Lossless bandwidth adjustment method, device and system
a bandwidth adjustment and lossless technology, applied in the field of communication technologies, can solve the problems of easy error and easy error in configuration, and achieve the effect of avoiding heavy work load and configuration error, fast satisfying bandwidth adjustment requirements of customers, and increasing bandwidth adjustment speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0052]Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a lossless bandwidth adjustment method. In this embodiment, that a downstream node of each link allocates a tributary slot is taken as an example for illustration. As shown in FIG. 1, the following steps are included:
[0053]Step 10: A downstream node of an ODUflex path receives a request message from an upstream node of the ODUflex path, where the request message carries a tunnel ID (tunnel identifier) of the ODUflex path and bandwidth information after adjustment, and the request message is used for requesting lossless adjustment of a bandwidth of the ODUflex path.
[0054]The request message is sent by a first node of the ODUflex path along the ODUflex path downstream node by node to a last node.
[0055]The first node of the ODUflex path allocates one new LSP ID (label switching path identifier) to the ODUflex path after adjustment, while the tunnel ID remains unchanged, and the new LSP ID is carried in the request message. That is, o...
example 1
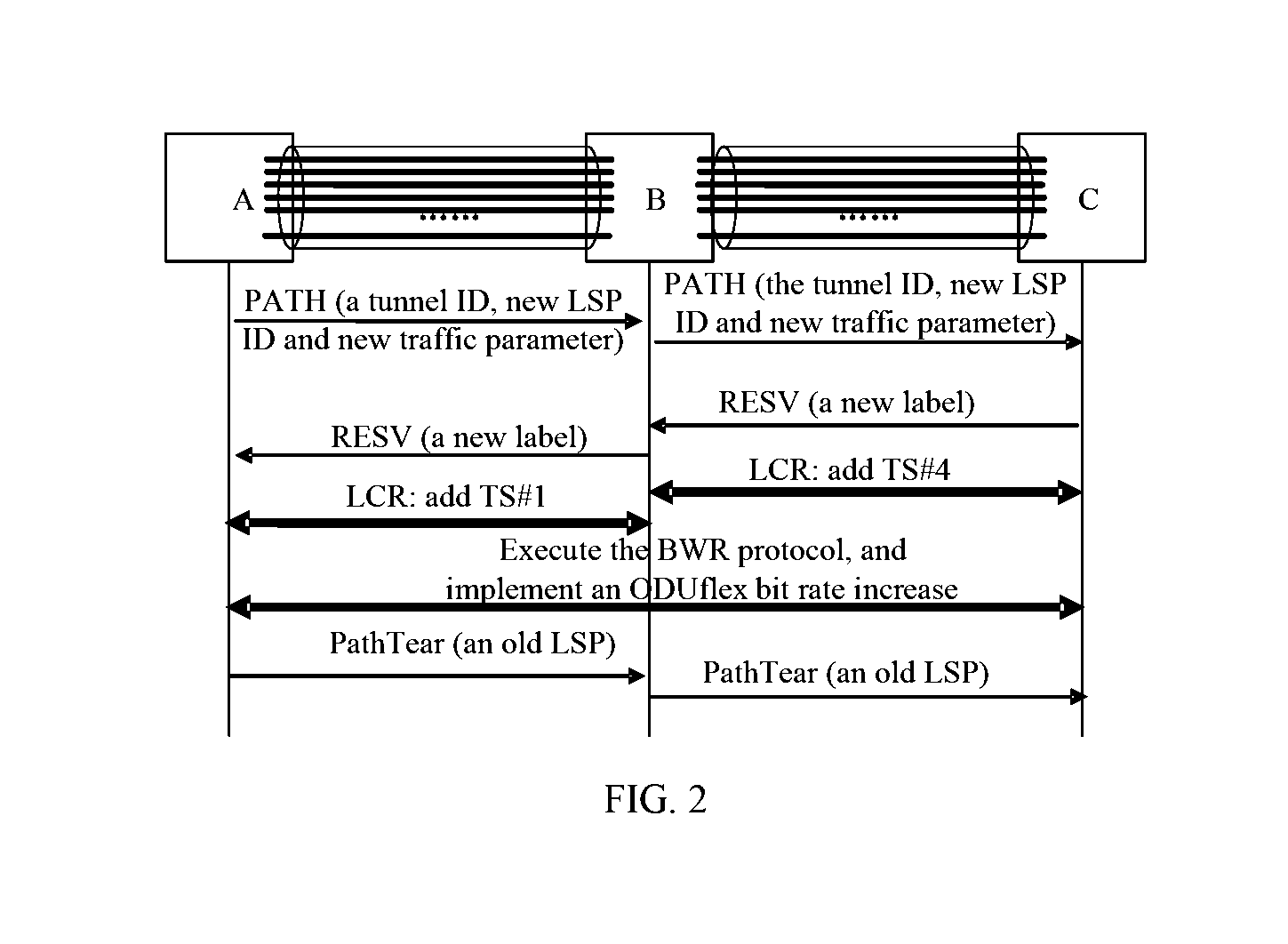
What is Shown in FIG. 2 is Taken as an Example, and is a Bandwidth Increase Procedure
[0081]It is assumed that an ODUflex path with a bandwidth of 3.75 Gbps exists among nodes A, B and C, its tunnel ID and LSP ID have been allocated, each node saves a control state of an ODUflex before bandwidth adjustment, where the control state of the ODUflex before bandwidth adjustment includes the tunnel ID, the LSP ID and a traffic parameter (used for describing a bandwidth value of the ODUflex) of the ODUflex, and a label value of the ODUflex in each link (used for describing a tributary slot occupied by the ODUflex in each link). If a first node A of the ODUflex receives a command requiring an increase of a bandwidth of the ODUflex to 5 Gbps, a lossless bandwidth adjustment process is as follows:
[0082](1) The first node A allocates one new LSP ID to the ODUflex path, while the tunnel ID remains unchanged.
[0083](2) The node A sends a Path message downstream node by node, until to a last node C...
example 2
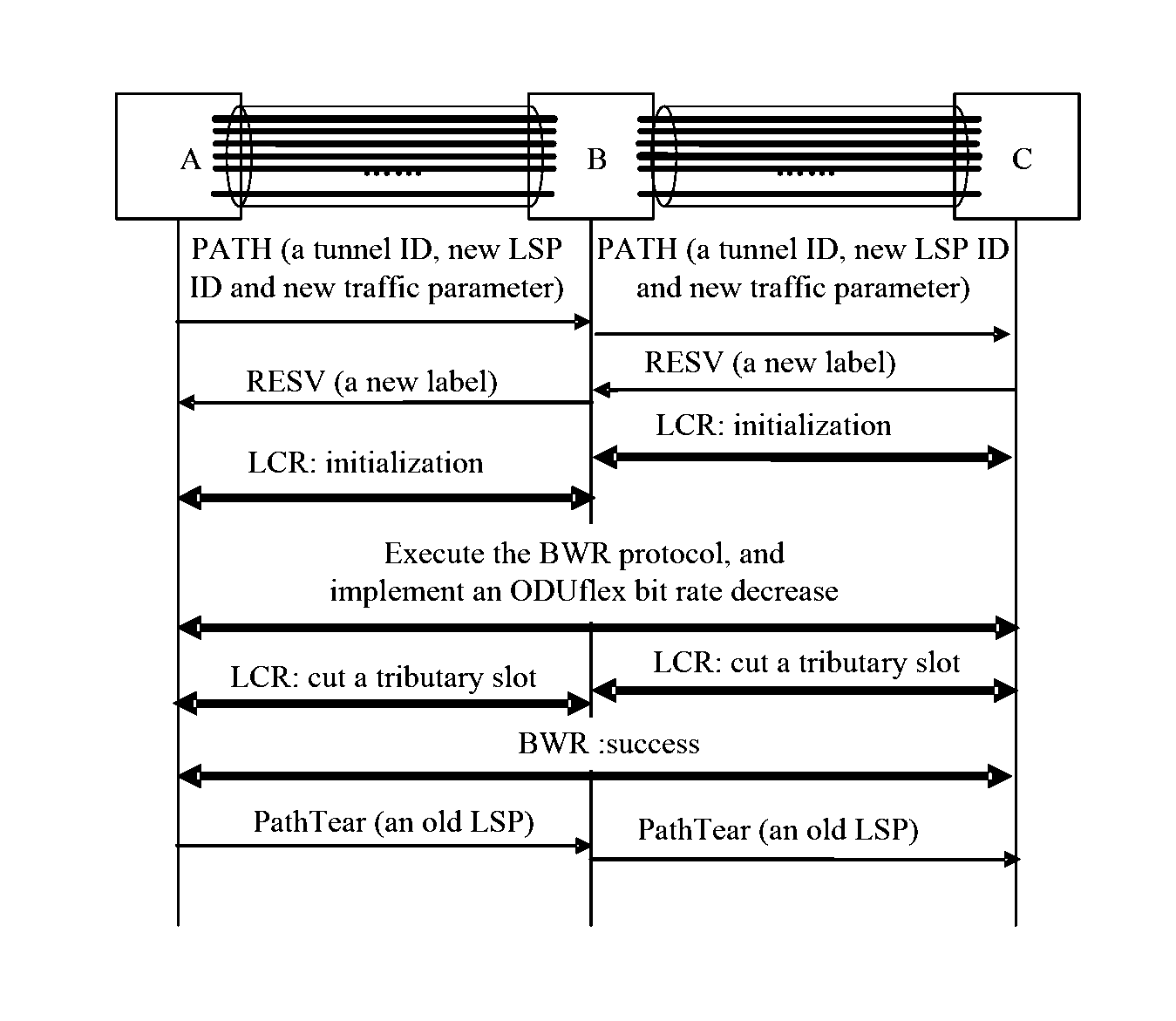
What is Shown in FIG. 3 is Taken as an Example, and is a Bandwidth Decrease Procedure
[0102]It is assumed that an ODUflex path with a bandwidth of 5 Gbps exists among nodes A, B and C, its tunnel ID and LSP ID have been allocated, each node saves a control state of an ODUflex before bandwidth adjustment, where the control state of the ODUflex before bandwidth adjustment includes the tunnel ID, the LSP ID and a traffic parameter (used for describing a bandwidth value of the ODUflex) of the ODUflex, and a label value of the ODUflex in each link (used for describing a tributary slot occupied by the ODUflex in each link). If a first node A of the ODUflex receives a command requiring a decrease of a bandwidth of the ODUflex to 3.75 Gbps, a lossless bandwidth adjustment process is relatively similar to the bandwidth increase process in Example 1, where main differences are as follows:
[0103](1) On a control plane, a bandwidth value in a new traffic parameter in a Path message is smaller tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com