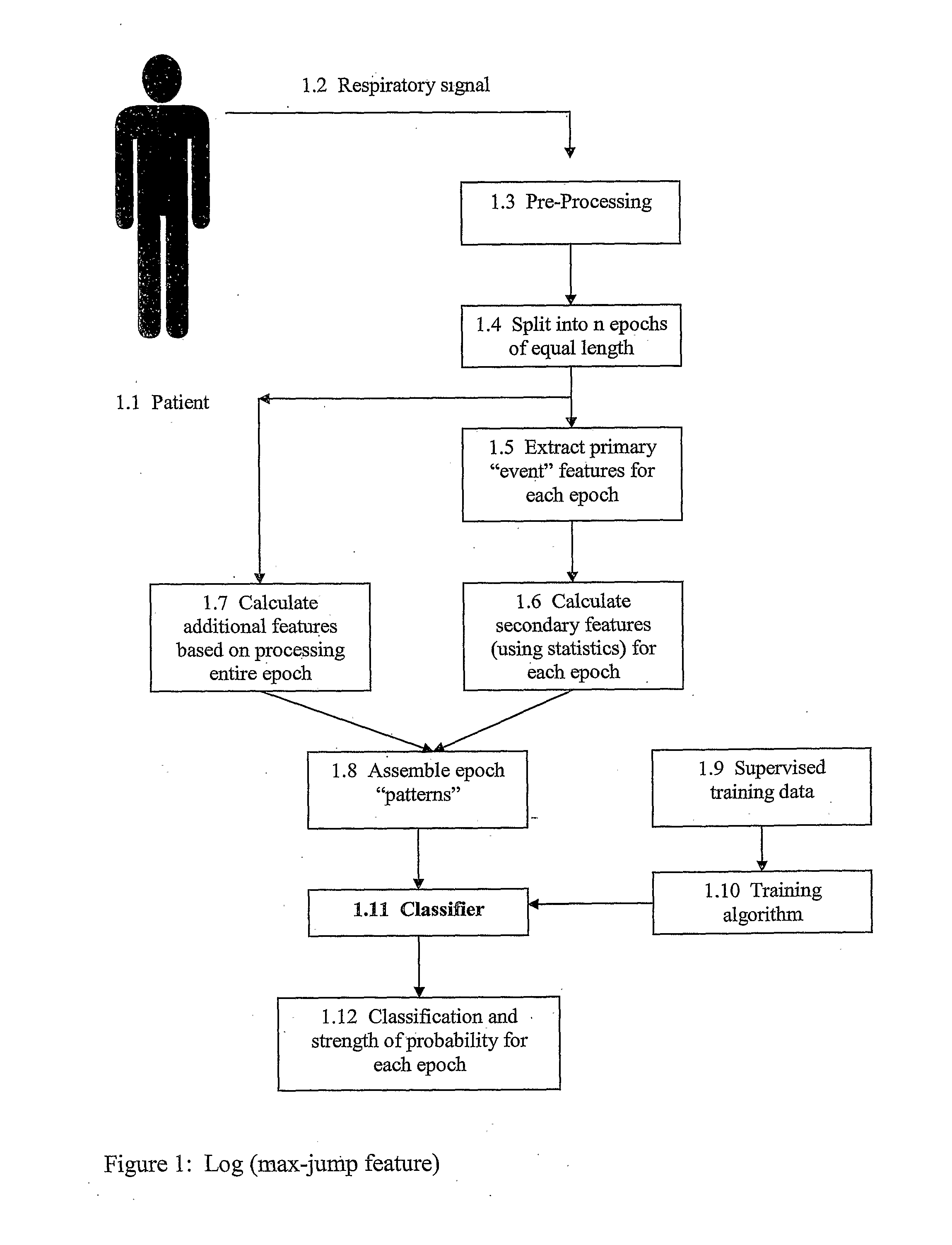
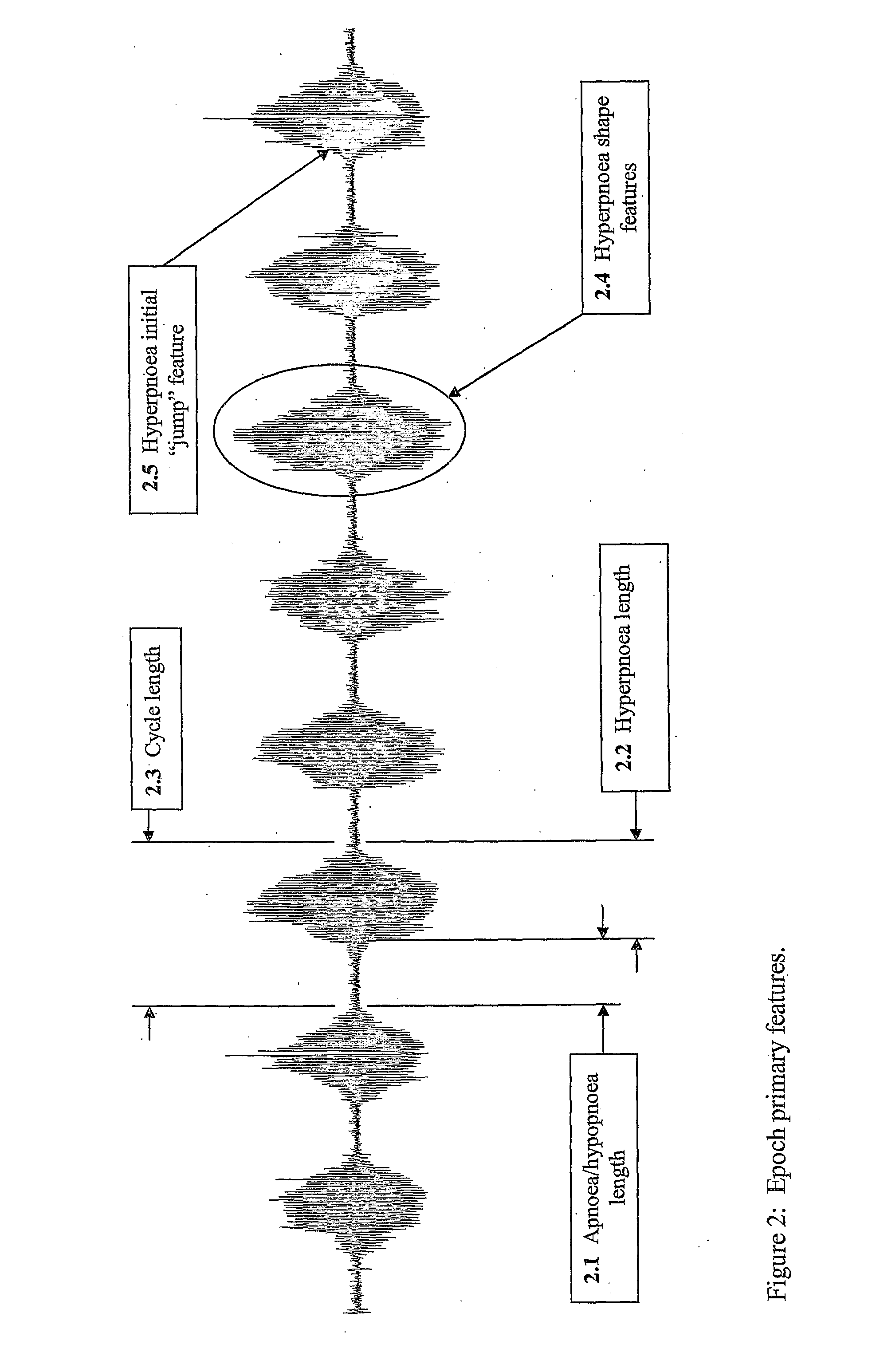
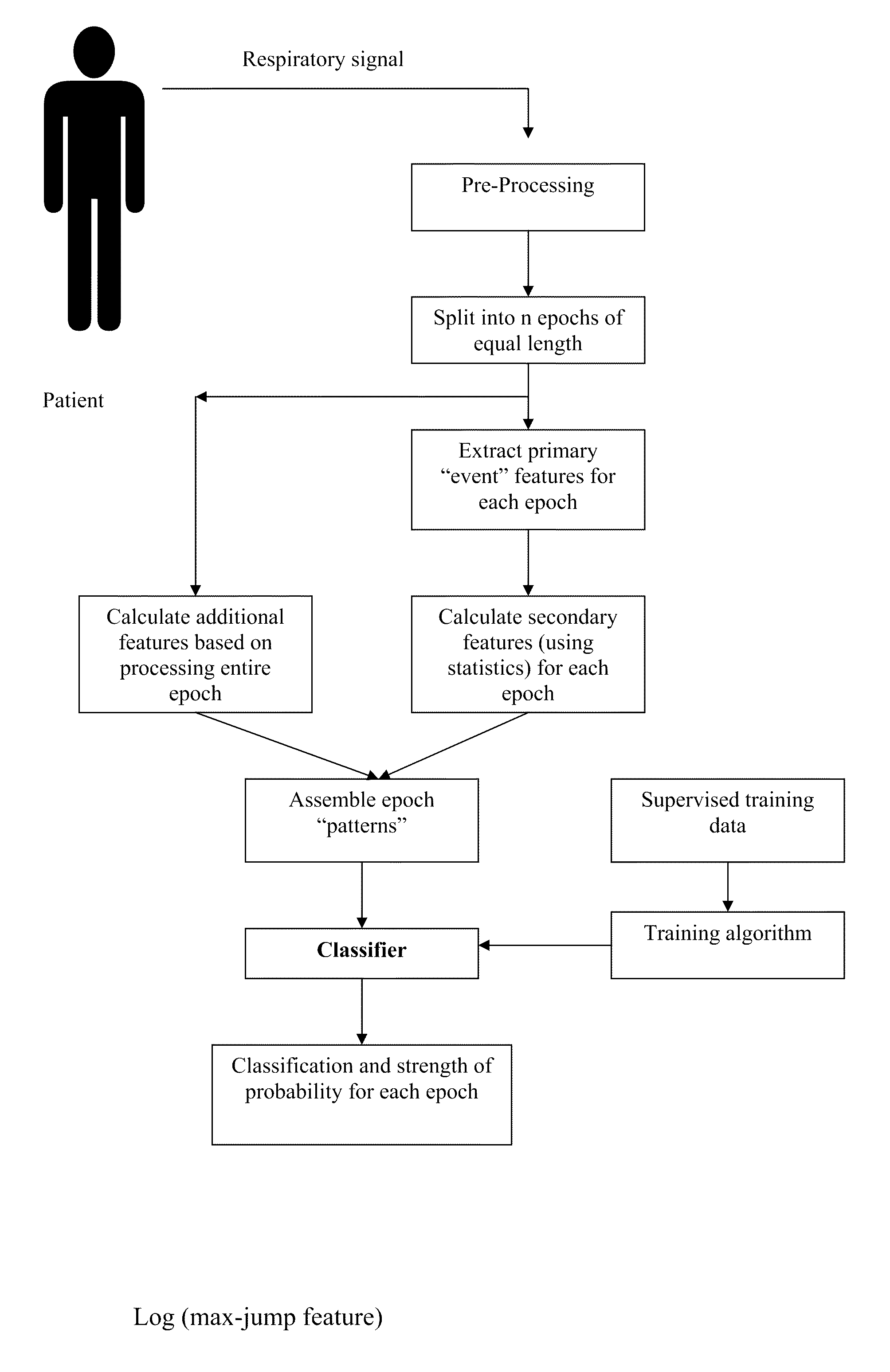
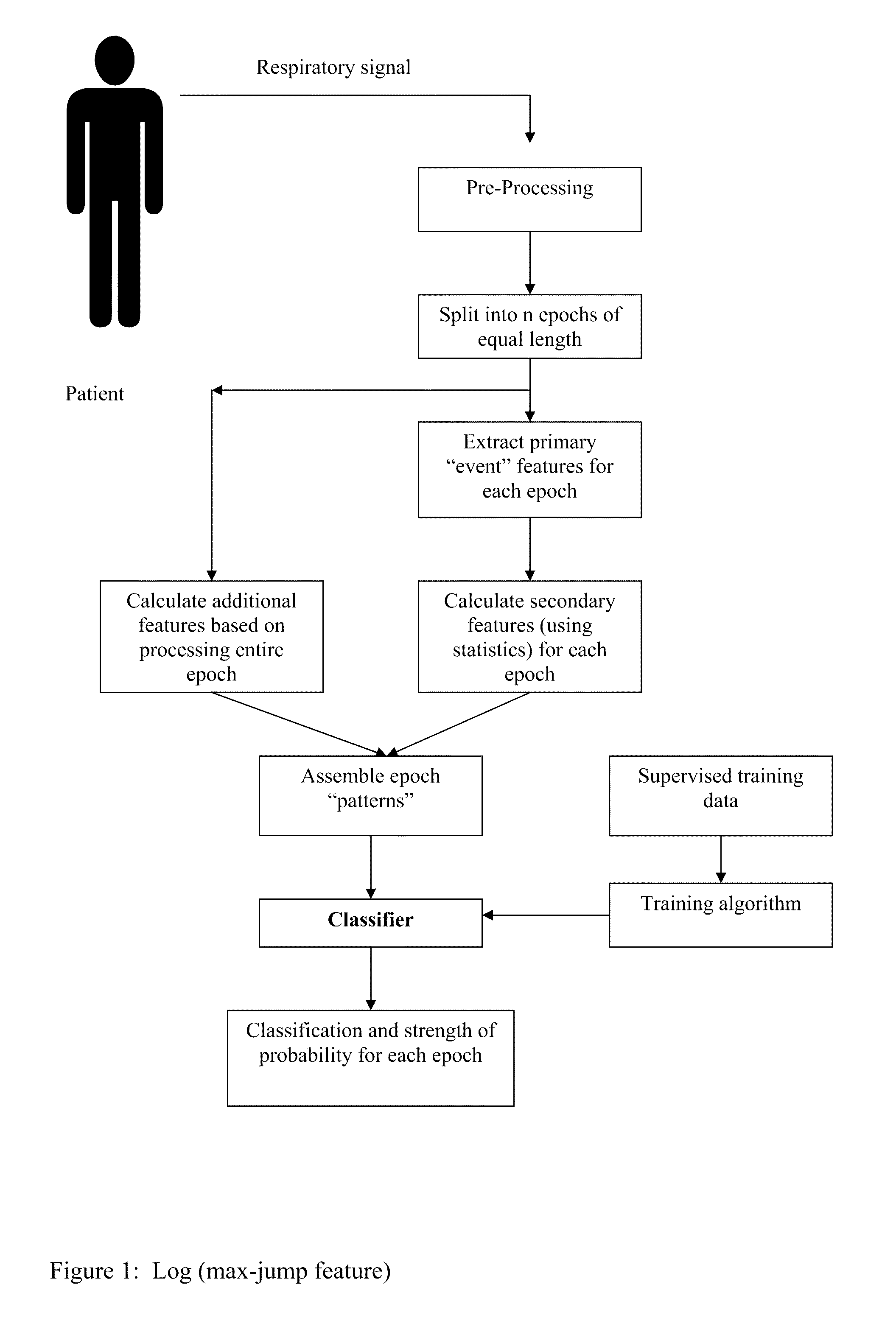
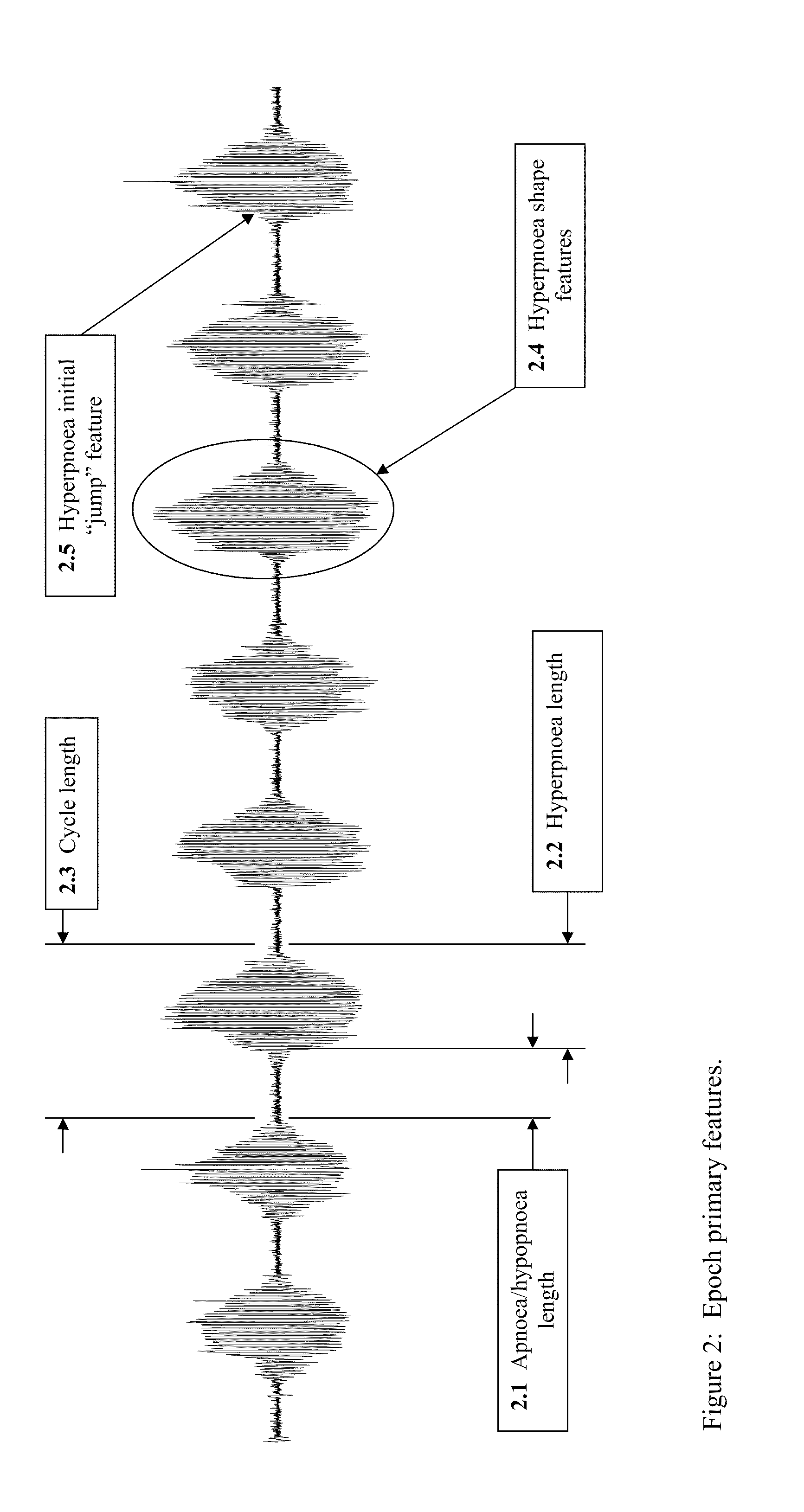
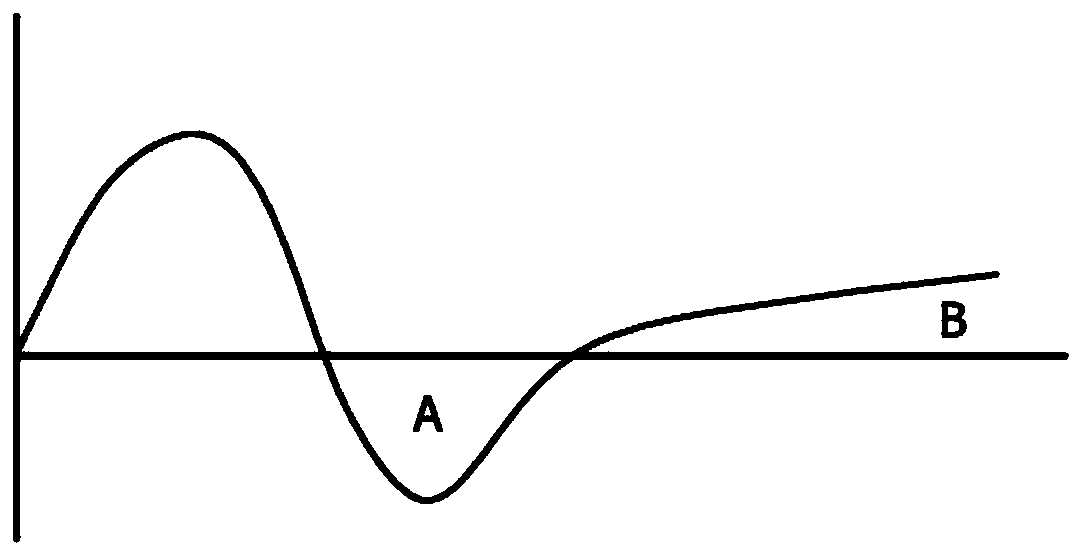
Method For Detecting and Discriminating Breathing Patterns From Respiratory Signals
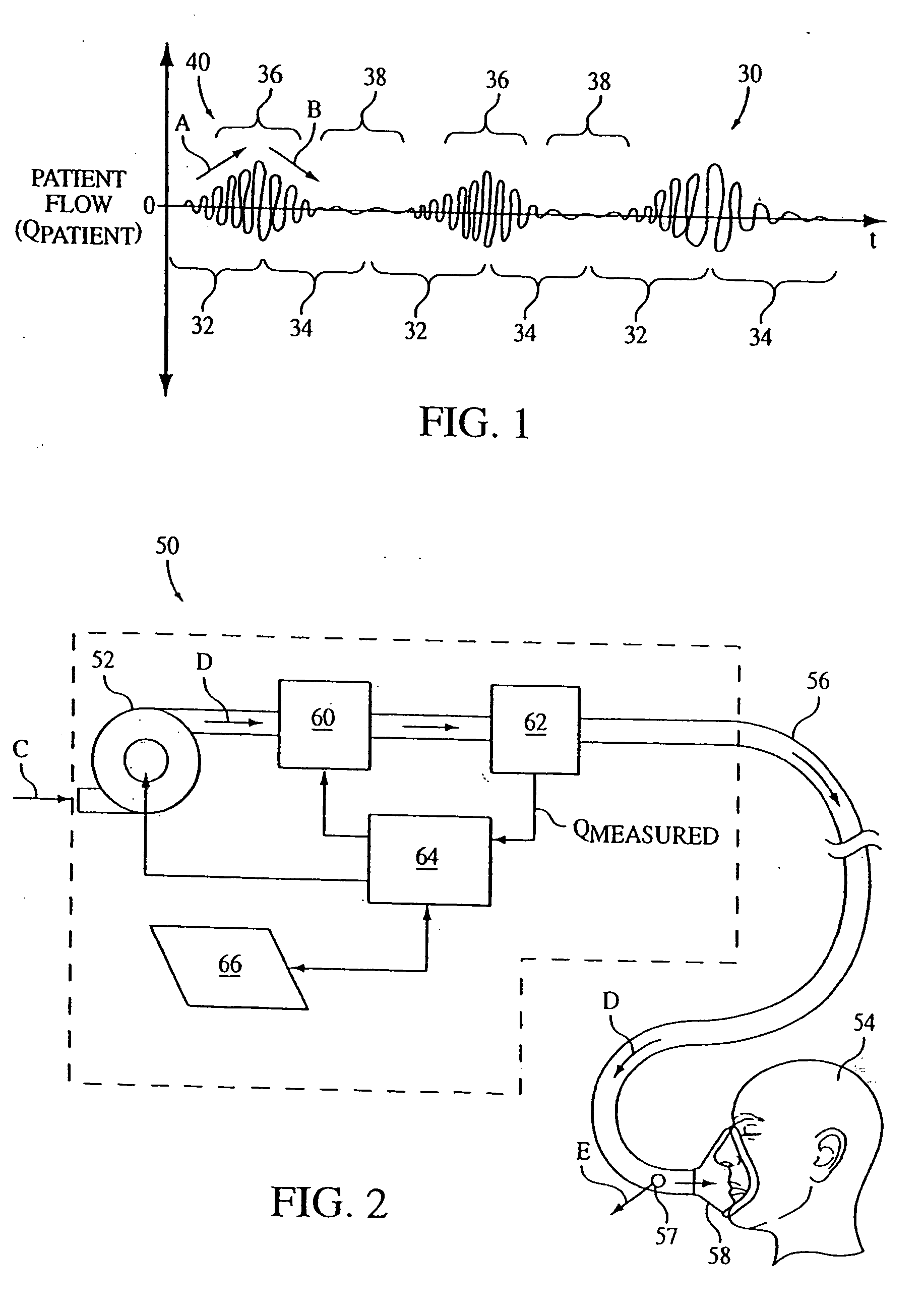
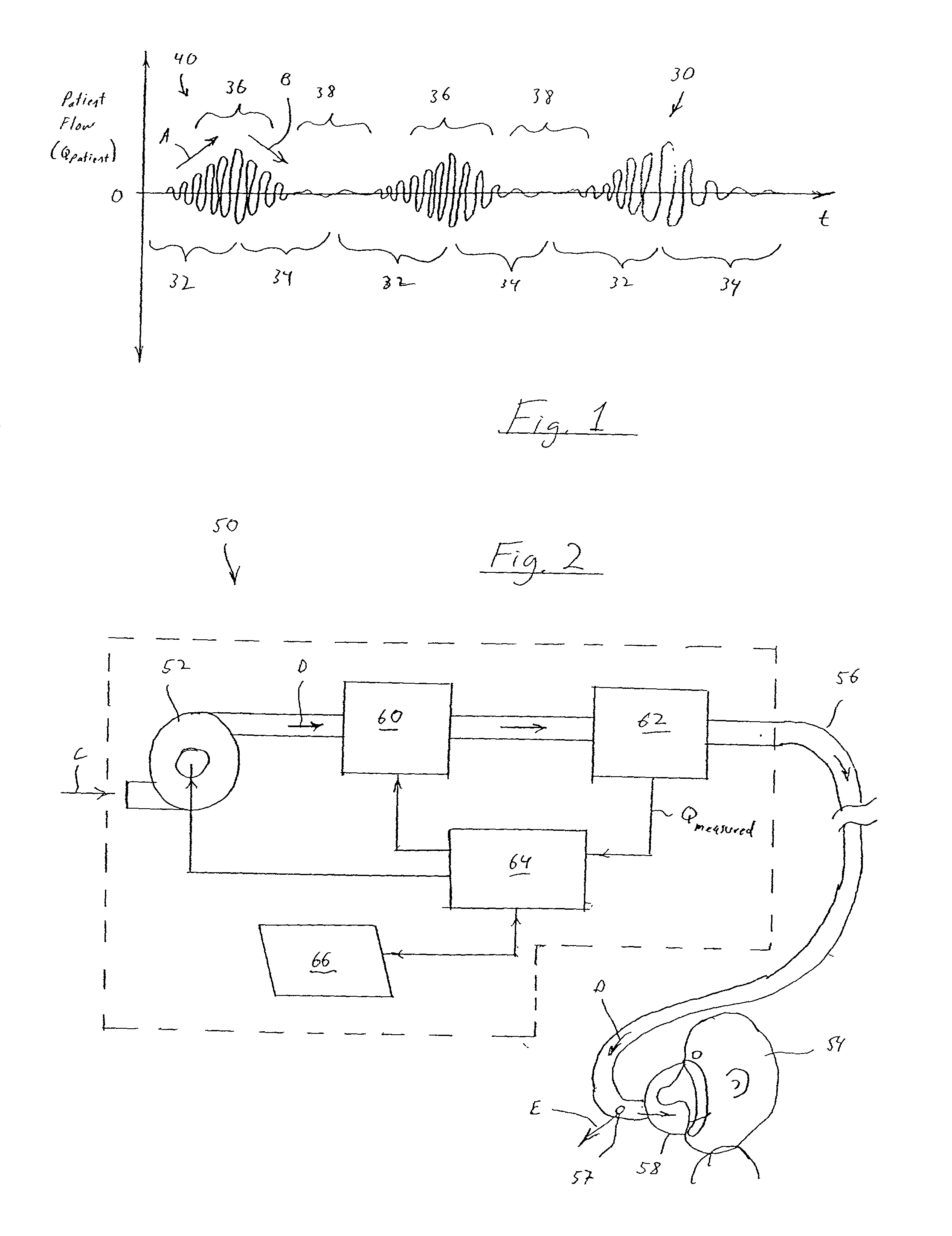
A signal representative of a patient's respiration is split into equal length epochs. A primary feature is extracted from each epoch that acts as a compressed representation of the signal events. Statistics are applied to the primary feature to produce one or more secondary features that represent the entire epoch. Each secondary feature is grouped with one or more other features that are extracted from the entire epoch rather than selected epoch events. This grouping is the epoch pattern. The pattern is manipulated with suitable classifier algorithm to produce a probability for each class within the algorithm, that the signal may be representative of a disease state (Cheyne-Stokes, OSA etc). The epoch is assigned to the class with the highest probability. Also defined are methods of detecting Cheyne-Stokes breathing by analysing a signal to detect one or regions of hyperpnoea and if the length of a hyperpnoea exceeds a parameter, Cheyne-Stokes is present.
Owner:RESMED LTD
System and method for applying therapy during hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20050240240A1Reducing cyclic blood chemistry imbalanceLowering intrathoracic pressureElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationCheyne–Stokes respirationTreatment typology
Techniques are provided for treating periodic breathing, such as Cheyne-Stokes Respiration, using an implantable medical system. In one technique, diaphragmatic stimulation is delivered during a hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing via electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves. Diaphragmatic stimulation is synchronized with intrinsic inspiration so as to increase the amplitude of diaphragmatic contraction during inspiration. This tends to decrease intrathoracic pressure leading to occlusion of the respiratory airway. Occlusion reduces actual ventilation during hyperpnea, thus reducing the cyclic blood chemistry imbalance that sustains periodic breathing so as to either mitigate periodic breathing or eliminate it completely. In another technique, respiration is instead inhibited during the hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing by blocking phrenic nerve signals to the extent necessary to reduce ventilation to terminate periodic breathing or at least mitigate its severity. Techniques are also described for controlling the type of therapy applied in response to periodic breathing.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for applying therapy during hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7245971B2Reduce ventilationReducing the cyclic blood chemistry imbalanceElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationCheyne–Stokes respirationElectrical stimulations
Techniques are provided for treating periodic breathing, such as Cheyne-Stokes Respiration, using an implantable medical system. In one technique, diaphragmatic stimulation is delivered during a hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing via electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves. Diaphragmatic stimulation is synchronized with intrinsic inspiration so as to increase the amplitude of diaphragmatic contraction during inspiration. This tends to decrease intrathoracic pressure leading to occlusion of the respiratory airway. Occlusion reduces actual ventilation during hyperpnea, thus reducing the cyclic blood chemistry imbalance that sustains periodic breathing so as to either mitigate periodic breathing or eliminate it completely. In another technique, respiration is instead inhibited during the hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing by blocking phrenic nerve signals to the extent necessary to reduce ventilation to terminate periodic breathing or at least mitigate its severity. Techniques are also described for controlling the type of therapy applied in response to periodic breathing.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Detection of periodic breathing
ActiveUS20160287122A1Improve comfortIncrease costElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsRR intervalAccelerometer
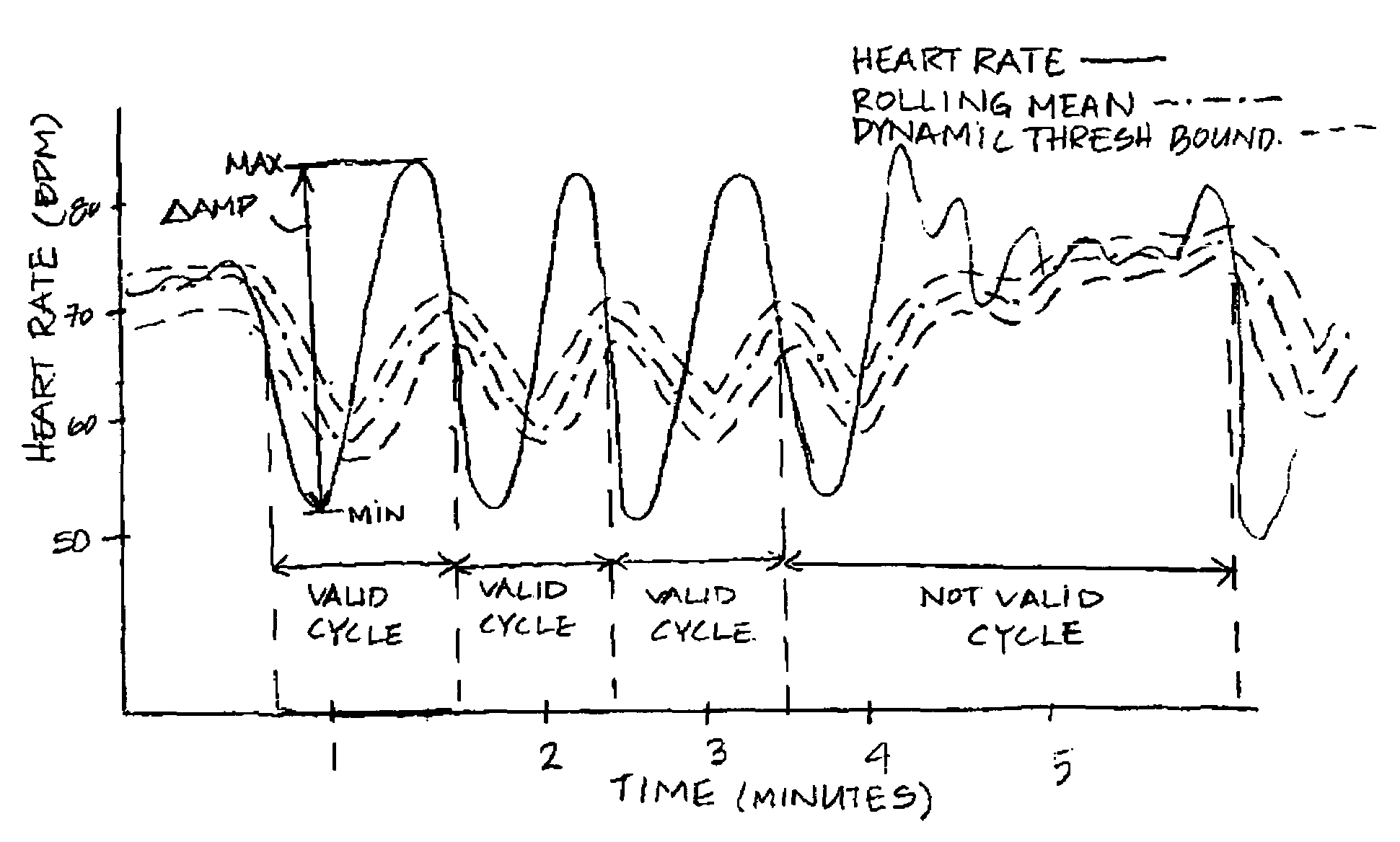
Methods and apparatus perform periodic breathing detection, such as Cheyne-Stokes respiration detection. The detection may be performed by one or more processors, such as by analysis of data from one or more sensors. In some cases, the detection may be based on an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal, such as from ECG electrodes and / or an accelerometer signal, such as from an accelerometer. An occurrence of periodic breathing may be detected based on features derived from the signal(s). For example, detection may be based on deriving a respiration signal from the sensed signal(s) and / or analysis of RR interval times or relative QRS amplitude values, which may be evaluated on a segment-by-segment basis. The detection may provide monitoring and reporting of the occurrence of periodic breathing by a monitoring device and / or provide a basis for controlling changes to a provided respiratory treatment or therapy, such as by a respiratory pressure therapy device.
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
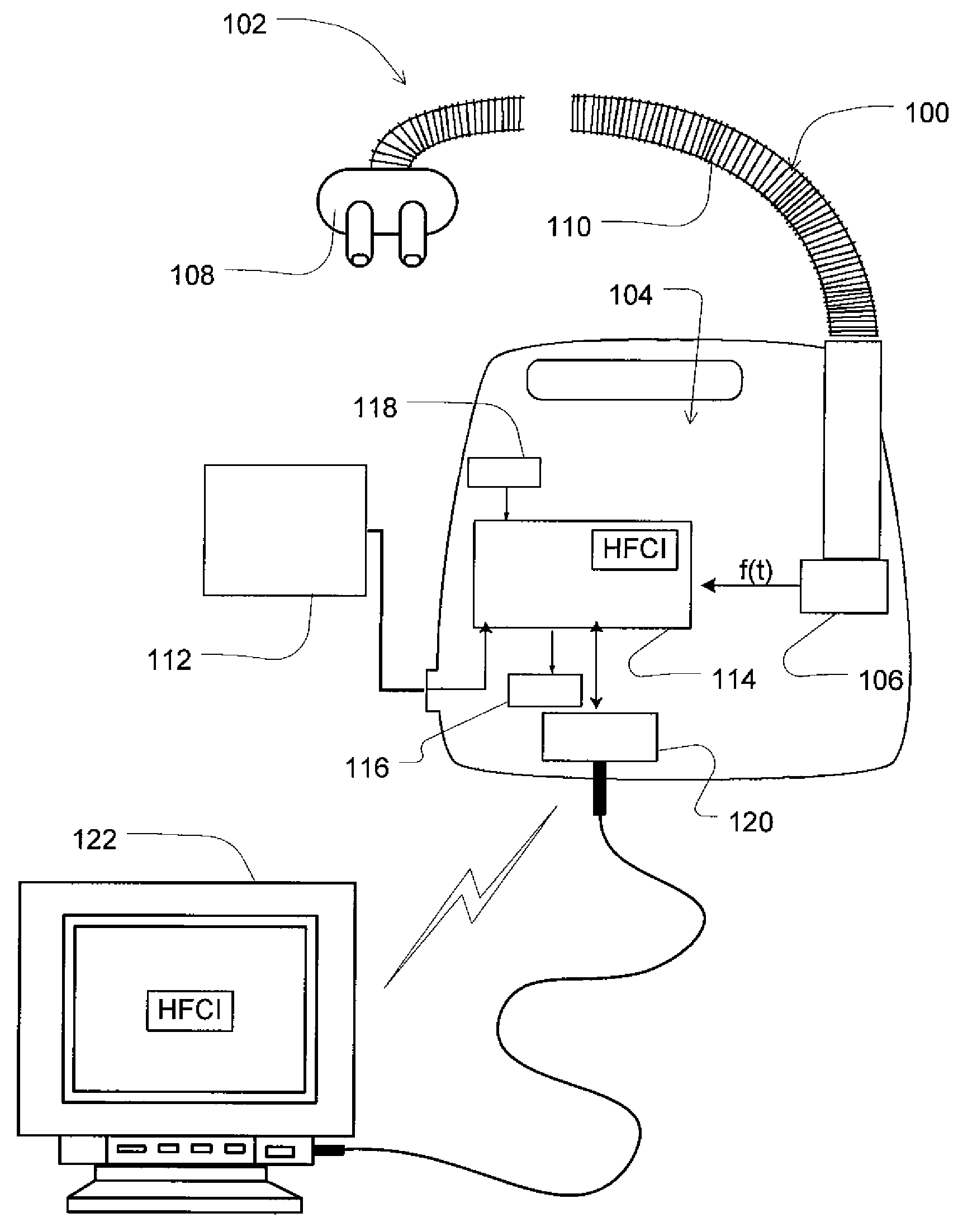
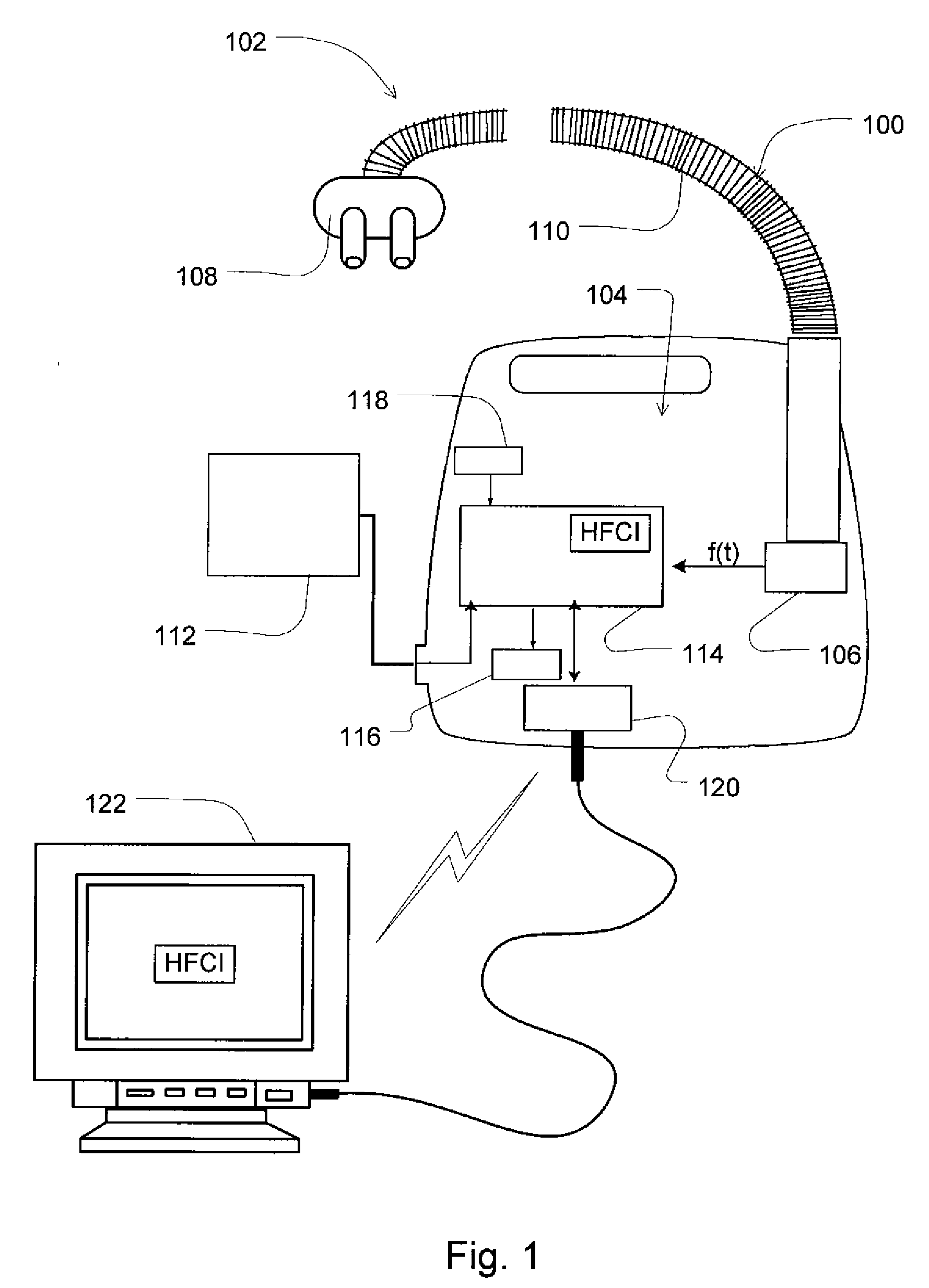
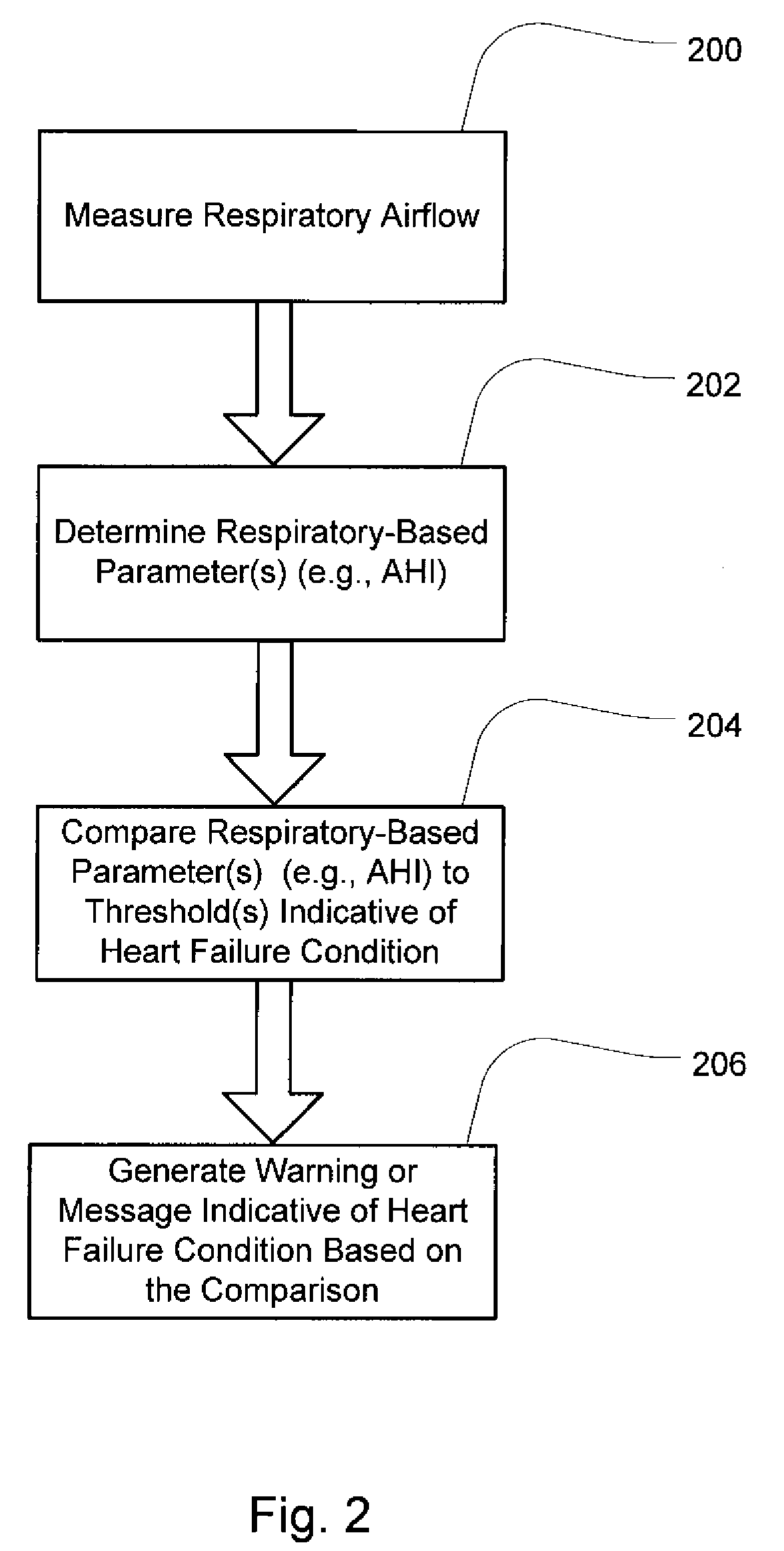
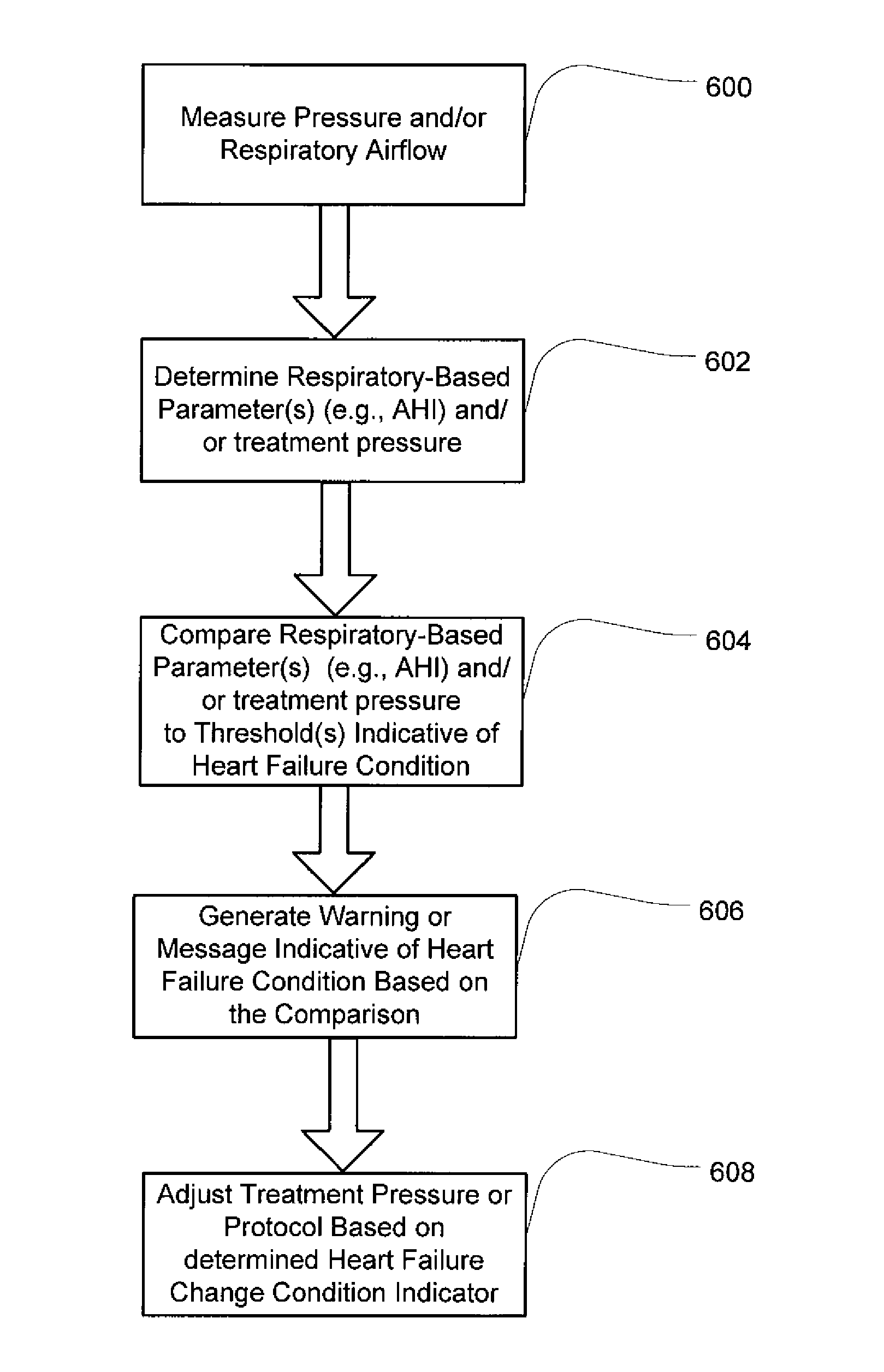
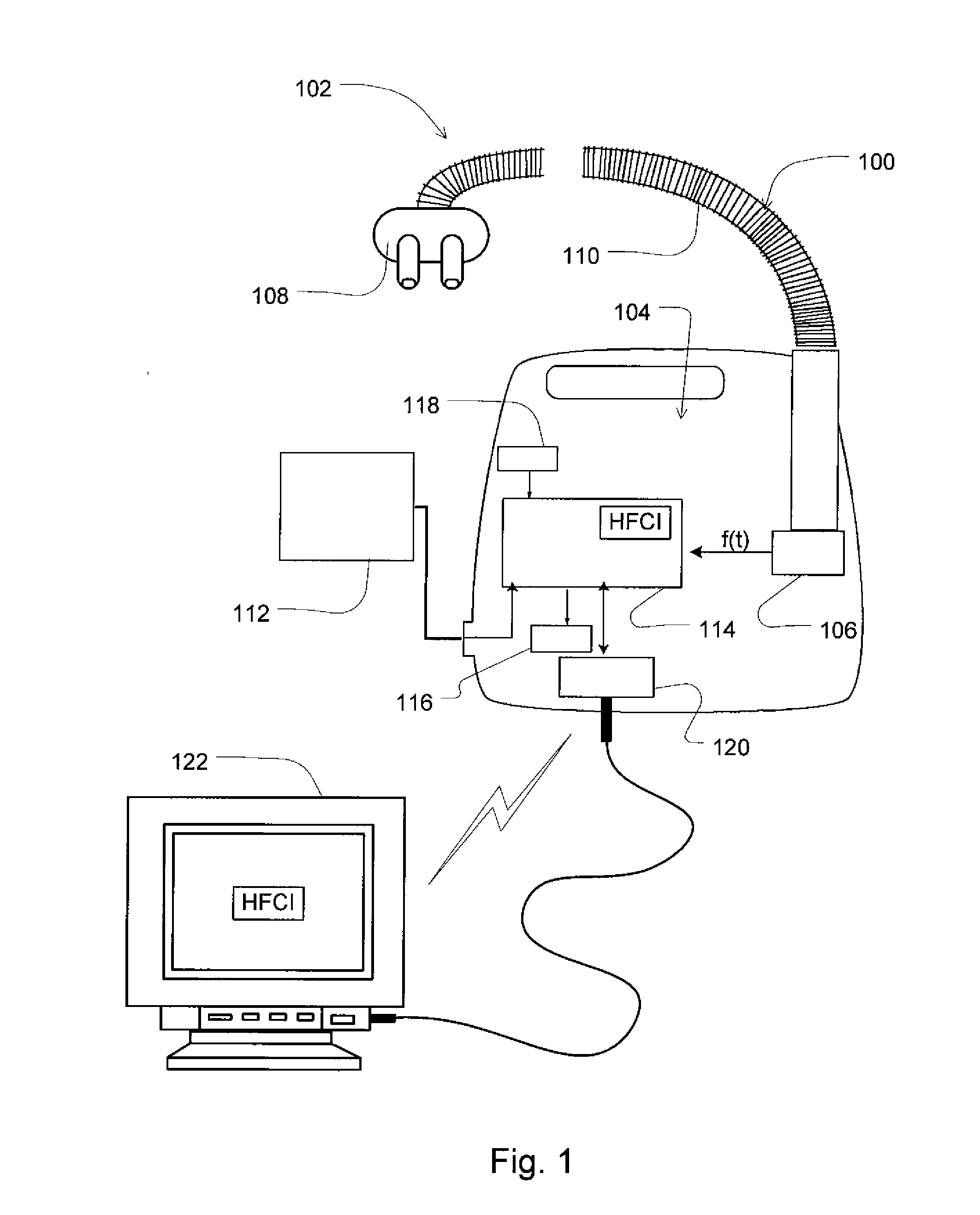
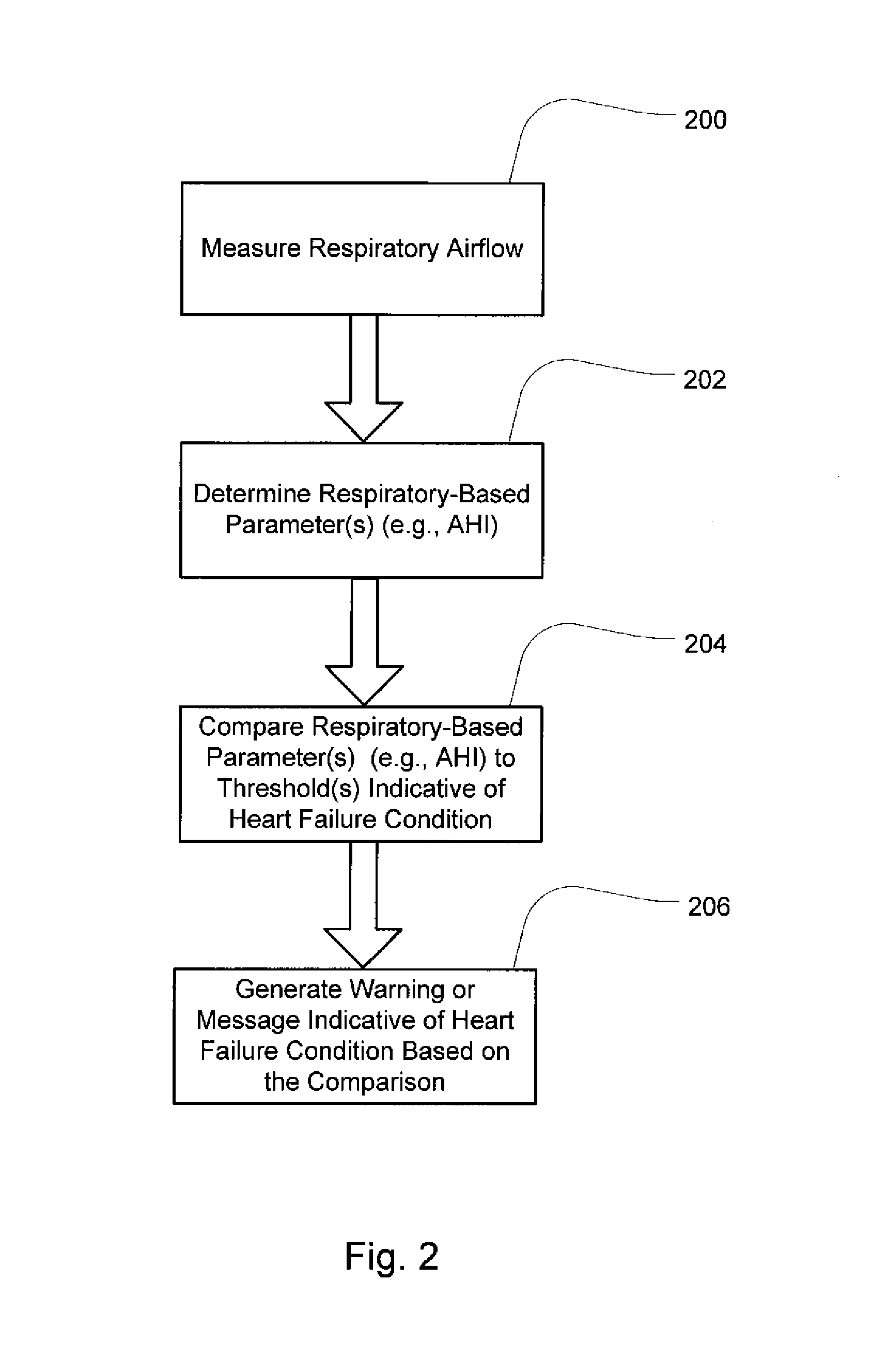
Method and apparatus for detecting and treating heart failure
ActiveUS20100018530A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesHypopneaCheyne–Stokes respiration
Devices and systems provide methods of detecting a heart failure condition of a patient that may be based on one or more respiratory parameters of a patient. In an example embodiment, a monitoring device determines one or more heart failure condition indicators based on a measure of the patient respiratory airflow and / or a measure of treatment pressure. Respiratory parameters such as respiration rate, hypopneas, apneas, Cheyne-Stokes breathing patterns or apnea-hypopnea counts may be compared to thresholds that are selected to represent a change in the condition of a heart failure patient such as an onset of a decompensation event. Results of the comparisons may trigger a pressure treatment change and / or one or more warnings or messages to notify a patient or physician of a pending change to the patient's heart failure condition so that the patient may more immediately seek medical attention to treat the heart failure condition.
Owner:RESMED LTD
System and method for applying therapy during hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7454250B1Reducing the cyclic blood chemistry imbalanceReduce ventilationElectrotherapyRespiratory organ evaluationCheyne–Stokes respirationTreatment typology
Techniques are provided for treating periodic breathing, such as Cheyne-Stokes Respiration, using an implantable medical system. In one technique, diaphragmatic stimulation is delivered during a hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing via electrical stimulation of the phrenic nerves. Diaphragmatic stimulation is synchronized with intrinsic inspiration so as to increase the amplitude of diaphragmatic contraction during inspiration. This tends to decrease intrathoracic pressure leading to occlusion of the respiratory airway. Occlusion reduces actual ventilation during hyperpnea, thus reducing the cyclic blood chemistry imbalance that sustains periodic breathing so as to either mitigate periodic breathing or eliminate it completely. In another technique, respiration is instead inhibited during the hyperpnea phase of periodic breathing by blocking phrenic nerve signals to the extent necessary to reduce ventilation to terminate periodic breathing or at least mitigate its severity. Techniques are also described for controlling the type of therapy applied in response to periodic breathing.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method for detecting and discriminating breathing patterns from respiratory signals
A signal representative of a patient's respiration is split into equal length epochs. A primary feature is extracted from each epoch that acts as a compressed representation of the signal events. Statistics are applied to the primary feature to produce one or more secondary features that represent the entire epoch. Each secondary feature is grouped with one or more other features that are extracted from the entire epoch rather than selected epoch events. This grouping is the epoch pattern. The pattern is manipulated with suitable classifier algorithm to produce a probability for each class within the algorithm, that the signal may be representative of a disease state (Cheyne-Stokes, OSA etc). The epoch is assigned to the class with the highest probability. Also defined are methods of detecting Cheyne-Stokes breathing by analyzing a signal to detect one or regions of hyperpnoea and if the length of a hyperpnoea exceeds a parameter, Cheyne-Stokes is present.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Method and apparatus for detecting and treating heart failure
ActiveUS8844525B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrocardiographyHypopneaCheyne–Stokes respiration
Devices and systems provide methods of detecting a heart failure condition of a patient that may be based on one or more respiratory parameters of a patient. In an example embodiment, a monitoring device determines one or more heart failure condition indicators based on a measure of the patient respiratory airflow and / or a measure of treatment pressure. Respiratory parameters such as respiration rate, hypopneas, apneas, Cheyne-Stokes breathing patterns or apnea-hypopnea counts may be compared to thresholds that are selected to represent a change in the condition of a heart failure patient such as an onset of a decompensation event. Results of the comparisons may trigger a pressure treatment change and / or one or more warnings or messages to notify a patient or physician of a pending change to the patient's heart failure condition so that the patient may more immediately seek medical attention to treat the heart failure condition.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Implantable medical device with cardiac output- based apnea suppression
InactiveUS7706881B1Promote breathingMinimal levelHeart stimulatorsHypopneaCardiac pacemaker electrode
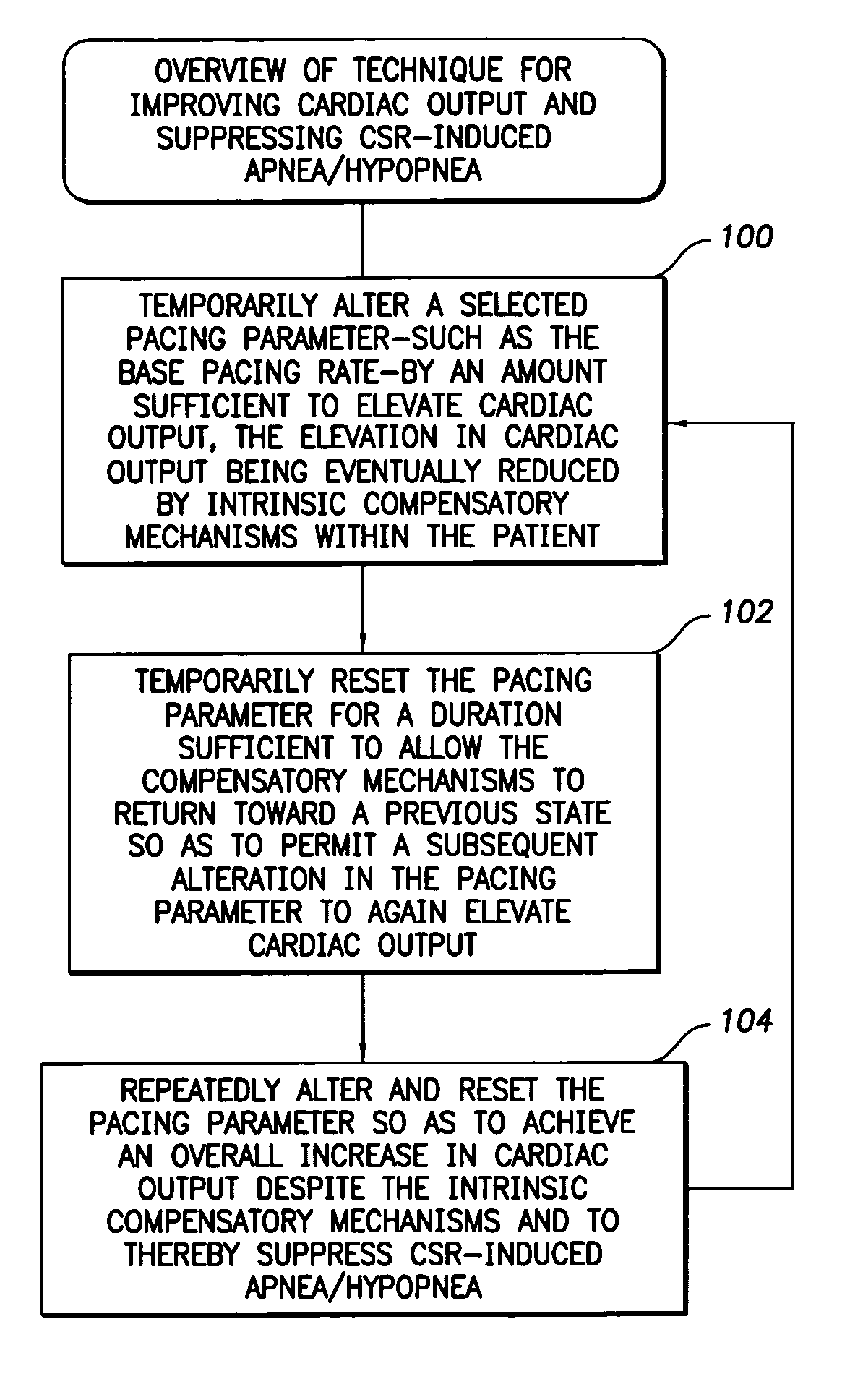
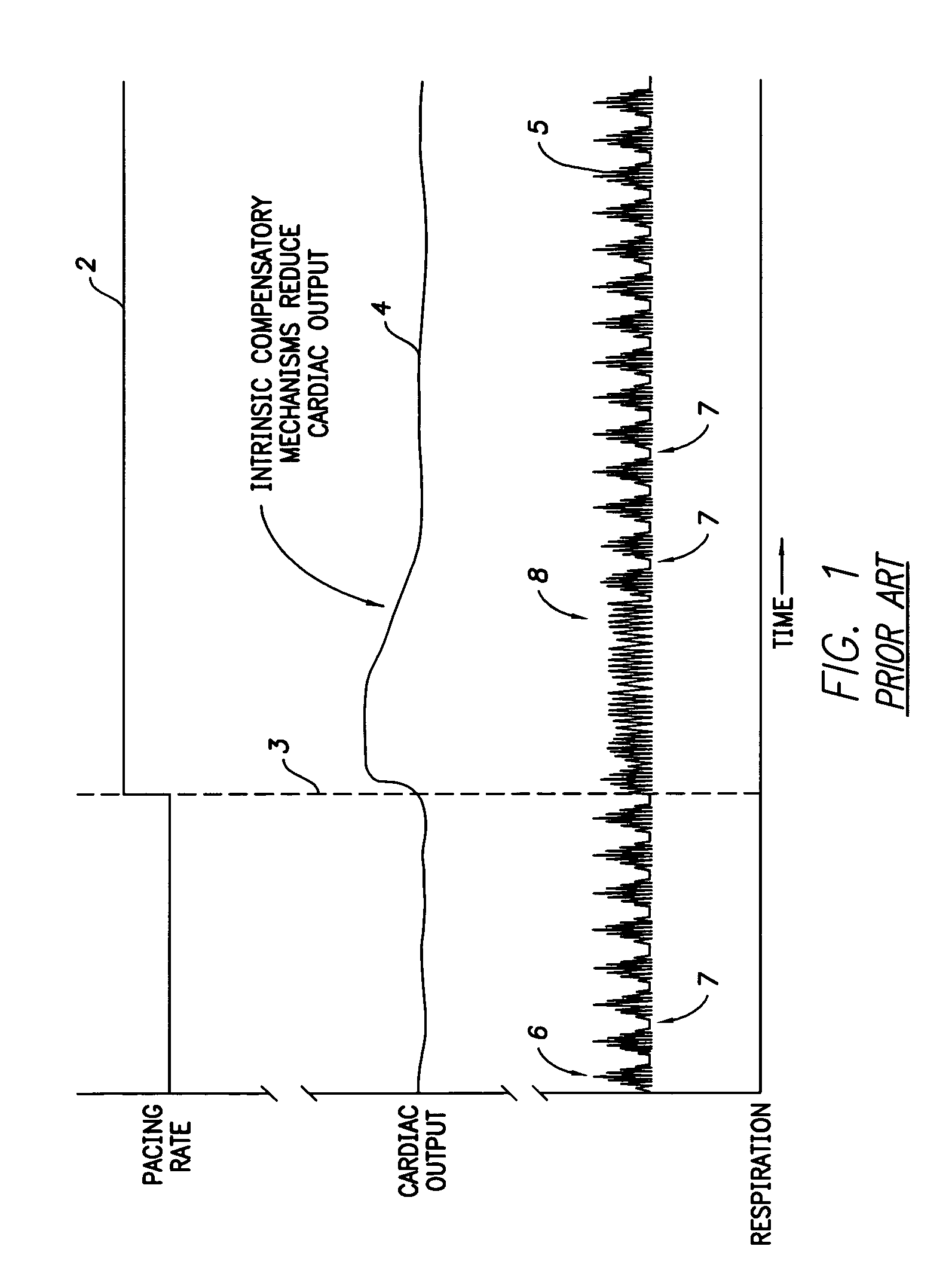
Techniques are provided for improving cardiac output and also suppressing certain forms of apnea / hypopnea within a patient using an implantable medical device, such as a pacemaker or ICD. In one example, a selected pacing parameter—usually the pacing rate—is temporarily altered by an amount sufficient to elevate cardiac output, the elevation in cardiac output being eventually reduced by intrinsic compensatory mechanisms within the patient. The pacing parameter is then temporarily reset for a duration sufficient to allow the compensatory mechanisms to return toward a previous state so as to permit a subsequent alteration in the pacing parameter to again elevate cardiac output. The pacing parameter is repeatedly altered and reset so as to achieve an overall increase in cardiac output despite the intrinsic compensatory mechanisms. The increase in cardiac output is often sufficient to suppress certain forms of apnea / hypopnea, particularly apnea / hypopnea arising from Cheyne-Stokes Respiration (CSR).
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for treating ventilatory instability
ActiveUS8794235B2Increase pressureMaximize effectivenessRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInstabilityCheyne-stokes breathing
A therapy system adapted to treat a patient's ventilatory instability using a ventilatory therapy, a gas modulation therapy, or both. The algorithm implemented by the therapy system monitors the ventilatory instability, such as Cheyne Stokes Respiration (CSR), mixed apneas, CPAP emergent apneas, and complex sleep disordered breathing (CSDB) and treats the ventilatory instability. The algorithm also determine a reference point with respect to the ventilatory instability. The therapy delivery system initiate the treatment based on the reference point.
Owner:PHILIPS RS NORTH AMERICA LLC
Method and device for therapy of periodic respiration
ActiveUS20150273166A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrocardiographyWaxApneustic breathing
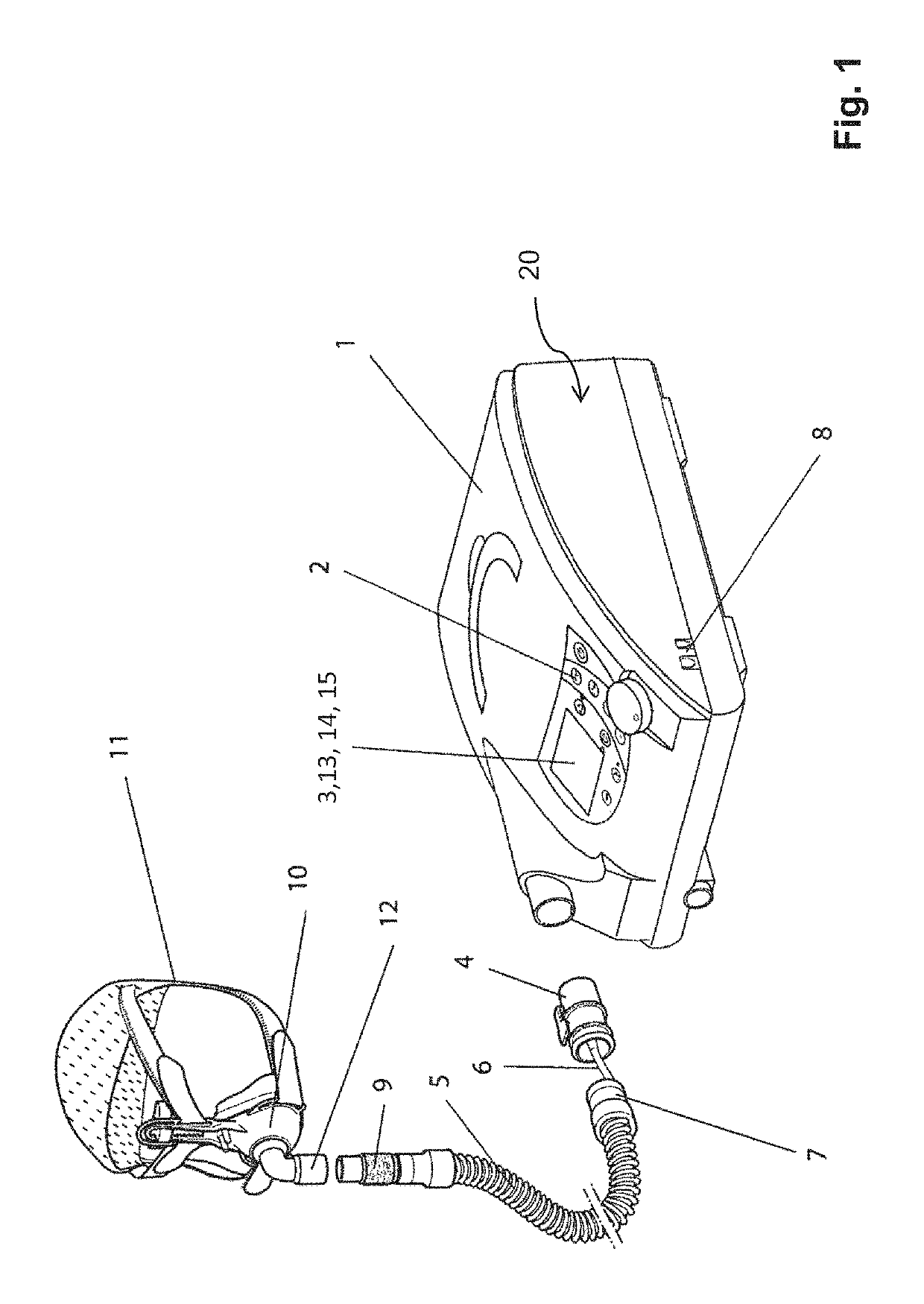
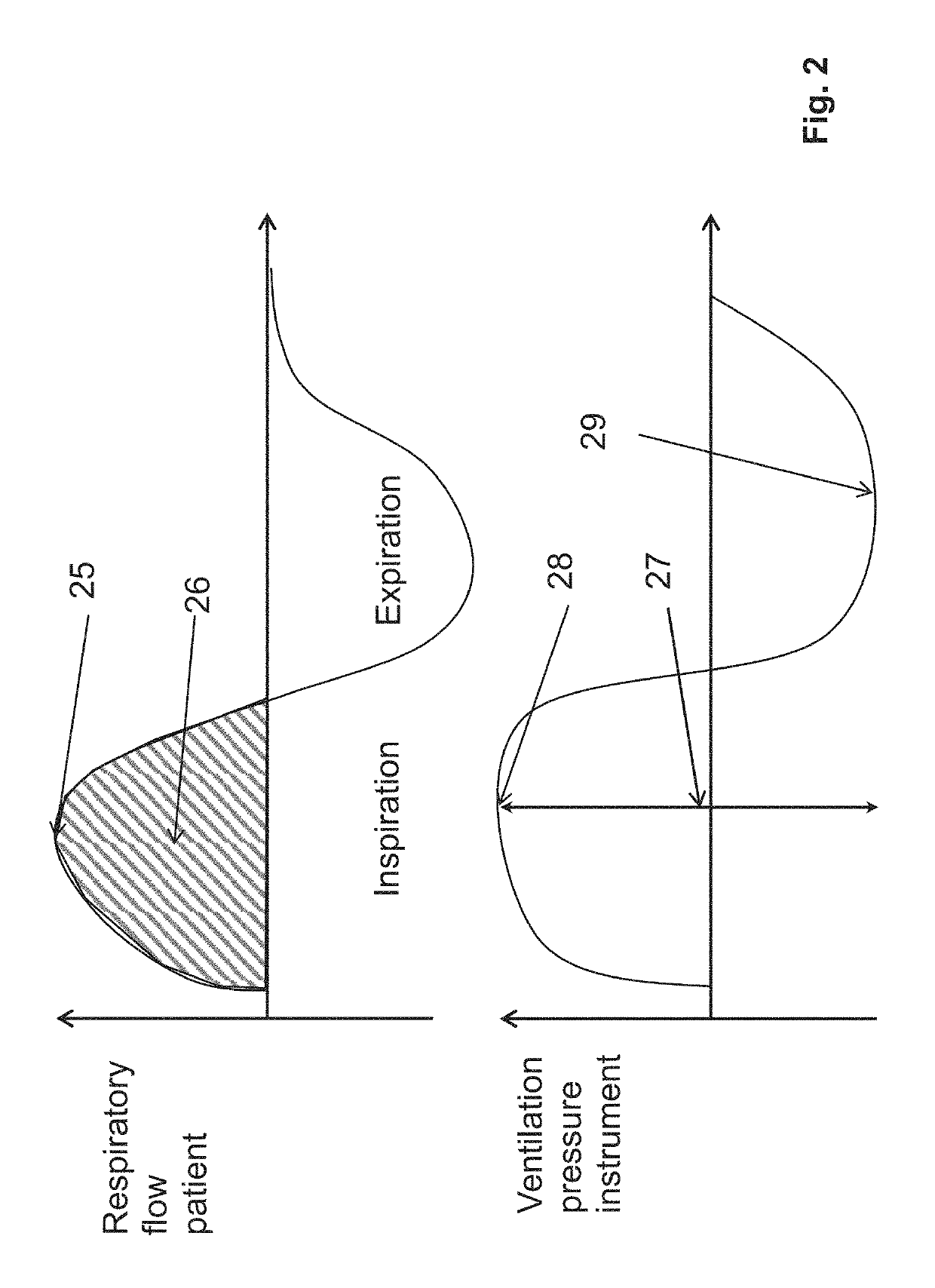
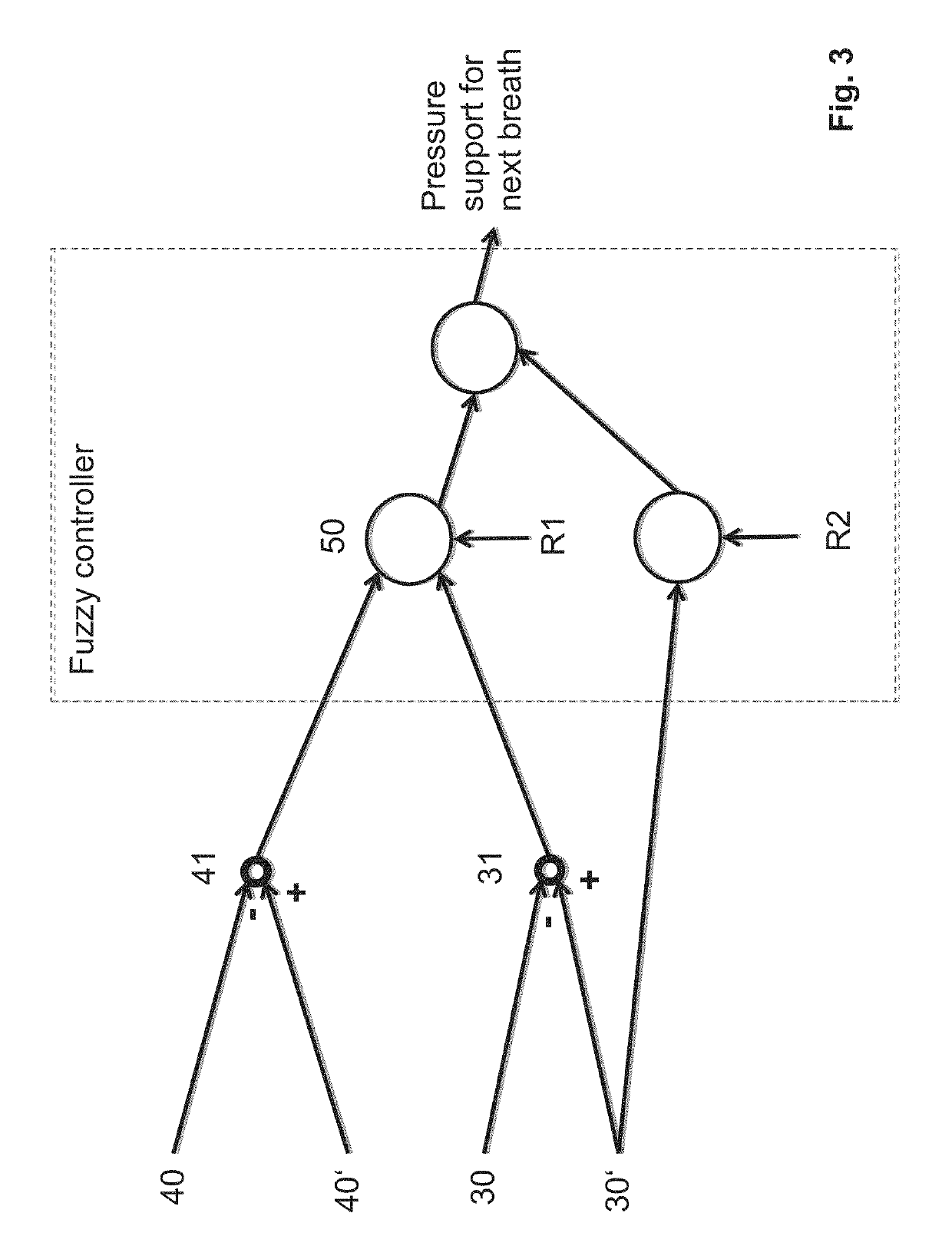
The invention relates to a method and a device for treating Cheyne-Stokes respiration, periodic respiration and central or mixed apnea. If the respiration waxes and wanes periodically, there is pressure support in phases of periodic respiration, taking into account the natural patient respiration.
Owner:LOWENSTEIN MEDICAL TECH SA
Detection of periodic breathing
ActiveUS10159421B2Minimise any dryingIncreases patient airway comfortElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsRR intervalAccelerometer
Methods and apparatus perform periodic breathing detection, such as Cheyne-Stokes respiration detection. The detection may be performed by one or more processors, such as by analysis of data from one or more sensors. In some cases, the detection may be based on an electrocardiogram (ECG) signal, such as from ECG electrodes and / or an accelerometer signal, such as from an accelerometer. An occurrence of periodic breathing may be detected based on features derived from the signal(s). For example, detection may be based on deriving a respiration signal from the sensed signal(s) and / or analysis of RR interval times or relative QRS amplitude values, which may be evaluated on a segment-by-segment basis. The detection may provide monitoring and reporting of the occurrence of periodic breathing by a monitoring device and / or provide a basis for controlling changes to a provided respiratory treatment or therapy, such as by a respiratory pressure therapy device.
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
Method and device for therapy of periodic respiration
The invention relates to a method and a device for treating Cheyne-Stokes respiration, periodic respiration and central or mixed apnea. If the respiration waxes and wanes periodically, there is pressure support in phases of periodic respiration, taking into account the natural patient respiration.
Owner:LOWENSTEIN MEDICAL TECH SA
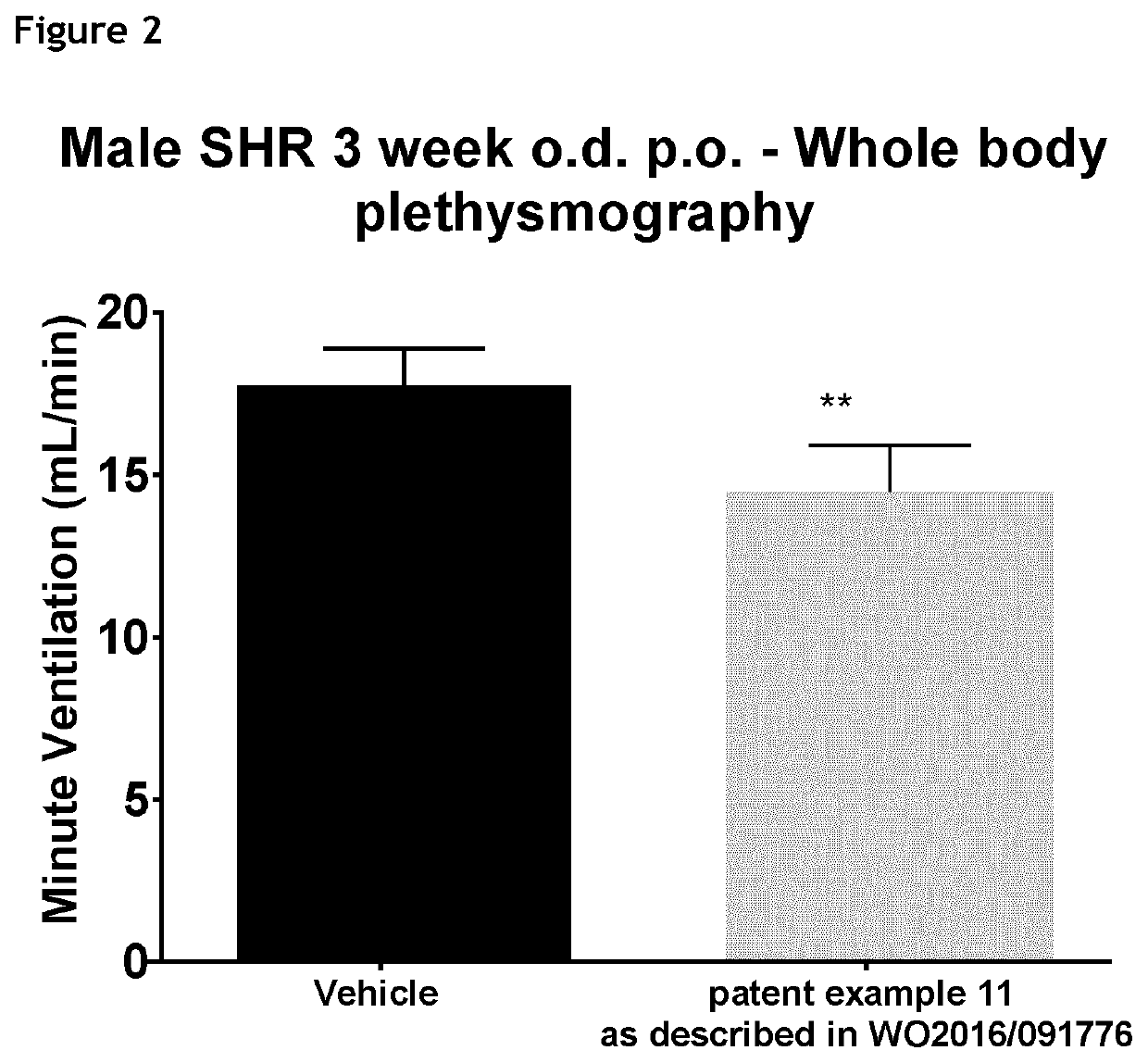
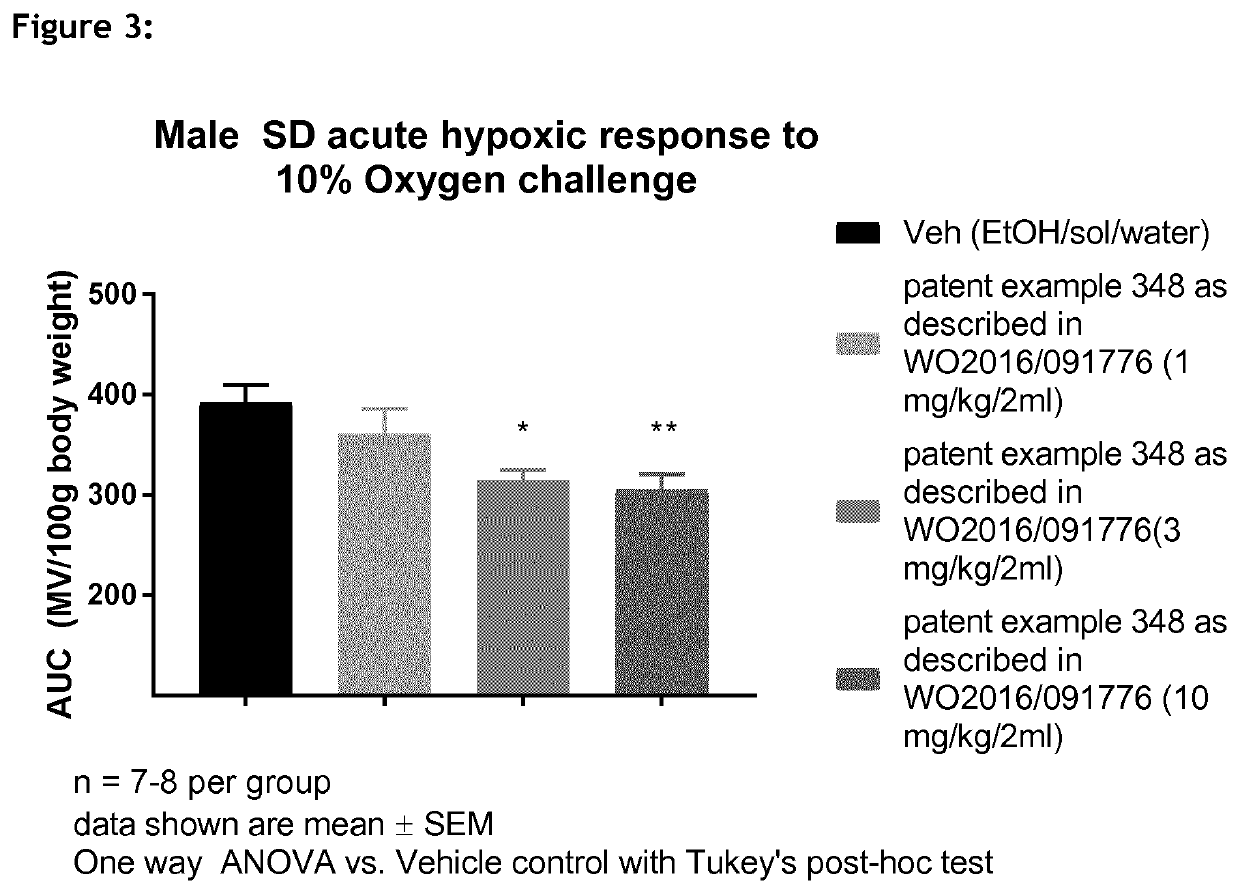
1,3-thiazol-2-yl substituted benzamides for the treatment of diseases associated with nerve fiber sensitization
PendingUS20210220357A1Improve side effectsWeaken potential clinical effectivenessOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderCheyne–Stokes respirationP2X3 Receptor
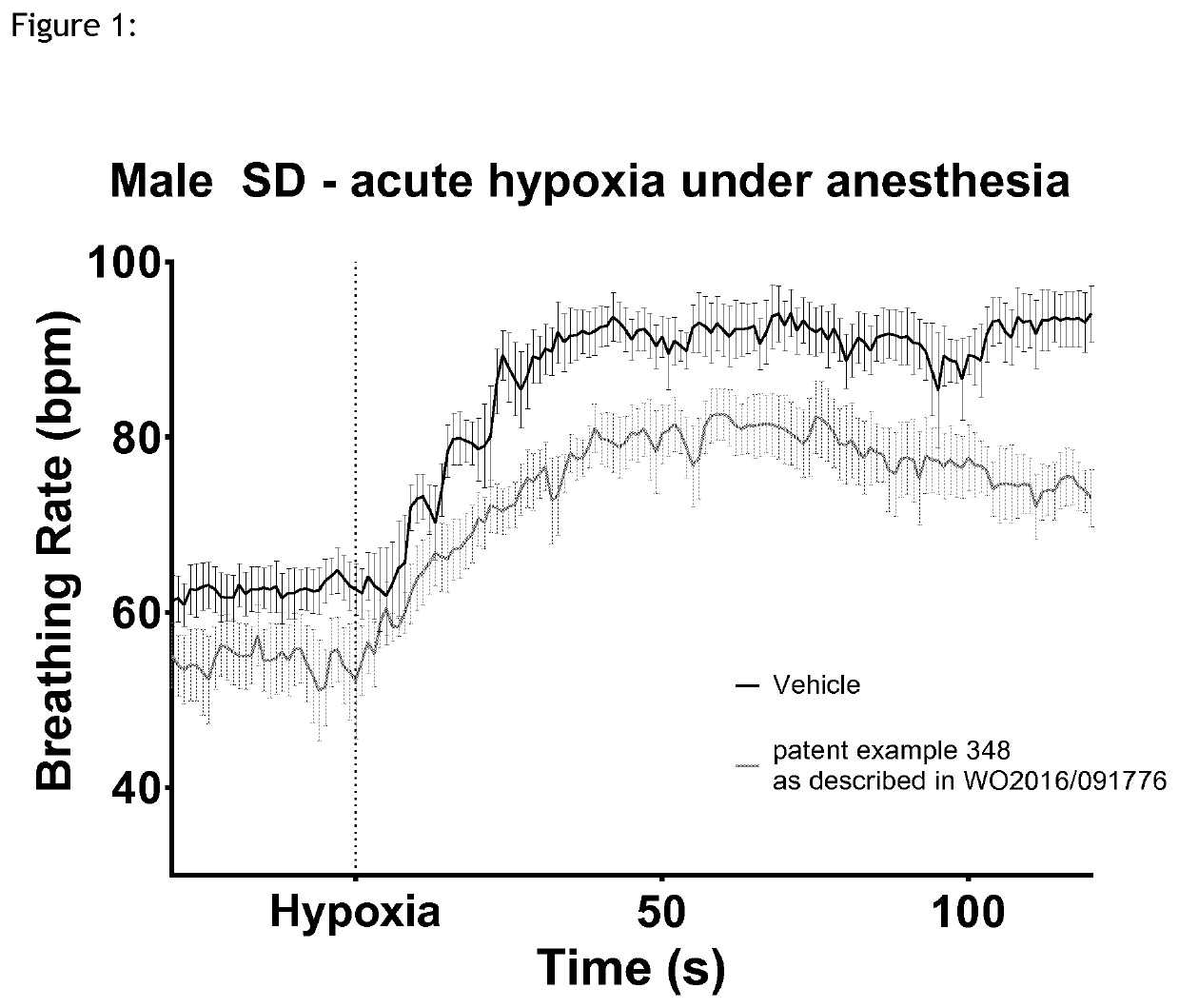
The present invention relates to use 1,3-thiazol-2-yl substituted benzamide compounds of general formula (I) as described and defined herein, to pharmaceutical compositions and combinations comprising said compounds for the treatment or prophylaxis of diseases which are associated with nerve fiber sensitization, and / or other pathological conditions associated with autonomic imbalance caused by increased chemoreceptor sensitivity, in particular for the treatment of breathing disorders, Cheyne Stokes respiration, central and obstructive sleep apnea, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, resistant hypertension, and heart failure, which are related to increased activity of P2X3 receptors.
Owner:BAYER AG +1
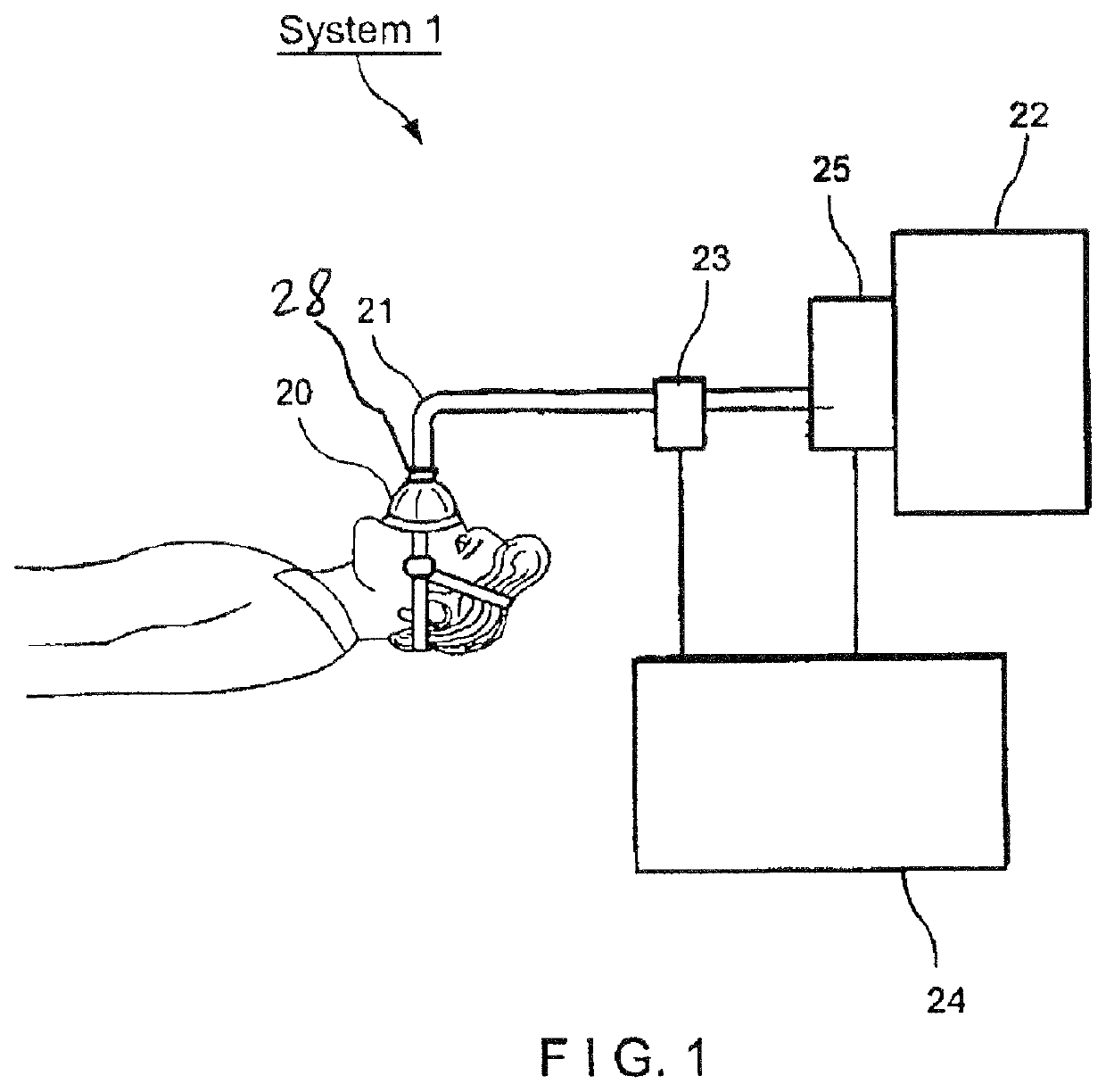
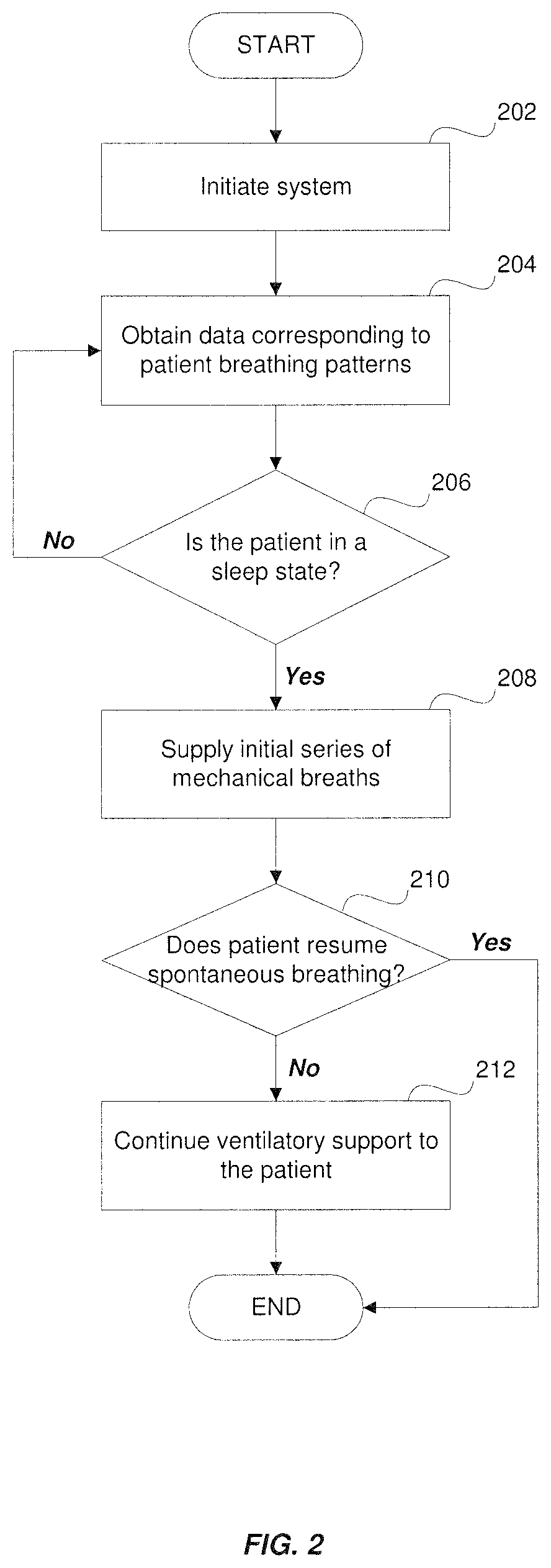
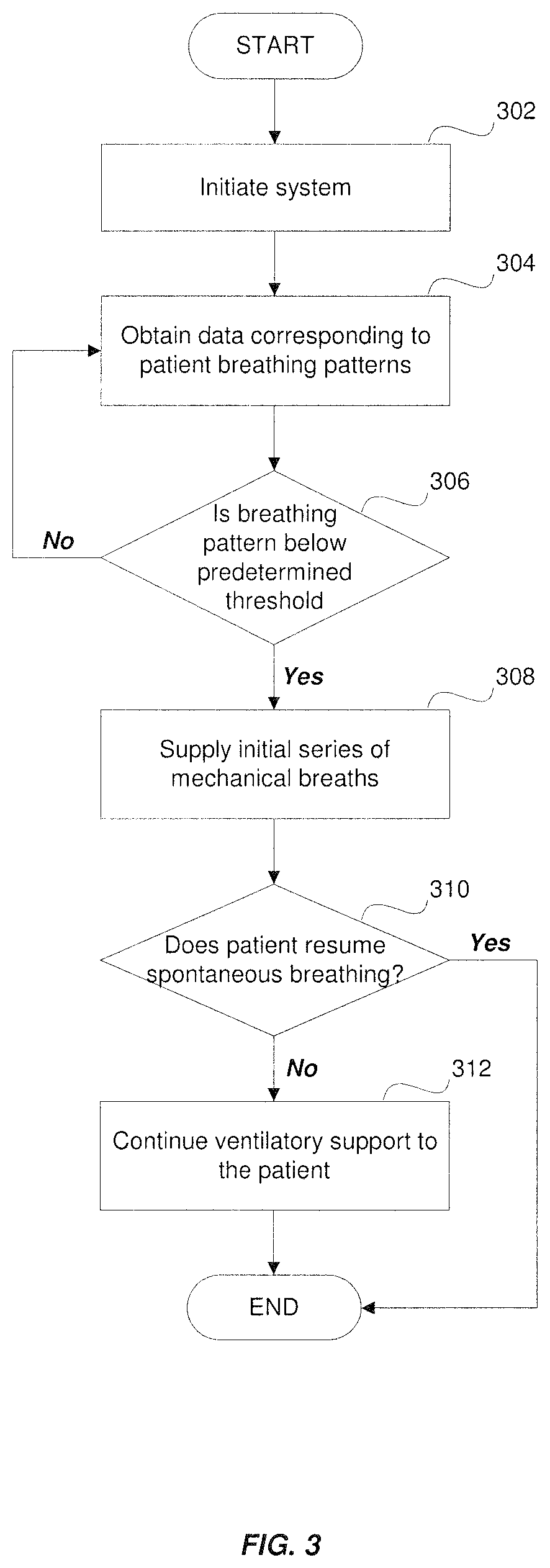
Method and system for diagnosis and treatment of sleep disordered breathing of a patient
ActiveUS10842958B1Respiratory masksMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationCheyne–Stokes respiration
A system and method for providing ventilatory support to a patient suffering from sleep disordered breathing (SDB), in particular, non-obstructive SDB, such as Cheyne Stokes respiration and hypoventilation, including obesity hypoventilation syndrome. The system and method monitor obtain data corresponding to a breathing pattern of a patient and determine when the patient experiences oscillating breathing or low spontaneous ventilation. In particular, the system and method determine when the patient's real-time breathing patterns fall below a predetermined baseline threshold, and subsequently initiate a short series of mechanical breaths to be delivered to the patient.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Respiration device and method for a respiration device
ActiveUS20160058964A1Reliably recognizeEasy to implementRespiratorsElectrocardiographyRadiologyCheyne-stokes breathing
The present invention relates to a method and a respiration device having a respiration unit for generating an airflow for the respiration and having a monitoring unit. The monitoring unit is used to detect a respiration parameter and to classify events in the respiration on the basis of monitoring of the respiration parameter. In this case, the monitoring unit is able and designed to carry out an event analysis to recognize an occurrence, which is characteristic for Cheyne-Stokes respiration, of chronologically successive events and for this purpose to ascertain the period length thereof and to compare them to one another and to register the presence of Cheyne-Stokes respiration when the compared period lengths each deviate by less than 40% from one another.
Owner:LOWENSTEIN MEDICAL TECH SA
Methods and systems to manage central sleep apnea by controlling accumulated retrograde volume
Methods and systems to treat Cheyne-Stokes respiration (CSR) and / or central sleep apnea (CSA) include monitoring retrograde breathing and detecting respiratory events. Based on the occurrences of certain respiratory events, a target volume of rebreathing is adjusted to reduce arousals as well as CSR / CSA.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
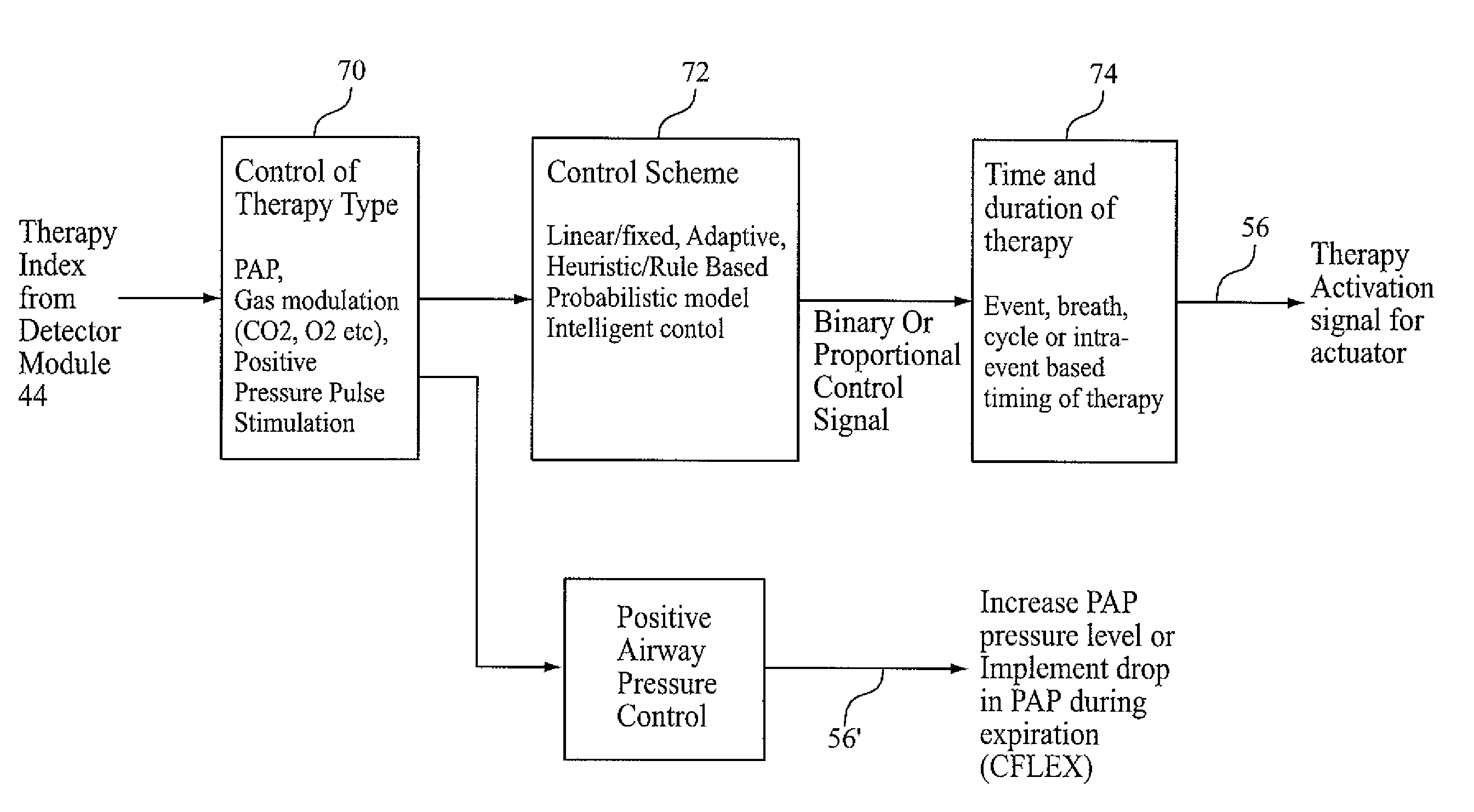
Methods and apparatus for treatment of respiratory disorders
ActiveUS20170361044A1Improve efficacyImprove manufacturabilityRespiratory masksMedical devicesDiseaseCheyne–Stokes respiration
Methods and apparatus for treating a respiratory disorder, in one aspect, include an apparatus that delivers backup breaths at a sustained timed backup rate that is a function of the patient's spontaneous respiratory rate. Other aspects include apparatus that delivers backup breaths at a rate that gradually increases from a spontaneous backup rate to a sustained timed backup rate or, alternatively, apparatus that oscillates a treatment pressure in antiphase with the patient's spontaneous respiratory efforts when a measure indicative of ventilation is greater than a threshold. Other aspects include apparatus configured to treat Cheyne-Stokes respiration by computing the treatment pressure so as to bring a measure indicative of ventilation of the patient towards a target ventilation that is dependent on the measure indicative of ventilation or, alternatively, by periodically elevating the treatment pressure to a high level for a short time, the high level being high enough and the short time being long enough to induce a central apnea in a patient. Depending on functionality, the foregoing apparatus may comprise an adaptive servo-ventilator or CPAP therapy device.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com